Urologists are highly specialized medical professionals trained to diagnose, treat, and manage a diverse array of conditions affecting the urinary tract and male reproductive system. From routine urinary issues to complex surgical interventions, urologists play a crucial role in promoting and maintaining urological health. In this article, we’ll delve into the extensive range of conditions that urologists commonly treat, highlighting their expertise and versatility in addressing various urological concerns.
Common Conditions Treated by Urologists:
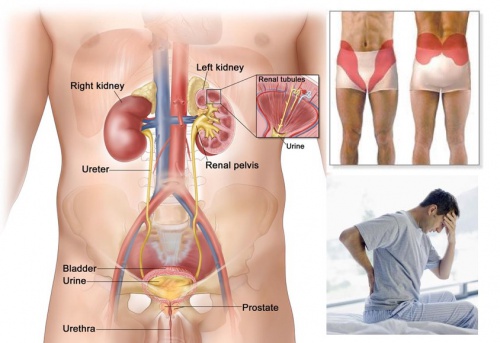
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): UTIs are bacterial infections that can affect any part of the urinary tract, including the bladder, urethra, ureters, and kidneys. Urologists diagnose and treat UTIs, prescribing antibiotics and providing guidance on prevention strategies.
- Kidney Stones: Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that form in the kidneys and can cause severe pain when they pass through the urinary tract. Urologists employ various treatment modalities, including medication, dietary modifications, and minimally invasive procedures such as lithotripsy or ureteroscopy, to manage kidney stones effectively.
- Bladder Disorders: Urologists treat a range of bladder disorders, including overactive bladder (OAB), urinary incontinence, bladder infections (cystitis), and bladder cancer. Treatment options may include medications, behavioral therapies, bladder training, or surgical interventions, depending on the specific condition and its severity.
- Prostate Conditions: The prostate gland, located below the bladder and surrounding the urethra, can be affected by various conditions, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate), and prostate cancer. Urologists evaluate prostate health, perform diagnostic tests such as prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening and prostate biopsies, and provide treatment options tailored to each patient’s needs.
- Male Reproductive Health: Urologists address a range of male reproductive health concerns, including erectile dysfunction (ED), male infertility, testicular pain or swelling, varicoceles (enlarged veins in the scrotum), and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) affecting the genitalia. Treatment approaches may include medications, surgical procedures, fertility treatments, or counseling services.
- Urologic Cancers: Urologists specialize in the diagnosis, staging, and treatment of cancers affecting the urinary tract and male reproductive organs, such as prostate cancer, bladder cancer, kidney cancer, testicular cancer, and penile cancer. Treatment options may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of these modalities, tailored to each patient’s cancer type and stage.
- Pediatric Urology: Pediatric urologists focus on diagnosing and treating urological conditions in children, including congenital anomalies of the kidneys and urinary tract, hypospadias (a birth defect affecting the urethra), undescended testes, and bedwetting (enuresis). They provide specialized care for pediatric patients, often collaborating with other medical specialists to ensure comprehensive management of complex conditions.
Conclusion:
Urologists possess expertise in diagnosing, treating, and managing a wide spectrum of urological conditions, ranging from common urinary issues to complex surgical interventions and cancer care. Whether it’s addressing kidney stones, bladder disorders, prostate conditions, male reproductive health concerns, or pediatric urological issues, urologists play a vital role in promoting optimal urological health and improving patients’ quality of life. If you’re experiencing any urological symptoms or concerns, don’t hesitate to consult a urologist for personalized evaluation and treatment.




Comments