Hijama treatment, also known as cupping therapy, is an ancient healing practice that has gained popularity in recent years for its potential health benefits. While this procedure offers various advantages, one common concern among individuals considering or undergoing Hijama treatment is the duration of bruises post-treatment. In this article, we will delve into the factors influencing the duration of Hijama Treatment bruises and provide insights into managing them effectively.
Understanding Hijama Treatment and its Benefits
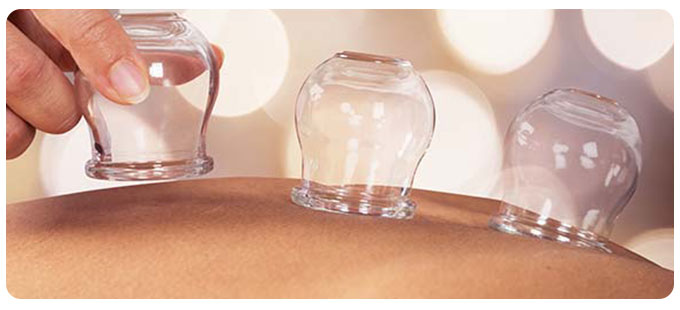
Hijama treatment involves creating suction on the skin's surface using cups to draw out stagnant blood and toxins from specific acupuncture points or areas of discomfort. This therapy is believed to improve blood circulation, alleviate pain, promote relaxation, and enhance overall well-being.
Key Points:
- Hijama treatment is an ancient therapeutic practice involving the use of suction cups on the skin.
- It aims to improve blood circulation, relieve pain, and detoxify the body.
The Bruising Phenomenon in Hijama Treatment
Bruising is a common occurrence after Hijama treatment due to the localized suction and release of blood from the capillaries beneath the skin's surface. The severity and duration of bruises can vary depending on several factors, including the individual's skin sensitivity, the intensity of suction applied during the procedure, and the specific area treated.
Key Points:
- Bruising is a natural consequence of Hijama treatment caused by the suction and release of blood.
- The severity and duration of bruises can vary based on individual factors and treatment intensity.
Factors Influencing Bruise Duration
Several factors contribute to how long bruises from Hijama treatment may last:
- Intensity of Suction: The level of suction applied during Hijama treatment can impact bruise severity. Higher suction levels may result in more pronounced bruises that take longer to fade.
- Skin Sensitivity: Individuals with sensitive skin may experience more noticeable bruises that persist for an extended period compared to those with less sensitive skin.
- Area Treated: Certain body areas are more prone to bruising due to differences in skin thickness and sensitivity. Areas with thinner skin layers may bruise more easily and take longer to heal.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Underlying health conditions, such as blood clotting disorders or vitamin deficiencies, can influence bruise formation and healing time.
Key Points:
- Intensity of suction, skin sensitivity, treated area, and pre-existing conditions affect bruise duration.
- Higher suction levels and sensitive skin may lead to longer-lasting bruises.
Managing Hijama Treatment Bruises
While bruising is a common side effect of Hijama treatment, several strategies can help alleviate discomfort and accelerate the healing process:
- Apply Cold Compress: Immediately after Hijama treatment, apply a cold compress or ice pack to the bruised area to reduce swelling and inflammation.
- Arnica Gel or Cream: Topical application of arnica gel or cream can help diminish bruising and promote faster healing.
- Gentle Massage: Lightly massaging the bruised area with gentle circular motions can stimulate blood flow and aid in dispersing trapped blood.
- Hydration and Nutrition: Ensure adequate hydration and consume a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals essential for skin health and wound healing.
- Avoid Sun Exposure: Protect bruised areas from direct sunlight, as UV rays can exacerbate discoloration and delay healing.
Key Points:
- Cold compress, arnica gel, gentle massage, hydration, nutrition, and sun protection aid in managing Hijama treatment bruises.
- These strategies can alleviate discomfort and expedite the healing process.
Expected Duration of Bruises
Typically, bruises from Hijama treatment may start to fade within a few days to a week post-treatment. However, individual variations exist, and some bruises may persist for up to two weeks or longer before completely resolving.
Key Points:
- Hijama treatment bruises usually fade within a week but may persist for up to two weeks or longer.
- Individual healing processes and treatment variables influence bruise duration.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While Hijama treatment bruises are generally harmless and resolve on their own, certain signs warrant medical attention:
- Excessive Pain: If bruised areas become excessively painful or sensitive, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation.
- Persistent Swelling: Prolonged swelling or inflammation beyond the expected healing period may indicate an underlying issue.
- Signs of Infection: If bruises show signs of infection, such as increased redness, warmth, or pus discharge, seek prompt medical care.
Key Points:
- Seek medical attention if Hijama treatment bruises cause excessive pain, persistent swelling, or signs of infection.
- Prompt evaluation is crucial to address potential complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Hijama treatment bruises are a common and temporary side effect of this ancient therapeutic practice. While bruises typically fade within a week or two, individual factors and treatment variables influence their duration. By employing appropriate management techniques and monitoring for signs of complications, individuals can safely navigate the bruising phenomenon associated with Hijama treatment. As always, consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance regarding any concerns related to Hijama treatment or its effects.
Key Points:
- Hijama treatment bruises are temporary and manageable with appropriate care.
- Consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance concerning Hijama treatment.




Comments