Acne scars are a common fear among those who have had severe or chronic acne. Scars can have an impact not just on the skin, but also on one’s self-esteem and confidence. Understanding what acne scars are, how they occur, and the various treatment options will help you manage and perhaps reduce their appearance.
What Are Acne Scars?
Acne scars are caused by inflammation in the skin’s dermal layer, which happens when acne lesions penetrate deep into the skin and harm the tissues beneath. As the body tries to heal the damage, it creates collagen. Scars occur when there is either too little or too much collagen generated.
There are several types of acne scars, each with distinct characteristics and causes:
Types of Acne Scars
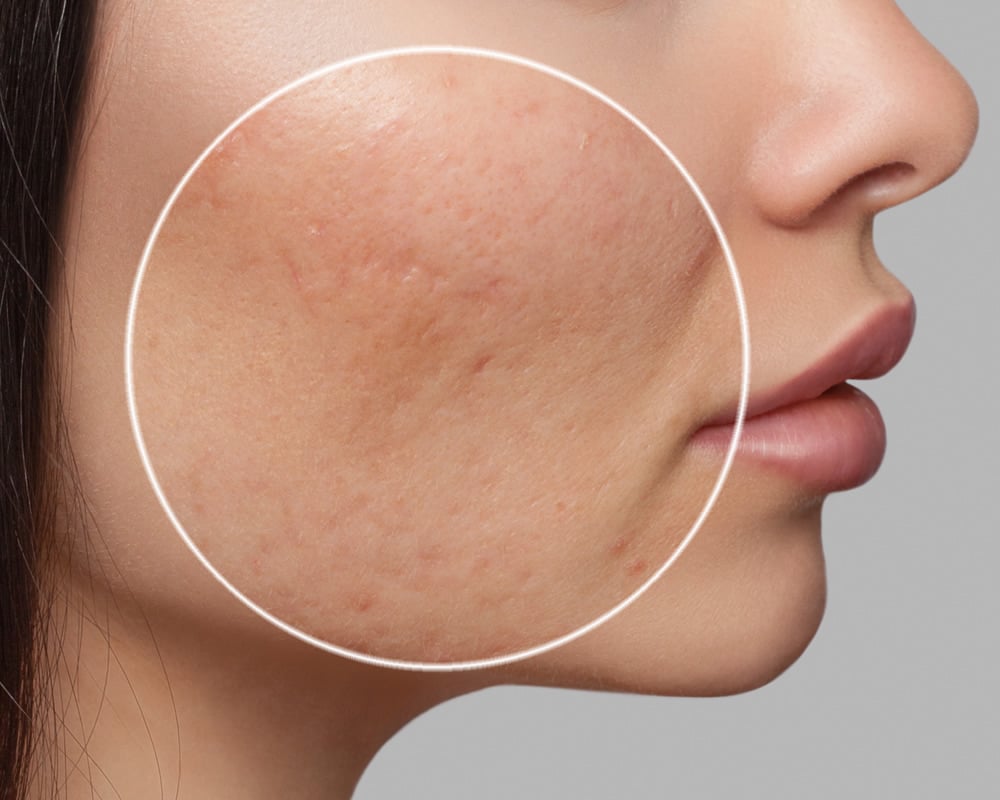
1. Atrophic Scars: These are the most common type of acne scars and occur when there is a loss of tissue. They can be further classified into three subtypes:
— Ice Pick Scars: Deep, narrow scars that extend into the dermis, giving the skin a pitted appearance.
— Boxcar Scars: Broad, box-like depressions with sharp edges, often found on the cheeks and temples.
— Rolling Scars: Wide, shallow scars that create a wavy texture on the skin.
2. Hypertrophic and Keloid Scars: These occur when the body produces too much collagen, resulting in raised scars that can be larger than the original acne spot. Hypertrophic scars are confined to the boundaries of the original wound, whereas keloid scars can grow beyond these boundaries.
Causes of Acne Scars
Several factors contribute to the development of acne scars:
- Severity and Duration of Acne: Severe and prolonged acne increases the likelihood of scarring.
- Inflammation: Greater inflammation leads to more significant damage to the skin.
- Picking and Squeezing: Manipulating acne lesions can worsen inflammation and damage the skin.
- Genetics: Some people are more prone to scarring due to their genetic makeup.
Treatment Options for Acne Scars
While acne scars can be stubborn, various treatments can help improve their appearance. The best treatment depends on the type and severity of the scars.
Topical Treatments
- Retinoids: These vitamin A derivatives can promote cell turnover and improve skin texture.
- Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): AHAs help exfoliate the skin and reduce the appearance of mild scarring.
- Silicone Gels: Effective for reducing hypertrophic and keloid scars by hydrating the skin and flattening raised scars.
Medical Procedures
1. Chemical Peels: These involve applying a chemical solution to the skin, causing it to exfoliate and peel off, revealing smoother skin underneath.
2. Microdermabrasion and Dermabrasion: These techniques mechanically exfoliate the skin to reduce the appearance of superficial scars.
3. Microneedling: Tiny needles create micro-injuries in the skin, stimulating collagen production and improving the appearance of scars.
4. Laser Therapy: Laser treatments, such as fractional lasers, can target deeper layers of the skin to stimulate collagen production and resurface the skin.
5. Fillers: Injecting fillers can help lift depressed scars, making them less noticeable.
6. Surgical Options: In severe cases, surgical procedures like punch excision or subcision may be necessary to remove or break up scar tissue.
Prevention Tips
Preventing acne scars starts with effective acne management:
- Early Treatment: Treat acne early to prevent severe outbreaks.
- Avoid Picking: Resist the urge to pick or squeeze pimples.
- Sun Protection: Protecting your skin from the sun can prevent scars from becoming more pronounced.
Conclusion
While acne scars are difficult to maintain, the appropriate therapy can substantially minimize their appearance. Consulting with a dermatologist is essential for designing a tailored treatment strategy that targets the exact type of scars and your skin type. Understanding the nature of acne scars and reviewing various treatment options allows you to take proactive efforts toward smoother, cleaner skin.





Comments