Alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss, typically in circular patches, and affects millions of people worldwide. Treatment options have advanced over recent years, and understanding their effectiveness for patients can be essential in choosing the right approach for each individual. Here’s a closer look at the effectiveness of various Alopecia Areata Treatment in Dubai, as well as factors that influence treatment success.
Understanding Alopecia Areata and Its Impact
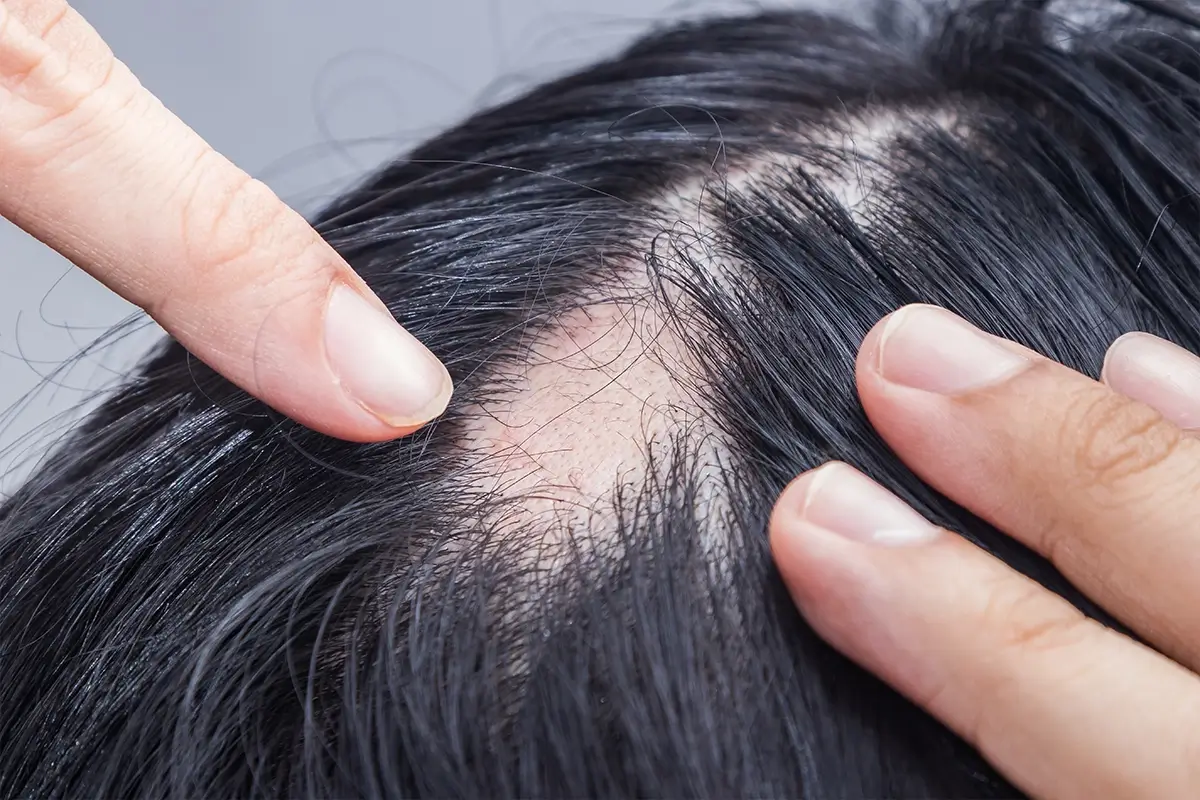
Alopecia areata occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss in specific areas, most commonly the scalp. The severity and pattern of hair loss can vary, and while some people experience only minor hair thinning, others may lose significant amounts of hair across their body.
Because the course of alopecia areata is unpredictable, treatment effectiveness can vary widely. Some people experience complete regrowth with treatment, while others may find that hair loss persists despite trying multiple options. Exploring different treatments and understanding what to expect can help individuals make informed decisions.
Topical Corticosteroids: Effectiveness for Mild Cases
Corticosteroids are often prescribed as a first-line treatment for mild cases of alopecia areata. These anti-inflammatory medications can suppress the immune response around hair follicles, promoting regrowth. Topical corticosteroids are often applied directly to the affected areas, and in cases where hair loss is localized, they can be quite effective.
Effectiveness:
For patients with mild, patchy alopecia, topical corticosteroids may offer noticeable regrowth within a few months. While effective, results are usually temporary, and ongoing treatment may be necessary to maintain hair growth.
Corticosteroid Injections: Faster Results in Targeted Areas
For patients with small, well-defined areas of hair loss, corticosteroid injections directly into the affected patches can be an effective treatment. Injections allow for concentrated delivery of the medication, often leading to quicker results than topical application.
Effectiveness:
In many cases, patients see regrowth within four to six weeks after receiving injections, making this option especially beneficial for people who seek faster results. However, injections may need to be repeated periodically, as results can diminish over time if the immune response continues.
