Introduction
Diabetes is a growing health concern worldwide, including in Muscat, Oman. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, the need for effective management options becomes more pressing. Traditionally, diabetes has been managed with lifestyle modifications, oral medications, and insulin therapy. However, newer treatments, such as Ozempic, have emerged as alternatives that promise improved outcomes. This article examines the differences between Ozempic Injection Muscat and traditional diabetes treatments, with a specific focus on the implications for individuals.
Understanding Diabetes Management
Diabetes is classified mainly into two types: Type 1 and Type 2. While Type 1 diabetes often requires insulin from diagnosis, Type 2 diabetes, which accounts for a larger percentage of diabetes cases, is typically managed through lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin.
Traditional Treatments for Diabetes
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Diet and exercise are the cornerstones of diabetes management. A balanced diet low in sugar and refined carbohydrates, combined with regular physical activity, can help control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
- Oral Medications
- Several classes of oral medications are available, including:
- Sulfonylureas: Stimulate insulin production from the pancreas.
- Biguanides: Improve insulin sensitivity and reduce liver glucose production (e.g., metformin).
- DPP-4 Inhibitors: Enhance the body's incretin levels, which help to lower blood sugar.
- Insulin Therapy
- For some patients, insulin injections become necessary to manage blood sugar levels effectively. Insulin therapy may be used alone or in combination with other medications.
Emerging Treatments: Ozempic
Ozempic (semaglutide) is a relatively new medication for managing Type 2 diabetes. It belongs to a class of drugs known as GLP-1 receptor agonists, which mimic the incretin hormones that the body produces naturally to stimulate insulin secretion in response to meals.
Mechanism of Action
Ozempic works by:
- Increasing insulin secretion in response to meals.
- Reducing glucagon release (which raises blood sugar levels).
- Slowing gastric emptying, which helps control appetite and reduces food intake.
Ozempic vs Traditional Treatments
Efficacy
Ozempic has shown superior efficacy in lowering HbA1c levels, a key indicator of long-term blood sugar control. Clinical trials have demonstrated that patients using Ozempic can achieve greater reductions in blood sugar compared to those on traditional oral medications alone.
Weight Management
Weight management is a significant concern for many individuals with Type 2 diabetes. Ozempic has been associated with weight loss, a crucial benefit for those who are overweight or obese, conditions that can exacerbate diabetes. Traditional treatments often do not offer the same advantages in weight control, and some oral medications may even lead to weight gain.
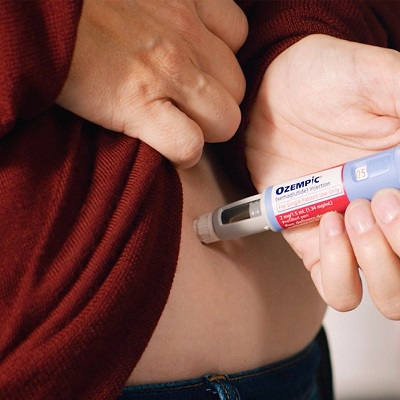
Administration and Convenience
Ozempic is administered as a once-weekly injection, which may be more convenient for some patients compared to daily oral medications or multiple insulin injections. The ease of use can significantly enhance adherence to treatment regimens, leading to better overall management of diabetes.
Side Effects and Considerations
While Ozempic offers numerous benefits, it is not without potential side effects. Common adverse effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. In contrast, traditional oral medications may have their own side effects, such as hypoglycemia with sulfonylureas or gastrointestinal issues with metformin.
The Muscat Perspective
In Muscat, the landscape of diabetes treatment is shaped by various factors, including healthcare access, cultural dietary practices, and the rising prevalence of obesity. The introduction of medications like Ozempic can offer new hope for individuals struggling to manage their diabetes effectively.
Access to Treatments
The availability of Ozempic in Muscat may vary, and healthcare providers must ensure that patients have access to the latest treatment options. Educational initiatives to inform patients about the benefits and risks of Ozempic compared to traditional therapies are vital for informed decision-making.
Cultural Considerations
Diet plays a crucial role in diabetes management, and traditional Omani cuisine may pose challenges for individuals trying to manage their blood sugar levels. The incorporation of Ozempic into treatment plans could empower patients to maintain better control over their diabetes while allowing for more flexibility in dietary choices.
Conclusion
The emergence of Ozempic as a treatment option for Type 2 diabetes presents exciting possibilities for individuals in Muscat. While traditional treatments have long been the foundation of diabetes management, the advantages of Ozempic—such as enhanced efficacy, weight loss benefits, and convenient dosing—make it a compelling alternative. However, the decision to use Ozempic or traditional treatments should be individualized, considering each patient's unique circumstances, preferences, and health profiles. As the landscape of diabetes care continues to evolve, ongoing education and access to new treatments will be essential in empowering individuals to manage their diabetes effectively.




Comments