Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a type of assisted reproductive technology used to increase the chances of conception. It involves placing sperm directly into the uterus around the time of ovulation, which can enhance the chances of sperm reaching the egg and fertilization occurring. Here’s a basic outline of how IUI works and how it differs from other fertility treatments:
How IUI Works:
1. Preparation: The woman’s menstrual cycle is monitored to determine the optimal time for ovulation. This may involve tracking through blood tests, ultrasounds, or ovulation predictor kits.
2. Sperm Collection: Sperm is collected from a partner or a donor. The sperm is then processed in a laboratory to concentrate the most motile sperm and remove any impurities.
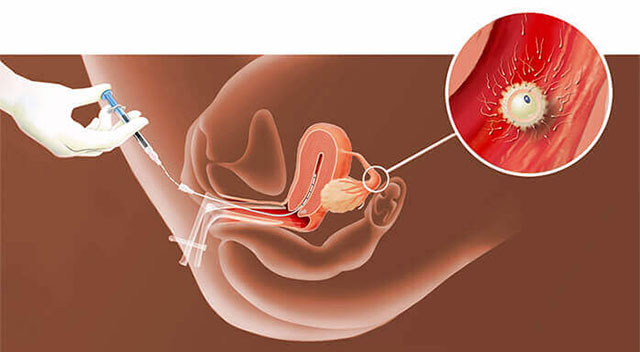
3. Insemination: Using a thin, flexible catheter, the prepared sperm is inserted directly into the uterus. This is typically done in a doctor’s office and does not require anesthesia.Test tube baby Centre Near me
4. Post-Insemination: After the procedure, the woman may be advised to rest briefly, but many resume normal activities almost immediately.
Differences from Other Fertility Treatments:
1. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF):
— Procedure: IVF involves stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, retrieving those eggs through a minor surgical procedure, fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory, and then transferring one or more embryos into the uterus.Test tube baby Centre Near me
— Complexity: IVF is generally more complex and invasive than IUI. It often involves hormone injections and multiple medical procedures.
— Success Rate: IVF generally has a higher success rate per cycle compared to IUI, especially in cases of severe infertility issues.
2. Ovulation Induction:
Procedure: Ovulation induction uses medications to stimulate the ovaries to release eggs. This can be used alone or in conjunction with IUI.
Purpose: It helps women who have irregular or absent ovulation to produce eggs, and is sometimes part of an IUI cycle to improve the chances of success.
3. Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI):
Procedure: ICSI is a type of IVF where a single sperm is injected directly into an egg. This technique is used for severe male infertility issues.
Complexity: Like IVF, ICSI is more complex and invasive, requiring egg retrieval and embryo transfer.
4. Artificial Insemination (AI):
— Procedure: AI is a broader term that includes IUI but can also refer to other methods of placing sperm into the reproductive tract, such as intracervical insemination (ICI), where sperm is placed directly into the cervix rather than the uterus.
— Location: IUI is more targeted, placing sperm directly into the uterus to increase the likelihood of fertilization.
5. Donor Eggs/Sperm:
— Procedure: Involves using eggs or sperm from a donor if there are issues with the quality or availability of the patient’s own gametes. This can be used with both IUI and IVF.
Overall, IUI is often chosen for its relative simplicity and lower cost compared to more invasive techniques like IVF. It is typically recommended for cases of mild male infertility, unexplained infertility, or issues with cervical mucus. The choice of treatment depends on individual factors such as the underlying cause of infertility, age, and overall health.




.png)
Comments