Rosacea Treatment in Dubai is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by redness, swelling, and visible blood vessels, it often presents on the face and can cause discomfort and embarrassment. While its exact cause is still unknown, certain triggers are known to exacerbate rosacea symptoms. One such trigger is food intolerance. Understanding the connection between rosacea and food intolerances can be crucial in managing and minimizing flare-ups.
Understanding Rosacea
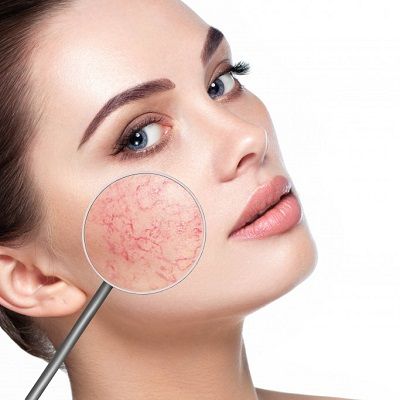
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face. It often appears as persistent redness across the nose, cheeks, chin, and forehead. In some cases, rosacea may also cause small, pus-filled bumps, visible blood vessels, and even eye irritation. While the condition is not life-threatening, its visibility and associated symptoms can significantly impact a person’s self-esteem and quality of life.
There are four subtypes of rosacea, and individuals can experience one or more simultaneously:
- Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR): Characterized by redness and visible blood vessels.
- Papulopustular Rosacea: Marked by acne-like breakouts.
- Phymatous Rosacea: Results in thickened skin, often around the nose.
- Ocular Rosacea: Affects the eyes, causing irritation and redness.
The exact cause of rosacea is not fully understood, but a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors is believed to contribute. One prominent factor linked to rosacea flare-ups is food intolerance.
What Are Food Intolerances?
Food intolerances occur when the body is unable to properly digest or react to certain foods. Unlike food allergies, which trigger an immune response, food intolerances result in digestive issues, inflammation, and other symptoms that can vary from person to person. Common symptoms of food intolerances include bloating, gas, diarrhea, and skin reactions.
For individuals with rosacea, certain food intolerances can aggravate their condition and lead to noticeable flare-ups. Identifying and eliminating these triggers is an important step in managing rosacea symptoms effectively.
How Food Intolerances Trigger Rosacea
Rosacea is closely linked to inflammation, and food intolerances can lead to increased inflammation in the body. When the body struggles to digest certain foods, it may trigger an inflammatory response that manifests on the skin. This inflammation can exacerbate existing rosacea symptoms such as redness, swelling, and breakouts.
In addition, certain foods that are difficult to digest or that the body reacts negatively to can cause a histamine response. Histamine is a compound involved in the body's immune response and can lead to flushing, which is a common symptom of rosacea.
Foods that are known to cause flare-ups in people with food intolerances and rosacea include:
- Dairy products: Lactose intolerance can lead to bloating, gas, and inflammation, which may worsen rosacea symptoms.
- Gluten: Many individuals with gluten intolerance or sensitivity notice an improvement in their rosacea symptoms after eliminating gluten from their diet.
- Spicy foods: Capsaicin, the compound responsible for the heat in spicy foods, can increase blood flow to the skin and lead to flushing, a common symptom of rosacea.
- Alcohol: Alcohol, particularly red wine, can trigger a histamine response and increase the likelihood of facial flushing.
- Sugary foods: High sugar intake can spike blood sugar levels and trigger inflammation, leading to worsened rosacea symptoms.
Identifying Food Triggers
Identifying which foods trigger rosacea flare-ups can be challenging but rewarding in managing the condition. Here are some steps to help individuals with rosacea identify and manage food triggers:
1. Keep a Food Diary
Tracking food intake and the corresponding skin reactions can help identify patterns between specific foods and rosacea flare-ups. Record meals, snacks, and drinks, as well as any symptoms that occur afterward. Over time, patterns will emerge that can point to problematic foods.
2. Elimination Diet
An elimination diet is a method of identifying food intolerances by removing specific foods from the diet for a period of time and then slowly reintroducing them one by one. Common triggers, such as dairy, gluten, spicy foods, and alcohol, can be eliminated first. After two to four weeks, these foods can be reintroduced individually, with time allowed between each reintroduction to monitor for flare-ups.
3. Consult a Nutritionist or Doctor
Working with a healthcare professional, such as a nutritionist or doctor, can provide guidance on identifying food intolerances and managing rosacea. They may recommend tests to determine food sensitivities or allergies and offer personalized dietary advice.
4. Monitor Portion Sizes
Even if a particular food is not entirely off-limits, consuming it in large quantities may trigger a flare-up. Monitoring portion sizes and limiting trigger foods can help reduce the likelihood of a reaction.
Common Food Triggers for Rosacea
Certain foods are more likely to trigger rosacea flare-ups due to their effects on the body. These include:
- Hot beverages: Coffee, tea, and hot chocolate can increase body temperature, which may lead to facial flushing in some individuals with rosacea.
- Spicy foods: Chili peppers, hot sauces, and other spicy ingredients can trigger flushing and aggravate rosacea symptoms.
- Alcohol: Red wine, beer, and hard liquor can cause vasodilation (widening of blood vessels), leading to flushing and redness.
- Dairy products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt can cause inflammation in individuals who are lactose intolerant, exacerbating rosacea symptoms.
- Histamine-rich foods: Aged cheese, cured meats, and fermented foods like sauerkraut and kimchi are high in histamines, which can trigger a histamine response and cause flushing.
Managing Rosacea Through Diet
Managing rosacea involves a combination of avoiding triggers and following a healthy, balanced diet. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce overall inflammation and promote healthier skin. Some anti-inflammatory foods to consider include:
- Omega-3 rich foods: Fatty fish like salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts contain omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Fruits and vegetables: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support skin health.
- Green tea: Green tea is known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which may help soothe rosacea-prone skin.
Conclusion
Rosacea and food intolerances are closely connected, and identifying and managing dietary triggers can make a significant difference in controlling symptoms. By paying attention to food intake, keeping a detailed food diary, and working with healthcare professionals, individuals with rosacea can better manage their condition and enjoy healthier, clearer skin. Understanding personal food intolerances and following an anti-inflammatory diet can help reduce flare-ups and improve the quality of life for those affected by rosacea.





Comments