Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, has transformed the field of surgery by offering patients a less invasive alternative to traditional open procedures. For more detail visit our site(وضع بالون المعدة بالمنظار في الرياض)In this comprehensive guide, we take a closer look at the techniques and principles behind laparoscopic surgery.
1. Introduction to Laparoscopic Surgery
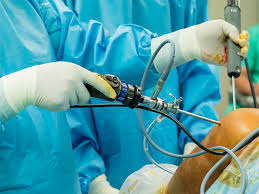
- Definition: Laparoscopic surgery involves performing surgical procedures through small incisions in the abdomen using specialized instruments and a camera called a laparoscope.
- Minimally Invasive Approach: Unlike traditional open surgery, which requires large incisions, laparoscopic surgery minimizes trauma to the body, resulting in reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times.
- Evolution and Advancements: Laparoscopic surgery has evolved significantly since its inception, with advancements in technology, instrumentation, and surgical techniques contributing to improved patient outcomes.
2. Key Components and Instruments
- Laparoscope: A thin, tube-like instrument equipped with a camera and light source that provides high-definition images of the surgical site.
- Trocar: Sharp, pointed instruments used to create access ports for inserting laparoscopic instruments into the abdomen.
- Laparoscopic Instruments: Specialized instruments designed for use in minimally invasive surgery, including graspers, scissors, dissectors, and energy devices.
3. Techniques and Principles
- Insufflation and Pneumoperitoneum: The process of inflating the abdomen with carbon dioxide gas to create a working space for the surgical instruments.
- Visualization and Imaging: Utilization of the laparoscope to provide a magnified view of the internal organs on a monitor, allowing for precise surgical navigation.
- Tissue Manipulation and Dissection: Techniques for manipulating tissues and performing surgical maneuvers using laparoscopic instruments with minimal tissue trauma.
- Suturing and Stapling: Methods for closing incisions and securing tissues using laparoscopic suturing and stapling devices, enabling precise tissue approximation.
4. Advantages of Laparoscopic Surgery
- Minimized Trauma: Laparoscopic surgery reduces trauma to the body, resulting in less postoperative pain and faster recovery times.
- Enhanced Visualization: High-definition imaging provided by the laparoscope allows for better visualization of the surgical field, enabling surgeons to perform procedures with greater precision and accuracy.
- Faster Recovery: Patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery typically experience shorter hospital stays and quicker return to normal activities compared to traditional open surgery.
- Reduced Scarring: Small incisions result in minimal scarring and improved cosmetic outcomes compared to the large scars associated with open surgery.
5. Common Laparoscopic Procedures
- Gynecological Surgery: Hysterectomy, myomectomy, ovarian cystectomy.
- General Surgery: Appendectomy, cholecystectomy, hernia repair.
- Urological Surgery: Nephrectomy, prostatectomy, pyeloplasty.
- Bariatric Surgery: Gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy.
- Colorectal Surgery: Colectomy, rectopexy, polypectomy.
6. Patient Considerations and Care
- Preoperative Evaluation: Assessment of patient candidacy for laparoscopic surgery, including medical history, physical examination, and preoperative tests.
- Postoperative Recovery: Guidance for patients on pain management, wound care, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments to ensure optimal recovery.
7. Future Directions and Innovations
- Advancements in Technology: Emerging technologies such as robotic-assisted surgery and augmented reality are poised to further enhance the capabilities of laparoscopic surgery.
- Research and Clinical Trials: Ongoing research and clinical trials are investigating novel techniques and applications of laparoscopic surgery to improve patient outcomes and expand treatment options.
- Global Access to Care: Efforts to increase access to laparoscopic surgery in low-resource settings and underserved communities are underway to address disparities in healthcare delivery.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic surgery continues to be at the forefront of surgical innovation, offering patients a less invasive approach to a wide range of surgical procedures. By understanding the techniques and principles behind laparoscopic surgery, healthcare providers can deliver optimal care and improve patient outcomes, while patients can make informed decisions about their treatment options. As technology continues to advance and new techniques emerge, laparoscopic surgery remains a cornerstone of modern surgical practice, shaping the future of healthcare delivery.




Comments