Spiral wound gaskets are renowned for their outstanding sealing capabilities, especially in applications that involve extreme temperatures, high pressure, and aggressive chemicals. The secret behind their exceptional performance lies in the unique combination of materials used in their construction. Designed for use in critical industrial sectors like oil and gas, petrochemical, power generation, and pharmaceuticals, spiral wound gasket provide a versatile solution for preventing leaks and ensuring system integrity. In this article, we will explore the various materials used in spiral wound gaskets and their significance in different industrial applications.

The Structure of Spiral Wound Gaskets
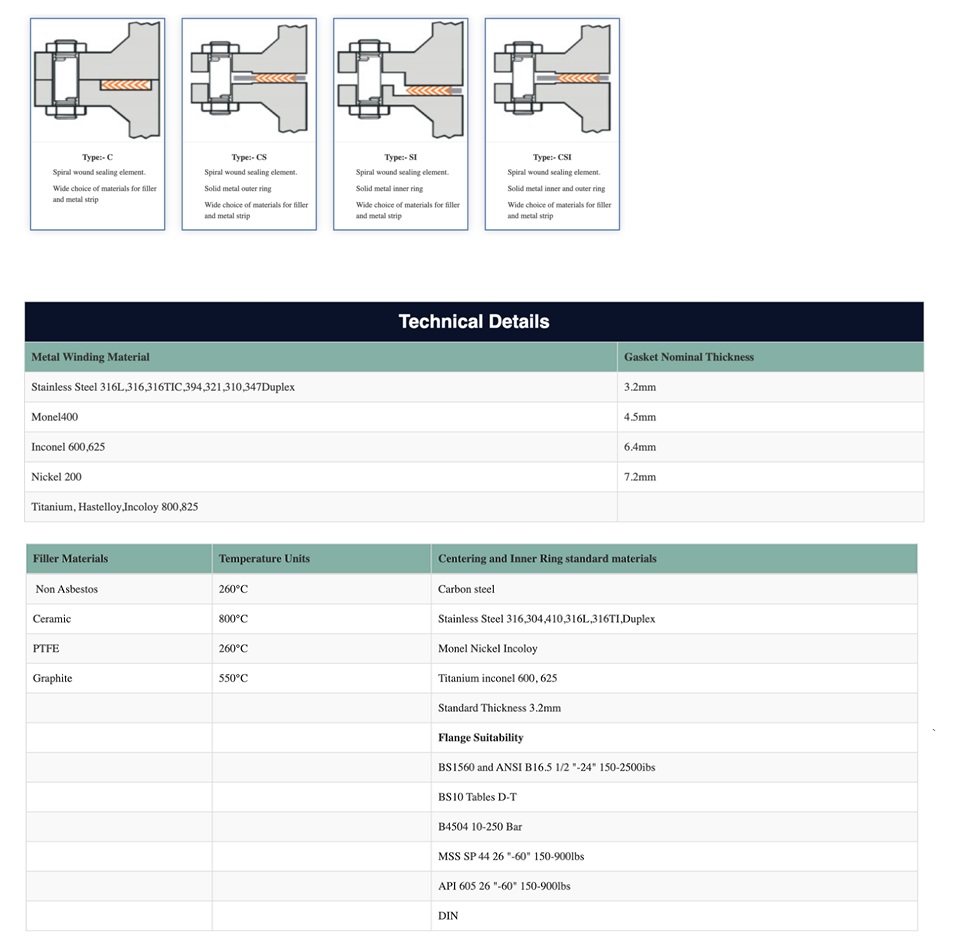
Spiral wound gasket consist of a combination of metallic and non-metallic materials. The gasket is formed by winding alternating layers of a metallic strip and a soft filler material in a spiral manner. This design allows the gasket to be both flexible and robust, making it ideal for handling the most demanding sealing applications.
Metallic Materials Used in Spiral Wound Gaskets
The metallic component of a spiral wound gasket provides structural integrity and strength, allowing it to withstand high pressures and temperatures. Common metals used include:
Stainless Steel:
- The most widely used metal for spiral wound gaskets, stainless steel (grades such as 304, 316, and 321) offers excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. This material is suitable for most applications involving exposure to chemicals, steam, and corrosive environments.
