Osteochondritis is a condition that develops in the joints where two bones are satisfied at their ends due to internal bone softening and a deficiency of blood flow. As an outcome, a small portion of the bone dies and splits off from the significant bone.
The loose bone and cartilage may slide into the joint area and induce fluctuation or stay in place.
Usually, osteochondritis dissecans concerns just one joint. Sporadic osteochondritis dissecans is an illness that arises when there is only one lesion in a single joint. When you speak with a Knee Pain doctor Long Island, ask queries regarding your ongoing knee pain.
Osteochondritis dissecans affects whom?
The age range of 10 to 20 years old is the most common for osteochondritis dissecans in children and adolescents, particularly in young athletes or physically active athletes. Nevertheless, the illness can strike anyone at any age.
Osteochondritis dissecans is an uncommon condition affecting several joints and possibly more than one family member (familial osteochondritis dissecans).
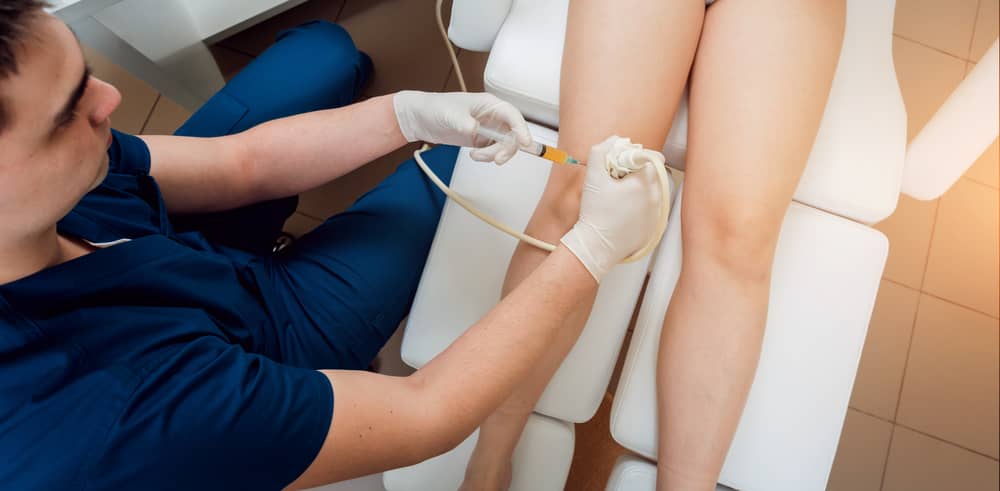
What signs of osteochondritis dissecans are present?
There might not be any symptoms if the split bone and cartilage remain near the more extensive bone. If symptoms are present, they may consist of:
- Joint pain, weakness, and edema, frequently following physical or sports exercise;
- Reduced range of motion includes the inability to fully extend the arm or leg. Range of motion is the average distance a joint move.
- Stiffness in the joint following rest; a joint locking or sticking in place;
- A sound that clicks when the joint is moved.
What is the cause of dissecans osteochondritis?
Most of the time, it is unknown what causes sporadic osteochondritis dissecans. One theory is that the illness may develop as a result of a joint experiencing repeated trauma or stress over time, such as from playing sports.
Inherited mutations (alterations) in the ACAN gene, the source of the cartilage-forming protein aggrecan, result in familial osteochondritis dissecans. The mutation prevents the protein from properly constructing cartilage, which results in weak and haphazard cartilage. The most suitable knee pain treatment jericho option will depend on the harshness and causes of knee discomfort and your signs.
How can one treat osteochondritis dissecans?
As they get older, sporadic osteochondritis dissecans in kids and young adolescents typically goes away on its own. Resting and taking a break from physically demanding activities like jogging and leaping can reduce pain and swelling.
The damaged joint will return to normal function within six to twelve weeks. The young athlete should progressively return to sports with mild workouts (yoga, swimming, riding, or stretching).
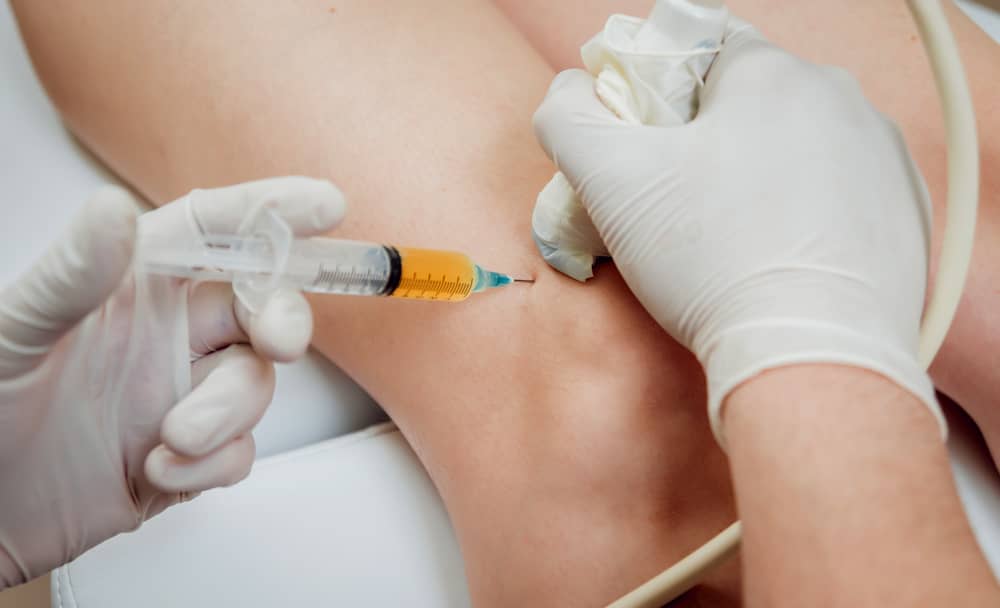
Should the healing process be sluggish, the Knee Pain doctor Fidi can advise using crutches or applying a brace, splint, or cast to the affected joint.
Is it possible to prevent osteochondritis dissecans?
Osteochondritis dissecans have unknown causes, making prevention challenging. For example, young athletes can take precautions to safeguard their joints by donning protective gear and pads. They should also stretch and warm up before engaging in strenuous physical activity and stretch and cool down afterward. They should also practice the correct physical methods for their sport.
Wrapping it up
The likelihood of a full recovery and a return to pre-injury activities increases with patient age. But sports involving repetitive motions, like pitching, may need the patient to give them up. After a patient heals, osteochondritis dissecans typically do not recur. Sometimes, though, the illness appears to get better when the symptoms momentarily disappear. In some situations, symptoms may eventually reappear. Arrange a meeting with your Knee Pain doctor financial district if your knee discomfort is not going well or you have pain due to any injury.





Comments