Dental bonding cementing is a common procedure in modern dentistry, used to restore, repair, and protect teeth by bonding materials directly to the tooth surface. Whether it’s attaching crowns, fixing chips, or filling gaps, Dental Bonding Cementing plays a crucial role in cosmetic and restorative treatments. This technique involves using a special adhesive (cement) to permanently secure dental work, such as veneers, bridges, or fillings, to the teeth. The process is quick, effective, and relatively non-invasive, making it a preferred choice for patients seeking both functional and aesthetic improvements.
Why Is Dental Bonding Cement Used?
Dental bonding cement is widely used for both temporary and permanent applications. Dentists choose this cement based on the specific restoration needed and the condition of the patient’s teeth. Its primary purpose is to provide a strong, lasting bond between the natural tooth and the applied material, such as ceramic crowns or resin-based fillings. This cement ensures:
- Long-term adhesion and stability
- Protection from bacteria and decay
- Improved cosmetic appearance
- Enhanced function of restored teeth
The type of cement used can vary—from resin-modified glass ionomer to composite resin—depending on the treatment objective and patient preference.
How the Dental Bonding Cementing Process Works?
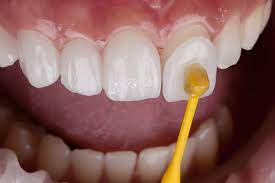
The dental bonding cementing process is usually performed in one visit and involves several detailed steps. First, the tooth surface is cleaned and lightly etched to prepare it for bonding. Next, the dentist applies the bonding cement, followed by the restoration material, which is then shaped and hardened using a special curing light.
- Tooth Preparation: Cleaning, drying, and etching
- Bonding Application: Cement applied in a thin, even layer
- Placement: The restoration is positioned onto the tooth
- Curing: A blue light hardens the cement quickly
- Finishing Touches: Polishing and bite adjustments
The entire procedure can be completed in under an hour, depending on the extent of the dental work being performed.
Benefits of Dental Bonding Cementing:
Dental bonding cementing offers multiple benefits that make it a valuable option for a wide range of dental problems. It provides both cosmetic enhancements and functional improvements, restoring a natural-looking smile and reinforcing weak or damaged teeth. Some of the top benefits include:
- Minimally invasive: Requires little to no removal of tooth structure
- Affordable: Less expensive than other cosmetic dental treatments
- Fast: Most procedures are completed in one visit
- Effective: High success rate for small to medium repairs
- Customizable: Shade can be matched to natural tooth color
These advantages make bonding an ideal solution for patients who want immediate results with minimal discomfort.
Common Uses for Dental Bonding Cement:
Dental Bonding Cementing Treatment isn’t just used for one type of procedure—it’s incredibly versatile. From repairing chipped teeth to securing orthodontic brackets, this cement adapts to many dental needs. Here are some of the most common uses:
- Cementing crowns, bridges, and veneers
- Fixing chipped, cracked, or worn-down teeth
- Filling small cavities or replacing old fillings
- Closing gaps between teeth
- Reattaching loose restorations
Because of its adaptability, dentists often keep multiple types of dental bonding cement on hand to ensure optimal results for different cases.
Care and Longevity After Cementing:
After dental bonding cementing, patients are advised to follow specific care guidelines to ensure the restoration remains strong and intact. While the bonding is durable, it isn’t indestructible. Daily habits and oral hygiene play a big role in its longevity.
- Avoid biting on hard objects (e.g., pens, ice, fingernails)
- Brush and floss regularly to prevent decay around the bonding
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings
- Limit staining foods and drinks to keep the bonded area looking natural
With proper care, dental bonding can last anywhere from 5 to 10 years or more. If the bonded material chips or wears down, it can usually be touched up or replaced easily in a quick dental visit.




Comments