Monel:
- Monel, a nickel-copper alloy, is known for its superior resistance to acids, alkalis, and seawater. Gaskets made from Monel are ideal for use in marine environments and chemical processing industries where harsh chemicals are present.
Inconel:
- Inconel is a high-strength nickel-chromium alloy that excels in high-temperature and high-pressure environments. This material is used in applications where extreme heat, such as in power generation plants and refineries, can degrade other metals.
Titanium:
- For applications requiring resistance to both high temperatures and aggressive chemicals, titanium is an excellent choice. Its lightweight yet durable properties make it ideal for use in aerospace and chemical processing industries.
Filler Materials in Spiral Wound Gaskets
While the metal provides strength and durability, the filler material ensures effective sealing. The choice of filler material depends on the application’s specific requirements, such as temperature, chemical exposure, and operating pressure. Common filler materials include:
Flexible Graphite:
- Flexible graphite is known for its excellent thermal conductivity and chemical resistance. It can handle temperatures up to 450°C (850°F) and is used in applications involving high temperatures, such as in steam systems, boilers, and heat exchangers. It also resists oxidation and can withstand exposure to a wide range of chemicals.
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene):
- PTFE is one of the most chemically resistant materials available. It provides exceptional resistance to corrosive chemicals and solvents, making it suitable for gaskets used in chemical processing and pharmaceutical industries. PTFE can operate in temperatures ranging from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to 500°F), making it highly versatile for both high and low-temperature applications.
Mica:
- Mica is a naturally occurring mineral known for its high heat resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 1000°C (1832°F) and is primarily used in applications involving extreme heat, such as power generation and high-temperature industrial furnaces.
Additional Components: Inner and Outer Rings
Spiral wound gaskets also incorporate inner and outer rings made from materials like carbon steel or stainless steel. These rings provide stability, help center the gasket within the flange, and prevent over-compression during installation. The rings also protect the sealing element from the corrosive environment and enhance the gasket’s longevity.
- Inner Ring: The inner ring prevents the filler material from being exposed to the inner media and maintains gasket integrity under high pressure.
- Outer Ring: The outer ring is used for accurate centering in the flange and to protect the spiral wound element from excessive tightening forces.
Advantages of Spiral Wound Gasket Materials
High Durability:
- The combination of metallic and non-metallic materials ensures that spiral wound gasket materials can withstand extreme operating conditions without deteriorating or losing sealing performance.
Versatility:
- By selecting different combinations of metals and fillers, spiral wound gasket can be customized to meet the specific needs of any industrial application, from cryogenic temperatures to high-temperature steam systems.
Resilience:
- Spiral wound gasket maintain flexibility, allowing them to adapt to flange imperfections and provide a secure seal even when there are changes in pressure and temperature.
Excellent Chemical and Thermal Resistance:
- The use of high-quality filler materials like PTFE and flexible graphite ensures resistance to a wide range of chemicals, high temperatures, and pressure fluctuations, making spiral wound gasket suitable for diverse applications.
Common Applications of Spiral Wound Gaskets
Oil and Gas:
- Spiral wound gaskets are widely used in pipelines, refineries, and offshore platforms where high pressure, extreme temperatures, and corrosive chemicals are common.
Power Generation:
- Power plants utilize spiral wound gasket in boilers, heat exchangers, and steam turbines, where they are exposed to high-temperature steam and varying pressure conditions.
Chemical Processing:
- The chemical industry benefits from the chemical resistance of spiral wound gasket, using them in reactors, pumps, and pipelines carrying aggressive chemicals.
Petrochemical:
- Refineries and petrochemical plants rely on these gaskets to seal joints in process equipment that handles corrosive chemicals and extreme heat.
Conclusion
Spiral wound gaskets, with their combination of durable metals and flexible filler materials, provide an unmatched sealing solution for the most challenging industrial environments. The versatility of material options ensures that spiral wound gasket can be tailored to meet the specific demands of any application, whether in the oil and gas sector, chemical processing, or power generation. The right selection of metallic and filler materials guarantees long-lasting performance, cost-efficiency, and safety, making spiral wound gasket a preferred choice for industries worldwide.
Original Source: Spiral Wound Gasket Materials




Comments