Moles are common skin growths that can appear anywhere on the body. While many moles are harmless, others may become a concern due to cosmetic reasons or potential health risks. This guide will explore various mole removal techniques, helping you understand the options available, the processes involved, and what to expect during and after the Mole Removal in Dubai procedure.
Understanding Moles
Moles, also known as nevi, are clusters of pigment-producing cells called melanocytes. They can vary in size, shape, and color, and can be flat or raised. Most people have between 10 to 40 moles, which can develop in childhood and continue to appear into adulthood. While most moles are benign, changes in their appearance or new moles that develop after age 30 should be evaluated by a dermatologist.
Mole Removal Techniques
When it comes to removing moles, there are several techniques available. The best method for you will depend on the size, type, and location of the mole, as well as your personal preferences and health considerations. Here are some common mole removal techniques:
1. Surgical Excision
Surgical excision is one of the most common methods for removing moles, especially those that are larger or deeper. During this procedure, a healthcare provider uses a scalpel to cut around the mole and remove it, along with a margin of surrounding skin. This technique is often performed under local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. After removal, the area is closed with stitches, and the excised tissue may be sent for laboratory analysis to check for any signs of malignancy.
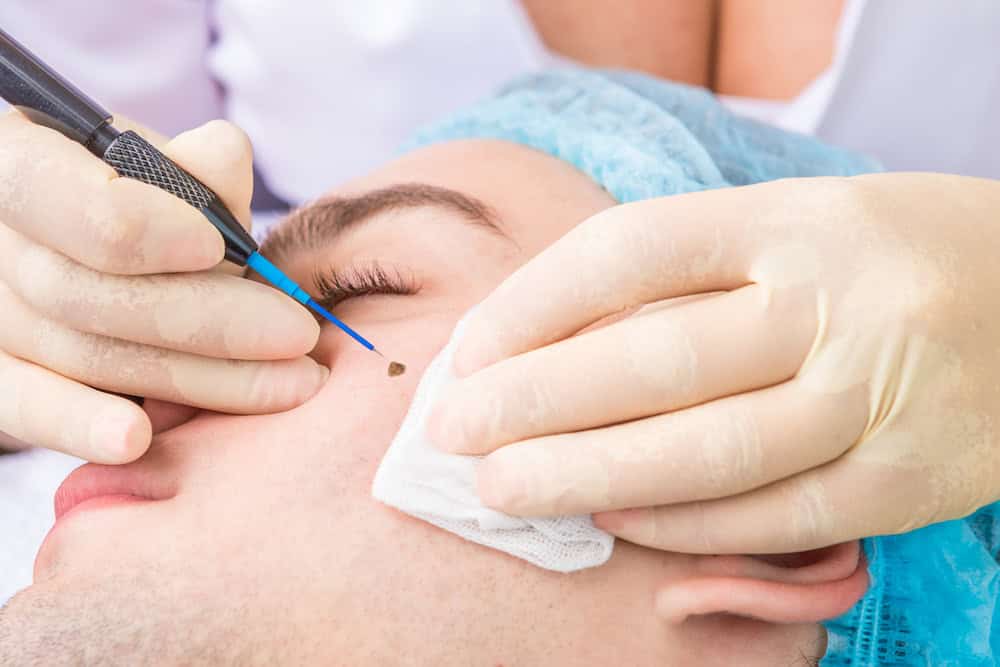
2. Surgical Shaving
Surgical shaving is another technique used for mole removal, particularly for flat moles or those that protrude slightly from the skin. In this method, the dermatologist uses a small, round blade to shave off the mole at the surface level. This technique is generally quicker and may leave minimal scarring. However, it is important to note that this method may not be suitable for deeper moles, as it may not remove all the pigment cells.
3. Laser Removal
Laser mole removal is a non-invasive technique that uses focused light beams to break down the pigment in the mole. This method is particularly effective for smaller, superficial moles and can minimize scarring. Patients may experience some discomfort during the procedure, similar to the sensation of a rubber band snapping against the skin. After laser treatment, the mole typically fades over time, although multiple sessions may be required for optimal results.
4. Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves freezing the mole using liquid nitrogen. This technique is effective for smaller moles and can be performed quickly in a dermatologist's office. The extreme cold destroys the mole's cells, causing it to fall off after a few days. Patients may experience redness and swelling in the treated area, but these symptoms typically resolve within a week. This method is less commonly used for larger or deeper moles, as it may not remove all the tissue.
5. Electrodesiccation
Electrodesiccation is a technique that uses high-frequency electrical currents to remove moles. This method is particularly useful for small, raised moles. During the procedure, the provider uses a specialized device to burn away the mole tissue while simultaneously cauterizing the area to minimize bleeding. Patients may experience a slight tingling sensation during the treatment, but local anesthesia can be used for comfort. After the procedure, the area may crust over and heal within a week or two.
6. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve applying a solution to the skin to exfoliate the outer layer, which can help reduce the appearance of some types of moles. This method is generally more suitable for superficial moles and may require multiple treatments for effective results. While chemical peels can improve skin texture and tone, they may not completely remove moles and are usually used for cosmetic enhancement rather than complete excision.
Post-Removal Care
After any mole removal procedure, proper aftercare is essential to promote healing and reduce the risk of infection. Here are some general post-removal care tips:
- Keep the area clean and dry: Follow your healthcare provider's instructions on how to care for the wound.
- Avoid sun exposure: Protect the area from direct sunlight to prevent pigmentation changes and scarring.
- Watch for signs of infection: Look out for increased redness, swelling, or pus, and contact your healthcare provider if you notice any concerning symptoms.
- Follow up: Attend any follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing and discuss any concerns with your provider.
Conclusion
Understanding the different mole removal techniques available can help you make an informed decision about which option is best for your situation. Whether you choose surgical excision, laser removal, or another method, working with a qualified healthcare professional will ensure the safest and most effective results. Always consult a dermatologist for advice tailored to your specific needs and to monitor any changes in your skin health. Remember, while most moles are benign, staying proactive about your skin health is vital in preventing potential issues in the future.





Comments