Introduction:
Orthopedics, the branch of medicine dedicated to the diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of musculoskeletal disorders, plays a crucial role in maintaining mobility, function, and overall well-being. From treating sports injuries to managing degenerative conditions, orthopedic specialists employ a diverse range of techniques to help individuals overcome challenges and regain optimal musculoskeletal health. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the fundamentals of orthopedics, common conditions treated, diagnostic approaches, treatment options, and the importance of proactive care in preserving mobility and preventing injuries.
1. Musculoskeletal Anatomy and Function:
- Bones: The structural framework of the body, bones provide support, protection, and anchorage for muscles and organs.
- Joints: Articulations where bones meet, allowing for movement and flexibility.
- Muscles: Contractile tissues responsible for generating force and facilitating movement.
- Ligaments and Tendons: Connective tissues that stabilize joints and attach muscles to bones, respectively, enabling coordinated movement and function.
2. Common Orthopedic Conditions:
- Osteoarthritis: A degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, resulting in pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
- Fractures: Breaks or cracks in bones caused by trauma, accidents, or underlying medical conditions.
- Tendonitis and Bursitis: Inflammation of tendons or bursae (fluid-filled sacs) due to overuse, repetitive motion, or injury, leading to pain and swelling.
- Rotator Cuff Tears: Tears or damage to the muscles and tendons surrounding the shoulder joint, often resulting from trauma or repetitive overhead movements.
- Spinal Disorders: Conditions affecting the spine, such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and scoliosis, which can cause pain, numbness, and limitations in mobility.
3. Diagnostic Techniques:
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRI scans, CT scans, and ultrasound are utilized to visualize bones, joints, and soft tissues, aiding in the diagnosis of orthopedic conditions.
- Physical Examination: Orthopedic specialists conduct thorough physical assessments, evaluating range of motion, strength, stability, and neurological function to identify musculoskeletal abnormalities.
4. Treatment Approaches:
- Non-Surgical Interventions: Conservative treatments such as rest, physical therapy, medication, bracing, and injections are often recommended for managing orthopedic conditions and injuries.
- Surgical Procedures: When conservative measures fail to provide relief or in cases of severe trauma or degeneration, surgical interventions may be necessary to repair, reconstruct, or replace damaged tissues or joints.
5. Prevention and Rehabilitation:
- Exercise and Conditioning: Regular physical activity, including strength training, flexibility exercises, and cardiovascular workouts, can help maintain musculoskeletal health, improve strength, and reduce the risk of injuries.
- Injury Prevention Strategies: Proper warm-up, technique modification, use of protective gear, and gradual progression in physical activities can minimize the risk of orthopedic injuries.
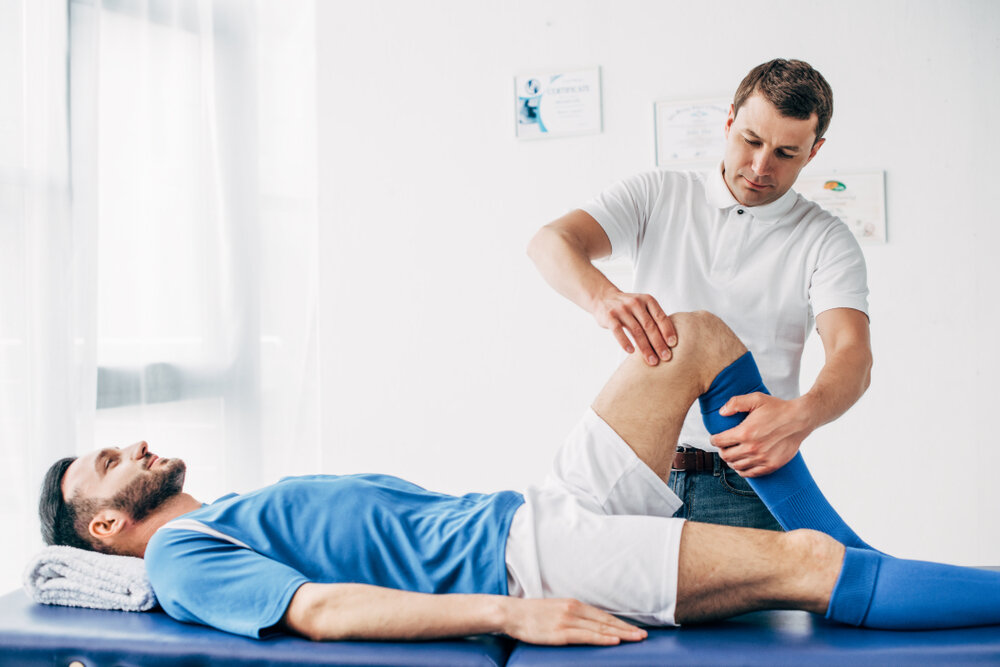
- Rehabilitation Programs: Following surgery or injury, structured rehabilitation programs guided by physical therapists focus on restoring mobility, strength, and function, facilitating a safe return to daily activities and sports.
Conclusion:Orthopedics encompasses a vast spectrum of conditions and treatments aimed at preserving and restoring musculoskeletal health. By understanding the principles of orthopedic care, recognizing the importance of early intervention, and embracing proactive measures for prevention and rehabilitation, individuals can optimize their mobility, function, and overall quality of life. Whether seeking treatment for an injury, managing a chronic condition, or striving for peak performance, orthopedic specialists stand ready to support and guide individuals on their journey to musculoskeletal wellness




Comments