What is cervical cancer?
The cervix is the bottom portion of the uterus. The HPV virus is responsible for over 70% of cervical cancer cases. The virus spreads by sexual interaction. Most women’s bodies can resist HPV infection. However, occasionally the virus causes cancer. If the patient smokes, has had a large number of children, has taken birth control pills for an extended period of time, or is HIV positive, the risk increases.
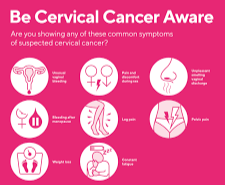
Symptoms of cervical cancer:
Abnormal bleeding can occur between menstrual cycles, after intercourse, after a pelvic check, or after menopause.
Discharge that is exceptional in quantity, color, consistency, or smell.
Having to urinate more frequently.
Pelvic discomfort.
Possible causes for painful urinating include:
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN)
The World Health Organization recommends an HPV vaccine for girls over the age of ten to protect them against cervical cancer.
Treatment of Cervical Cancer:
Dr. Chandrakanta Gynecology Centre in Jaipur specializes on gynecological cancer treatment. They offer complete assistance for women with gynecological malignancies by combining innovative therapies, competent specialists, and patient-centered care.
The treatment of cervical cancer depends on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and their preferences. Treatment may involve one or more of the following modalities:
Surgery: Surgery is often recommended for early-stage cervical cancer. The type of surgery may vary depending on the extent of the cancer and whether the patient desires to preserve fertility. Common surgical procedures include:
Conization (LLETZ or CKC): Removal of a cone-shaped piece of tissue from the cervix.
Simple Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus and cervix.
Radical Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus, cervix, surrounding tissue, and possibly nearby lymph nodes.
Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells. It can be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
Types of radiation therapy for cervical cancer include:
External Beam Radiation: Radiation delivered from outside the body.
Brachytherapy: Radiation delivered internally using radioactive implants placed near the tumor.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. It may be used before surgery (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) to shrink tumors, after surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy) to kill any remaining cancer cells, or in combination with radiation therapy (chemoradiation) for advanced cervical cancer.
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy: These newer treatment approaches target specific molecules involved in cancer growth or harness the body’s immune system to fight cancer. While not yet standard treatments for cervical cancer, they are being investigated in clinical trials and may offer additional options in the future.
Palliative Care: For advanced or metastatic cervical cancer that cannot be cured, palliative care focuses on relieving symptoms, improving quality of life, and providing emotional support for patients and their families.




Comments