Joint replacement surgery, often recommended to relieve pain and improve mobility in individuals with severe joint damage, can be a life-changing procedure. However, like any surgical procedure, it comes with potential risks and complications. Understanding these risks is crucial for patients considering joint replacement surgery. In this article, we'll explore the common risk factors associated with joint replacement surgery to help individuals make informed decisions about their healthcare.
1. Medical History: A patient's medical history plays a significant role in determining the risks associated with joint replacement surgery. Conditions such as obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders can increase the risk of complications during and after surgery. Patients with a history of blood clots or infections may also face heightened risks.
2. Age: While joint replacement surgery can be performed at any age, older patients may be at a higher risk of complications due to factors such as reduced bone density, slower healing, and the presence of other age-related health conditions. However, advanced age alone should not necessarily deter patients from undergoing surgery, as many older adults experience successful outcomes.
3. Overall Health: In addition to specific medical conditions, a patient's overall health and fitness level can influence the risks associated with joint replacement surgery. Poor physical conditioning, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a lack of nutritional support can all increase the likelihood of complications and slow the healing process.
4. Type of Surgery: The type of joint replacement surgery being performed can also affect the associated risks. For example, total hip replacement and total knee replacement are commonly performed procedures with relatively low complication rates, while more complex surgeries, such as revision joint replacement or simultaneous bilateral joint replacement, carry higher risks.
5. Surgical Technique and Experience: The skill and experience of the surgical team performing the procedure are crucial factors in minimizing risks and achieving successful outcomes. Patients should seek out surgeons who specialize in joint replacement surgery and have a proven track record of success.
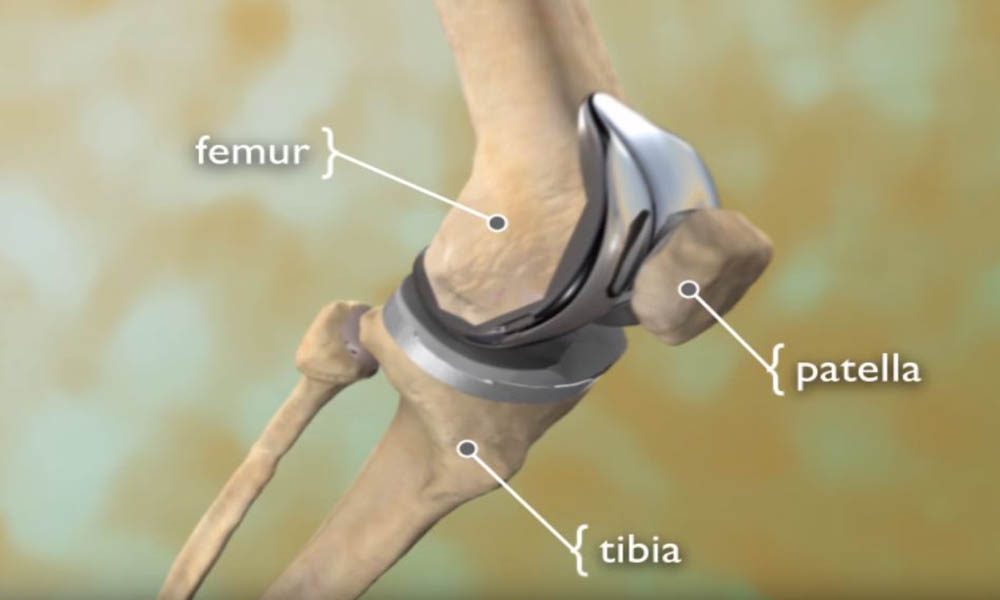
6. Implant Selection: The type of implant used in joint replacement surgery can impact the risk of complications. While modern implants are designed to be durable and biocompatible, there is still a risk of implant failure, loosening, or dislocation. Patients should discuss their options with their surgeon and weigh the benefits and risks of different implant materials and designs.
7. Rehabilitation and Recovery: Proper rehabilitation and post-operative care are essential for minimizing the risk of complications and optimizing outcomes following joint replacement surgery. Patients should adhere to their surgeon's recommendations regarding physical therapy, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments to ensure a smooth recovery process.
8. Infection: Infection is a serious complication that can occur after joint replacement surgery. While strict sterile techniques are used during surgery to minimize the risk of infection, patients should be vigilant about practicing good hygiene, monitoring for signs of infection, and promptly reporting any concerns to their healthcare provider.
9. Blood Clots: Blood clots, or deep vein thrombosis (DVT), are a potential risk following joint replacement surgery, particularly in the lower extremities. Patients may be prescribed blood thinners or compression stockings to reduce the risk of DVT, and early mobilization and activity are encouraged to promote healthy blood circulation.
In conclusion, while joint replacement surgery can offer significant relief and improvement in quality of life for individuals with debilitating joint pain, it is not without risks. Patients should carefully consider their own medical history, overall health, and the expertise of their surgical team when weighing the potential risks and benefits of joint replacement surgery. Open communication with healthcare providers and adherence to pre- and post-operative guidelines are essential for minimizing risks and achieving successful outcomes.





Comments