Oral Immunosuppressants: Effective for Severe Alopecia
For individuals with more extensive alopecia, oral immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids, methotrexate, and cyclosporine can help reduce immune activity and halt hair loss. These medications are often used in severe cases or when other treatments haven’t provided satisfactory results.
Effectiveness:
Oral immunosuppressants can be highly effective in slowing or reversing hair loss, particularly for severe cases. However, their long-term use is limited by potential side effects, such as high blood pressure, liver issues, and infection risk, which may deter patients from relying on them as a permanent solution.
JAK Inhibitors: Promising Results in Clinical Trials
One of the most promising advancements in alopecia areata treatment is JAK inhibitors (Janus kinase inhibitors), a class of medication that blocks specific enzymes involved in the autoimmune response. Tofacitinib and ruxolitinib are two JAK inhibitors that have shown notable success in clinical trials, especially for patients with severe or long-standing alopecia.
Effectiveness:
Clinical trials have reported that many patients experience significant hair regrowth, with some achieving nearly complete regrowth within months. However, these medications are not yet FDA-approved specifically for alopecia areata, and there can be risks associated with their use, including infections and other immune-related side effects. Patients considering JAK inhibitors should consult a dermatologist to discuss potential benefits and risks.
Topical Immunotherapy: A Suitable Option for Extensive Hair Loss
Topical immunotherapy is used for patients with extensive hair loss or recurrent episodes of alopecia areata. In this treatment, chemicals like diphenylcyclopropenone (DPCP) are applied to the scalp, provoking a mild allergic reaction that stimulates the immune system away from hair follicles.
Effectiveness:
Topical immunotherapy has been shown to be effective in many cases, with gradual hair regrowth seen over several months. However, it may require consistent weekly treatments and can cause itching, redness, and irritation. Some patients achieve significant regrowth, while others may experience only partial results.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Non-Invasive Hair Stimulation
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) uses red light to stimulate hair growth and improve circulation to hair follicles. It is a non-invasive option for people looking for a supplementary treatment and is often delivered through devices like laser combs, caps, or helmets.
Effectiveness:
LLLT can be effective as an adjunct treatment, especially when combined with other therapies, but its results vary. While it may improve hair density and support follicle health, it is generally not as effective as other treatments in producing dramatic regrowth for those with more severe alopecia areata.
Light Therapy (Phototherapy)
Ultraviolet (UV) light therapy, or phototherapy, is another option, often used for people with larger areas of hair loss. It involves exposing affected areas to UV light under controlled medical supervision, which can help reduce inflammation and immune activity.
Effectiveness:
Phototherapy can be moderately effective, with some patients seeing a reduction in hair loss and gradual regrowth. However, it requires regular sessions and can sometimes cause skin irritation or sunburn-like reactions. Results may vary significantly from patient to patient.
Dietary and Lifestyle Factors: Enhancing Treatment Outcomes
Though not a direct treatment, maintaining a nutritious diet and managing stress can help optimize the effectiveness of other treatments. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals such as biotin, vitamin D, zinc, and iron can promote hair and immune health. Stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, and regular exercise are also essential, as stress has been associated with hair loss triggers.
Effectiveness:
While dietary and lifestyle changes alone may not resolve alopecia areata, they can support overall health, potentially improving the body’s response to treatments. Many patients report better results when combining lifestyle modifications with medical treatments.
Considerations for Long-Term Effectiveness
The effectiveness of alopecia areata treatment can be influenced by several factors:
- Severity and Extent of Hair Loss: Patients with mild, patchy hair loss tend to respond better to treatments like corticosteroids, while those with more severe cases may require immunosuppressants or JAK inhibitors.
- Consistency and Follow-Through: Regular treatment is essential to achieve and maintain results, especially for therapies like topical immunotherapy or corticosteroid injections.
- Treatment Combinations: Some patients benefit most from a multi-therapy approach, combining topical treatments with light therapy or laser therapy for better results.
Challenges in Predicting Treatment Success
Because alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition with unpredictable progression, even the most effective treatments may not guarantee long-lasting results. Some patients experience regrowth only to face relapses later, and others may find that hair loss stabilizes without additional treatment.
The condition’s variability makes it essential for patients to work closely with healthcare providers to monitor progress and adjust treatments as necessary. Regular evaluations help manage expectations and optimize treatment plans, allowing for adjustments based on the individual’s response.
Conclusion: Finding the Right Approach
While there is no one-size-fits-all cure for alopecia areata, a range of treatment options offers hope for hair regrowth and management of symptoms. Corticosteroids, JAK inhibitors, topical immunotherapy, and lifestyle modifications have all shown effectiveness for different patient needs. Working closely with a dermatologist can help individuals navigate these options and find the most suitable approach for their specific type of hair loss.
The success of alopecia areata treatments varies widely from patient to patient, making it essential for individuals to set realistic expectations and remain open to adjusting their treatment plans as needed.





Comments