Lipomas are benign, slow-growing lumps of fatty tissue that commonly develop under the skin. While they are generally harmless, many people seek lipoma treatment for cosmetic reasons or to alleviate discomfort. If you've recently discovered a lipoma or have been diagnosed with one, you're likely seeking answers and guidance on what to expect from treatment. This article covers essential information for first-timers who are considering lipoma treatment.
What is a Lipoma?
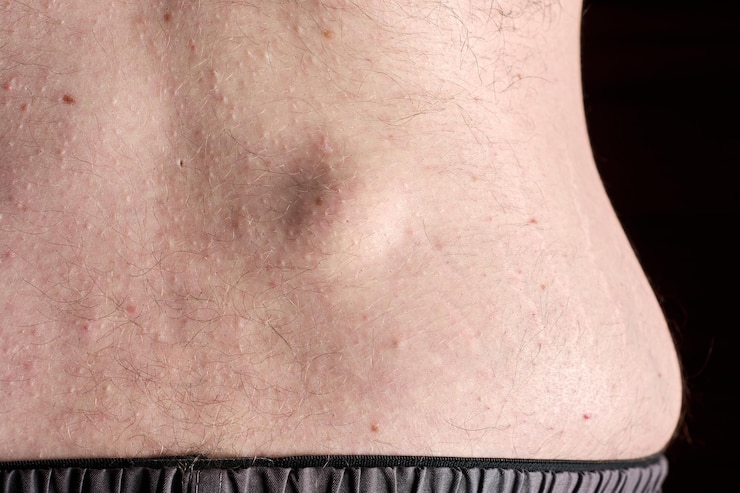
A lipoma is a soft, movable mass that forms beneath the skin, often appearing on the arms, back, neck, or thighs. Let's delve into Lipoma Treatment in Dubai. These fatty lumps are typically painless and can vary in size, ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. Lipomas are made up of fat cells and grow slowly over time. Although they are not cancerous, some individuals may choose to have them removed if they become uncomfortable or interfere with daily activities.
Common Symptoms of Lipomas
While lipomas are generally not painful, they may cause mild discomfort depending on their location. Some of the common signs and symptoms include:
- Soft, doughy texture: Lipomas usually feel soft and are easily movable under the skin.
- Round or oval shape: Most lipomas are round or oval in shape and have smooth edges.
- Slow growth: Lipomas grow slowly over the years, often without any noticeable change for long periods.
- Painless lumps: Most lipomas do not cause pain, but if they press against nerves or develop in sensitive areas, discomfort can occur.
If a lump is growing rapidly or becomes painful, it is important to seek medical advice, as these could be signs of a different condition.
Lipoma Treatment: Essential Info for First-Timers
Lipoma treatment is often considered when the lump becomes bothersome, cosmetically undesirable, or interferes with physical movement. While many people live with lipomas without requiring treatment, understanding your options is crucial for first-timers. The approach to treatment varies depending on the size, location, and the patient's overall health. Here are the primary methods of treating lipomas.
Diagnosis Before Treatment
Before any treatment can begin, it is essential to get a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional. In most cases, a doctor can identify a lipoma through a physical examination. However, in some situations, additional tests like ultrasounds, MRI, or CT scans may be required to confirm the diagnosis. These imaging tests are particularly useful when the lipoma is located deeper within the body or if the doctor suspects a different type of growth.
Surgical Excision
Surgical excision is the most common method of removing a lipoma. This procedure involves cutting out the lipoma through a small incision in the skin. It is typically performed under local anesthesia, meaning the patient remains awake, but the area around the lipoma is numbed to prevent pain. In cases where the lipoma is large or located in a sensitive area, general anesthesia may be used.
- Procedure: The surgeon will make a small incision over the lipoma, carefully remove it, and then close the incision with stitches. The procedure usually takes about 30 minutes to an hour, depending on the size and location of the lipoma.
- Recovery: After surgery, the recovery period is relatively short. Most patients can return to their normal activities within a few days. The incision will heal in about one to two weeks, although there may be some minor scarring.
Liposuction
Liposuction is another option for removing lipomas, especially larger ones. This minimally invasive procedure involves using a suction device to remove the fatty tissue. Liposuction is often preferred for individuals who want to avoid the scarring that comes with surgical excision.
- Procedure: A small incision is made near the lipoma, and a thin tube (cannula) is inserted to break up and suction out the fat. This technique is less invasive than surgery and can be done under local anesthesia.
- Recovery: Liposuction typically has a faster recovery time compared to traditional surgery. Patients can expect some mild swelling and bruising around the area, but this usually subsides within a few days. As with any procedure, there is a slight risk of infection, but complications are rare.
Steroid Injections
In some cases, doctors may recommend steroid injections as a treatment for lipomas. Steroids can shrink the size of the lipoma by breaking down the fatty tissue. However, this method is not always effective at completely removing the lipoma, and it is generally used for smaller growths.
- Procedure: The doctor injects a corticosteroid directly into the lipoma. This reduces its size over the following weeks.
- Recovery: Recovery is almost immediate, with little to no downtime. However, steroid injections may not provide a permanent solution, as lipomas can regrow after treatment.
Observation (Watchful Waiting)
For many people with small, asymptomatic lipomas, treatment may not be necessary. In these cases, a doctor may recommend a "watch and wait" approach, especially if the lipoma is not growing or causing discomfort. Regular check-ups can help monitor the size and any potential changes in the lipoma.
- Procedure: No medical intervention is performed. Instead, the patient and doctor monitor the lipoma for growth or any signs of discomfort.
- Recovery: Since no treatment is given, there is no recovery needed. This approach is best suited for individuals with lipomas that are small, painless, and not bothersome.
What to Expect After Lipoma Treatment
Regardless of the treatment method chosen, most patients experience a smooth and straightforward recovery process. Here’s what first-timers can expect:
- Mild pain and swelling: After surgical removal or liposuction, there may be some discomfort and swelling in the treated area. Pain is usually mild and can be managed with over-the-counter pain medications.
- Scar formation: For surgical excision, a small scar will likely form where the incision was made. Over time, the scar will fade, but it may not disappear completely.
- Follow-up care: Depending on the size and location of the lipoma, follow-up appointments may be necessary to ensure proper healing and to check for any recurrence of the lipoma.
Preventing Recurrence
While most lipomas do not regrow after treatment, there is a small chance of recurrence. To minimize this risk, it is essential to follow your doctor's aftercare instructions and attend any recommended follow-up appointments.
Final Thoughts
Lipomas are common and generally harmless growths, but for first-timers considering treatment, it's important to understand the available options. Whether through surgery, liposuction, or observation, lipoma treatment is typically straightforward with minimal risks. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the best course of action based on your specific needs and health.




Comments