Cervical cancer is a significant health concern affecting women worldwide. It develops in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. While cervical cancer can be a serious and potentially life-threatening condition, understanding its causes, treatment options, and preventive measures can empower women to take proactive steps in managing their health.
Causes of Cervical Cancer:
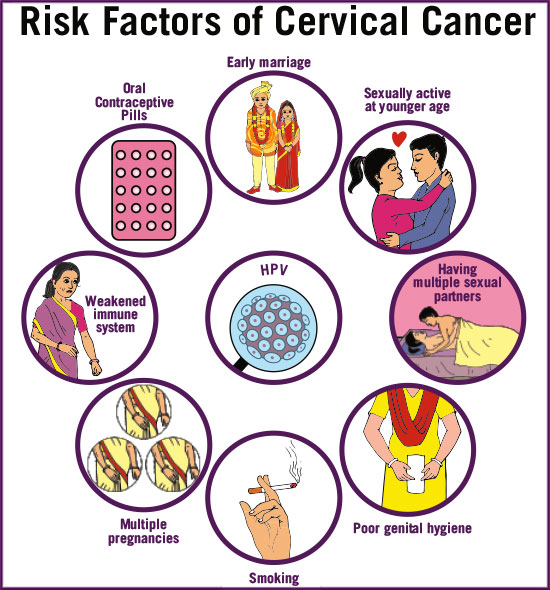
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is the primary cause of cervical cancer. HPV is a common sexually transmitted infection, and certain strains of the virus, particularly HPV types 16 and 18, are strongly associated with the development of cervical cancer. Other factors that may increase the risk of cervical cancer include:
- Smoking: Women who smoke are at a higher risk of developing cervical cancer than non-smokers.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those living with HIV/AIDS or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, are more susceptible to HPV infection and subsequent cervical cancer.
- Multiple Sexual Partners:Engaging in sexual activity with multiple partners increases the risk of HPV infection and cervical cancer.
Treatment Options for Cervical Cancer:
The treatment approach for cervical cancer depends on various factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and their preferences. Common treatment options for cervical cancer include:
- Surgery: Surgical procedures such as hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) or trachelectomy (removal of the cervix) may be recommended for early-stage cervical cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells. It may be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of powerful drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. It may be administered before or after surgery, or in combination with radiation therapy.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy drugs target specific molecules involved in cancer growth and progression. They may be used in cases where standard treatments are not effective.
Preventive Measures and Precautions:
Preventing cervical cancer primarily involves reducing the risk of HPV infection and undergoing regular screenings for early detection. Here are some preventive measures and precautions women can take:
- HPV Vaccination:The HPV vaccine is highly effective in preventing infection with the most common cancer-causing strains of HPV. It is recommended for both girls and boys starting at age 11 or 12, although it can be given as early as age 9 and up to age 26.
- Practice Safe Sex: Using condoms consistently and correctly during sexual activity can reduce the risk of HPV transmission.
- Regular Pap Smears: Pap smears, also known as Pap tests, are screening tests that can detect abnormal changes in the cells of the cervix before they develop into cancer. Women should undergo regular Pap smears as recommended by their healthcare provider.
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke, quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk of cervical cancer and improve overall health.
Cervical cancer is a preventable and treatable disease, especially when detected early. By understanding the causes, treatment options, and preventive measures outlined above, women can take proactive steps to protect their health and reduce the burden of cervical cancer worldwide. Regular screenings, HPV vaccination, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits are essential components of cervical cancer prevention and control efforts. Through education, awareness, and access to healthcare services, we can strive towards a future where cervical cancer is no longer a significant public health threat.




Comments