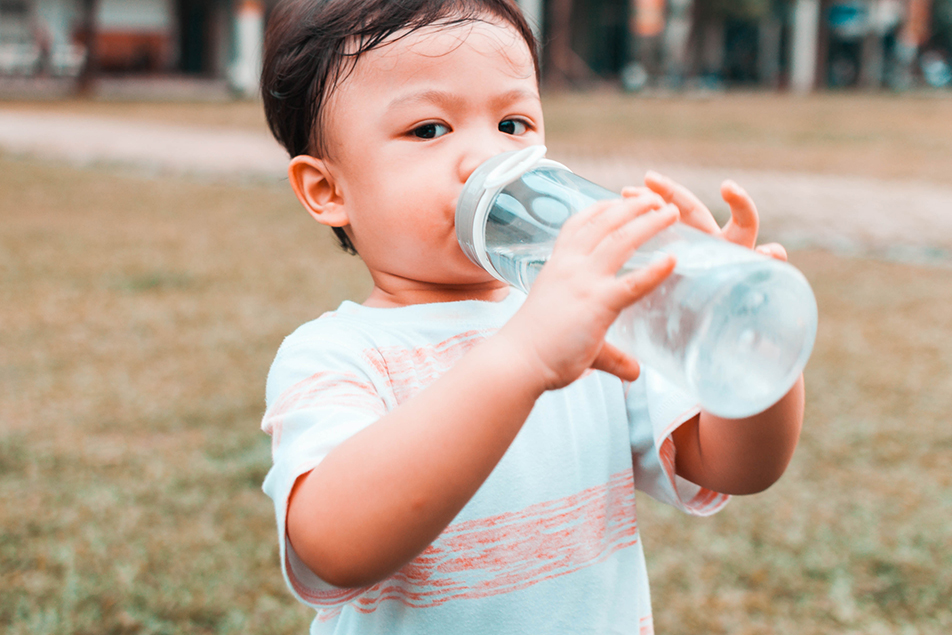
Dehydration in children is a common concern, especially during hot weather, illness, or when fluid intake is insufficient. Early recognition of dehydration symptoms at home is essential for prompt care and comfort. Understanding the signs can help caregivers respond quickly and prevent complications.
Understanding Pediatric Dehydration
Pediatric at Home Dubai occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in. Children are particularly vulnerable due to their smaller body size and higher fluid requirements relative to adults. Fluid loss can happen through sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, or reduced fluid intake during illness. Recognizing the signs early allows caregivers to intervene and support the child’s hydration effectively.
Early Signs of Dehydration
Early signs of dehydration may appear gradually and can be subtle. Observing changes in behavior and physical appearance helps identify these signs promptly. Caregivers should look for unusual thirst, dry lips, and a decrease in urine output. A child may also appear tired, irritable, or less active than usual. Early recognition allows for simple measures to increase fluid intake and prevent progression.
Physical Indicators of Dehydration
Physical signs often provide clear evidence of dehydration. Dry mouth and cracked lips are visible indicators, while sunken eyes or cheeks can signal more significant fluid loss. A noticeable decrease in skin elasticity may also be present, where the skin does not return quickly to its normal position after being gently pinched. Observing these signs helps caregivers respond with appropriate fluid support at home.
Changes in Urination Patterns
Monitoring urination is an important method to assess hydration. Infants may produce fewer wet diapers, while older children may urinate less frequently or in smaller amounts. Dark-colored urine is another sign that the body is conserving fluids. Tracking these changes provides valuable information about the child’s hydration status and helps caregivers take timely action.
Behavioral and Mood Changes
Dehydration can impact a child’s mood and energy levels. Children may become unusually sleepy, lethargic, or irritable. Some may refuse to eat or drink, further complicating hydration. Recognizing these behavioral shifts is important because they often accompany other physical signs and indicate the need for immediate attention to fluid intake.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Vomiting and diarrhea are common causes of dehydration in children. Persistent vomiting prevents adequate fluid intake, while diarrhea increases fluid loss. Monitoring the frequency and severity of these gastrointestinal symptoms is crucial. Caregivers should be alert to signs of dehydration in children experiencing prolonged gastrointestinal disturbances, as early intervention is essential to prevent complications.
Fever and Dehydration
Fever increases the risk of dehydration as the body loses fluids more rapidly. Children with fever may require additional fluids to compensate for the loss. Signs of dehydration during a fever can include dry mouth, reduced urination, and fatigue. Observing these indicators helps caregivers provide timely hydration support at home.
Recognizing Severe Dehydration
Severe dehydration requires urgent attention. Symptoms may include rapid heartbeat, very dry mouth, extreme lethargy, or a lack of tear production when crying. A child may appear pale, have sunken eyes, or feel unusually cold. Identifying these severe signs promptly ensures that the child receives immediate care to prevent serious complications.
Home Strategies for Supporting Hydration
Encouraging fluid intake is essential for preventing and addressing dehydration. Small, frequent sips of water or other suitable fluids can help maintain hydration. Monitoring the child’s fluid consumption, offering fluids regularly, and observing their response is important. Caregivers should remain vigilant for changes in behavior, physical signs, and urine output to ensure the child stays adequately hydrated.
Monitoring Recovery
After identifying dehydration, tracking improvement is crucial. Increasing energy levels, improved mood, and more frequent urination indicate that fluid balance is restoring. Observing these positive changes reassures caregivers that home hydration measures are effective. Continued monitoring ensures that the child remains well-hydrated and prevents recurrence.
Prevention Strategies
Pediatric at Home in Dubai, preventing dehydration involves consistent attention to fluid intake, especially during illness, hot weather, or high physical activity. Encouraging regular drinking habits, offering water-rich foods, and monitoring signs of fluid loss help maintain hydration. Educating children about recognizing thirst and encouraging them to drink fluids proactively supports ongoing prevention.
FAQs
How can a caregiver tell if a child is mildly dehydrated?
Mild dehydration may present as dry lips, slight fatigue, decreased urine output, and irritability. Monitoring these signs early allows caregivers to increase fluid intake promptly.
What are the signs of severe dehydration in children?
Severe dehydration may include extreme lethargy, rapid heartbeat, very dry mouth, sunken eyes, and cold extremities. Recognizing these signs requires urgent attention.
Can behavior changes indicate dehydration?
Yes, children may become unusually sleepy, irritable, or less active, which often accompanies other dehydration signs.
How can caregivers support hydration at home?
Offering small, frequent sips of fluids, monitoring urine output, and observing physical signs like skin elasticity or lip moisture are effective strategies.
How long does it take for a child to recover from dehydration?
Recovery varies depending on the severity. Mild cases may improve within hours of adequate fluid intake, while more severe dehydration requires careful monitoring over a longer period.
Recognizing the symptoms of dehydration in children at home is essential for maintaining health and preventing complications. Observing physical, behavioral, and urinary signs enables caregivers to respond promptly. Consistent monitoring, encouraging fluids, and awareness of early and severe indicators provide effective support for pediatric hydration. Early attention ensures that children remain healthy, energetic, and well-hydrated, promoting overall well-being.





Comments