Cobalt is a critical metal used primarily in the production of rechargeable batteries, particularly in lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles (EVs), electronics, and energy storage systems. It also has significant applications in the aerospace and defense industries, where it is used in superalloys and magnetic materials. Due to its essential role in modern technologies, the price trend of cobalt is closely monitored by manufacturers, investors, and policymakers.
The cobalt market has experienced considerable volatility over the years, driven by changes in global demand, supply chain challenges, geopolitical factors, and technological advancements. This article examines the key factors influencing cobalt prices, provides an analysis of historical trends, and offers insights into future price projections.
Factors Influencing Cobalt Prices
Several factors contribute to the fluctuations in cobalt prices. These factors include supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical influences, technological advancements, and external economic conditions. The following are some of the primary drivers of cobalt price movements:
1. Global Demand for Electric Vehicles and Batteries
One of the most significant drivers of cobalt demand is its use in the production of lithium-ion batteries, which power electric vehicles (EVs) and consumer electronics. As the global push for cleaner energy and reduced carbon emissions accelerates, the demand for EVs and energy storage systems has surged. This increased demand directly impacts cobalt prices, as it is a key component in the cathodes of lithium-ion batteries.
2. Supply Chain Constraints and Mining Operations
Cobalt is primarily mined as a byproduct of copper and nickel mining, with the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) being the largest producer, accounting for more than 60% of global cobalt supply. The concentration of production in a single country makes the supply chain vulnerable to disruptions caused by political instability, labor strikes, or logistical challenges. Any interruptions in mining operations or export restrictions can lead to supply shortages, driving up cobalt prices.
3. Geopolitical Tensions and Trade Policies
Geopolitical factors, including trade disputes, sanctions, and diplomatic relations, can significantly influence the cobalt market. For example, sanctions on countries that produce or process cobalt can lead to supply shortages, pushing prices higher. Conversely, favorable trade agreements or the lifting of restrictions can increase supply, potentially lowering prices.
4. Technological Advancements in Battery Chemistry
Technological advancements in battery chemistry can impact the demand for cobalt. For instance, the development of alternative battery chemistries that use less or no cobalt, such as lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, could reduce demand for cobalt in the long term. However, as of now, cobalt remains an essential material in high-energy-density batteries, particularly for EVs.
5. Environmental and Social Considerations
Environmental and social concerns related to cobalt mining, particularly in the DRC, have gained increasing attention. Issues such as child labor, poor working conditions, and environmental degradation have led to calls for more sustainable and ethical sourcing of cobalt. Companies are increasingly focusing on responsible sourcing practices, which may lead to higher production costs and influence cobalt prices.
6. Currency Exchange Rates and Global Economic Conditions
Cobalt is traded internationally, and fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact prices. A stronger local currency in producing countries can make exports more expensive, potentially reducing demand and lowering prices. On the other hand, a weaker currency can make cobalt exports more competitive, increasing demand and supporting higher prices. Additionally, global economic conditions, such as inflation, recession, or economic recovery, can influence cobalt demand and prices.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/cobalt-price-trends/pricerequest
Historical Price Trends
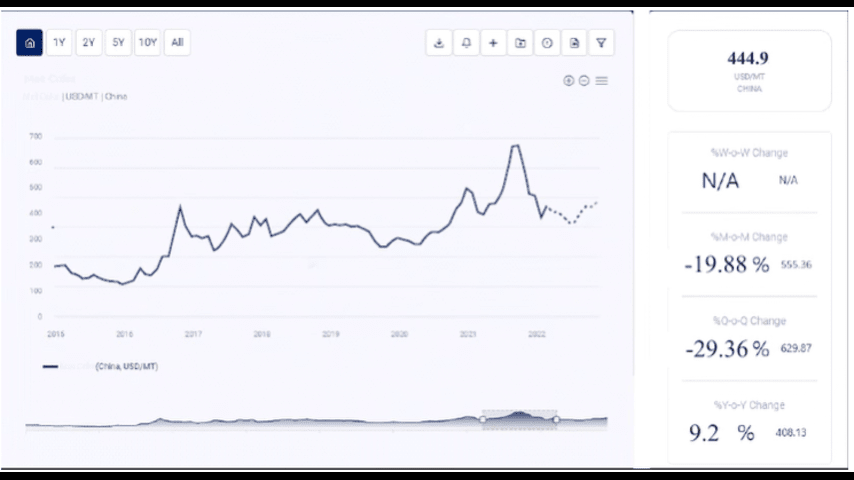
To better understand potential future movements in cobalt prices, it is essential to analyze historical price trends. Over the past two decades, cobalt prices have experienced significant volatility, reflecting changes in global demand, supply constraints, and market conditions.
1. Early 2000s: Stability and Gradual Increase
In the early 2000s, cobalt prices remained relatively stable, with gradual increases driven by steady demand from traditional industries, such as aerospace and chemicals. The market was characterized by consistent supply from established mining operations, with little volatility in prices.
