Urology is a medical specialty that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of illnesses affecting the urinary tract and male reproductive system. Urologists are medical experts trained to treat these diseases, and they care for patients ranging from young children to the elderly. This blog will explore the various diseases and conditions that urologists treat, shedding light on their critical role in maintaining urological health.
1. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections are one of the most prevalent diseases treated by urologists. UTIs develop when bacteria enter the urinary system, causing symptoms such as frequent urination, burning when peeing, and murky urine. While primary care physicians frequently treat simple UTIs, recurring or complex infections need the services of a urologist.
2. Kidney Stones
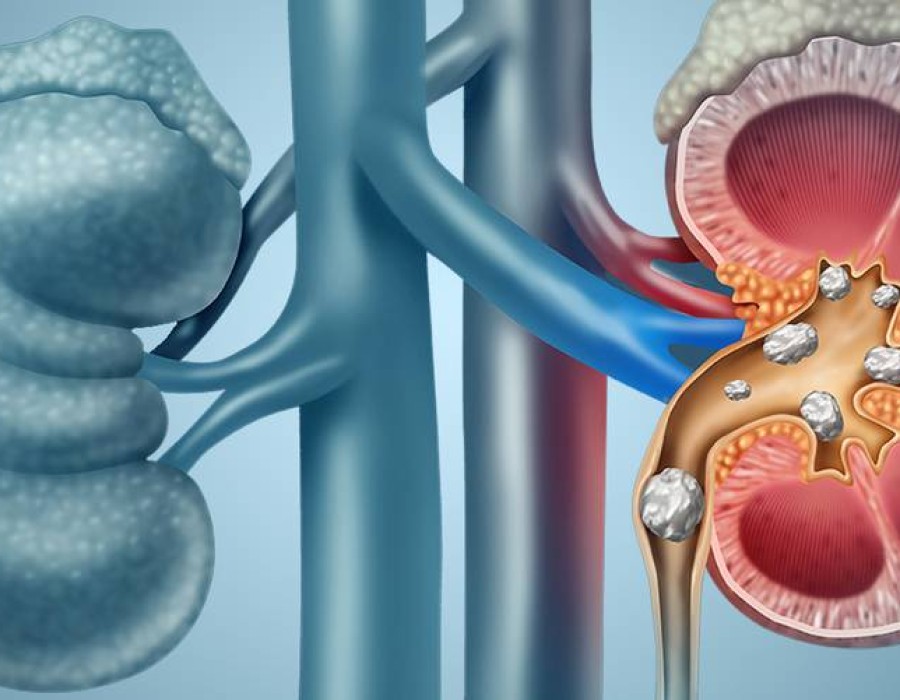
Kidney stones are hard mineral deposits that grow in the kidneys and cause considerable discomfort when they pass through the urinary canal. Urologists specialize in identifying and treating kidney stones with a variety of techniques, including medicine, shock wave lithotripsy, and minimally invasive surgical treatments.
Kidney Stones
3. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
BPH, or enlarged prostate, is a frequent problem among elderly men. It can cause bladder difficulties such as difficulty commencing urination, decreased urine flow, and frequent midnight urination. Urologists treat BPH with drugs, lifestyle modifications, and surgical procedures such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP).
4. Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most common malignancies in males. Urologists play an important role in early detection, diagnosis, and treatment. They provide a variety of treatment choices, including active surveillance, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and surgical treatments like as radical prostatectomy.
5. Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer frequently causes symptoms such as blood in the urine, frequent urination, and pelvic discomfort. Urologists use cystoscopy and imaging examinations to identify bladder cancer, which is then treated with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation treatment, and immunotherapy.
6. Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence, often known as lack of bladder control, can have a substantial influence on one’s quality of life. Urologists investigate the underlying reasons, which may include weak pelvic floor muscles, nerve damage, or prostate problems in males. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, pelvic floor exercises, medicines, and surgical treatments.
7. Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Erectile dysfunction refers to the inability to produce or maintain an adequate erection for sexual intercourse. Urologists investigate the reasons of ED, which can be psychological, neurological, or associated with underlying health issues such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Lifestyle modifications, drugs, vacuum erection devices, and penile implants are all possible treatments.
8. Male Infertility
Male infertility can be caused by a variety of causes, such as insufficient sperm production, obstructions, or hormone abnormalities. Urologists are experts in identifying and treating these conditions, using treatments such as hormone therapy, surgical repair of anatomical abnormalities, and assisted reproductive technologies such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
9. Interstitial Cystitis (IC)
IC, also known as painful bladder syndrome, is a chronic illness characterized by bladder pressure, bladder discomfort, and pelvic pain. Urologists treat IC with a variety of therapies, including diet modifications, physical therapy, medicines, and bladder instillations.
10. Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cell carcinoma, requires specialist care to be effectively treated. To identify kidney cancer, urologists employ a variety of diagnostic methods such as CT scans, MRIs, and biopsies. Treatment options include partial or radical nephrectomy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
11. Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer, albeit less prevalent, mostly affects young men. Urologists are in charge of diagnosing and treating the condition, which may involve surgery (orchiectomy), radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
12. Pediatric Urological Conditions
Urologists also treat a variety of juvenile diseases, including vesicoureteral reflux (a condition in which urine runs backward from the bladder to the kidneys), undescended testicles, and congenital urinary system anomalies.
Conclusion
Urologists play an important role in treating a wide range of disorders affecting the urinary tract and male reproductive system. Their competence guarantees that patients receive complete care, from diagnosis to treatment and management of complicated urological problems. If you are experiencing symptoms connected to your urinary or reproductive health, a urologist can offer you with the specialist treatment you need to properly address these concerns.





Comments