2. 2007-2008: Price Surge
Between 2007 and 2008, cobalt prices experienced a significant surge, reaching an all-time high. This price increase was driven by strong demand from the rapidly growing electronics industry, coupled with concerns over supply disruptions from the DRC. The speculative activity in commodity markets also contributed to the sharp rise in prices.
3. 2009-2015: Price Decline and Stabilization
Following the global financial crisis of 2008, cobalt prices declined sharply as demand from the electronics and automotive industries weakened. The economic downturn led to reduced industrial activity, resulting in lower demand for cobalt. From 2009 to 2015, cobalt prices stabilized at lower levels, with occasional fluctuations driven by changes in supply and demand dynamics.
4. 2016-2018: Rapid Price Increase
The period between 2016 and 2018 saw a rapid increase in cobalt prices, driven by the booming electric vehicle market. The growing demand for lithium-ion batteries, particularly for EVs, led to concerns about potential supply shortages, pushing prices higher. The concentration of cobalt production in the DRC, coupled with geopolitical risks, further exacerbated supply concerns and fueled the price surge.
5. 2019-2020: Market Correction and Price Decline
In 2019 and 2020, cobalt prices experienced a market correction as supply began to catch up with demand. The introduction of new mining projects and the expansion of existing operations increased cobalt supply, leading to a decline in prices. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 caused disruptions in global supply chains and reduced industrial activity, further contributing to the decline in cobalt prices.
6. 2021-Present: Price Recovery and Volatility
Since 2021, cobalt prices have experienced a recovery, driven by the resurgence of demand from the electric vehicle industry as economies began to reopen following the COVID-19 pandemic. The push for decarbonization and the transition to renewable energy sources have further supported demand for cobalt. However, prices have remained volatile due to ongoing supply chain challenges, geopolitical tensions, and environmental concerns related to cobalt mining.
Future Price Forecast for Cobalt
Looking ahead, the price of cobalt is expected to be influenced by several key factors. Based on historical trends, current market conditions, and future projections, the following are potential scenarios for cobalt prices over the next few years:
1. Short-Term Forecast (2024-2025)
In the short term, cobalt prices are likely to remain relatively high, with potential for further increases due to strong demand from the electric vehicle and energy storage sectors.
- Electric Vehicle Demand: The continued growth of the electric vehicle market, particularly in China, Europe, and the United States, will drive strong demand for cobalt. As automakers ramp up production of EVs, the demand for lithium-ion batteries containing cobalt is expected to increase, supporting higher prices.
- Supply Chain Challenges: Ongoing supply chain disruptions, whether due to logistical challenges, geopolitical tensions, or production issues in the DRC, could lead to supply shortages and upward pressure on prices.
- Technological Advancements: While advancements in battery chemistry could reduce the amount of cobalt used in batteries, it is unlikely to significantly impact demand in the short term. Cobalt will remain a critical component in high-energy-density batteries for EVs.
2. Medium-Term Forecast (2026-2028)
In the medium term, cobalt prices could experience increased volatility due to shifts in battery technology, changes in global trade dynamics, and environmental considerations.
- Battery Technology Evolution: The development of alternative battery chemistries, such as solid-state batteries or cobalt-free cathodes, could reduce the demand for cobalt, leading to downward pressure on prices. However, the pace of adoption of these new technologies will be a key factor.
- Geopolitical Factors: Geopolitical tensions, particularly in the DRC, will continue to impact cobalt supply. Any escalation in conflict or changes in trade policies could lead to supply disruptions and price volatility.
- Environmental and Social Concerns: Increasing focus on ethical and sustainable sourcing of cobalt may lead to higher production costs, potentially supporting higher prices. Companies may need to invest in traceability and certification programs to ensure responsible sourcing.
3. Long-Term Forecast (2029 and Beyond)
In the long term, cobalt prices are expected to be shaped by broader macroeconomic trends, the transition to sustainable energy, and technological advancements in battery technology.
- Global Energy Transition: As the world continues to transition to cleaner energy sources and decarbonize the transportation sector, demand for cobalt in batteries will remain strong. However, the development of alternative energy storage solutions could reduce reliance on cobalt over time.
- Technological Innovations: The long-term impact of technological advancements in battery chemistry and recycling technologies will be critical in determining cobalt demand. The adoption of cobalt-free batteries or improved recycling processes could reduce the need for newly mined cobalt, potentially lowering prices.
- Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing: The emphasis on sustainability and ethical sourcing practices will continue to shape the cobalt market. Companies that prioritize responsible sourcing and invest in cleaner production methods may influence long-term price trends.
Conclusion
The price of cobalt is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including global demand, supply chain dynamics, geopolitical tensions, and technological advancements. While historical trends provide valuable insights into past price movements, the future remains uncertain, with several variables at play. However, by closely monitoring these factors and understanding the underlying market dynamics, stakeholders can make informed decisions to navigate the evolving cobalt market.
As the world moves toward a more sustainable energy future, cobalt will continue to play a critical role in the production of electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies.




Comments