Trading strategies are essential for any trader aiming to achieve consistent profitability in the financial markets. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced trader, having a well-defined strategy can be the difference between success and failure. This comprehensive guide explores the most effective trading strategies, how to create one, and how to optimize it for long-term success.
What is a Trading Strategy?
A trading strategy is a systematic plan that outlines how a trader will enter and exit positions in financial markets. It is based on predefined criteria, rules, and analysis of market data. A well-crafted strategy helps traders make objective decisions rather than emotional ones, ensuring discipline and consistency.
Trading strategies can be applied to various asset classes, including stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. They leverage technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or a combination of both.
Types of Trading Strategies
1. Day Trading
Day trading involves buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day. The goal is to profit from small price fluctuations throughout the day.
Key Characteristics
- Holding Period: Seconds to hours.
- Time Commitment: High; traders must monitor the market throughout the day.
- Risk Level: High; requires quick decision-making and high focus.
Day Trading Techniques
- Scalping: Quick trades to profit from small price changes.
- Momentum Trading: Trading based on price momentum and trend direction.
2. Swing Trading
Swing trading aims to capture price swings over a period of days to weeks. It takes advantage of short- to medium-term price movements.
Key Characteristics
- Holding Period: Days to weeks.
- Time Commitment: Moderate; less time-intensive than day trading.
- Risk Level: Moderate; less stressful compared to day trading.
Swing Trading Techniques
- Trend Following: Trading in the direction of the prevailing trend.
- Counter-Trend Trading: Trading against the trend at key reversal points.
3. Scalping
Scalping is a fast-paced strategy focused on making small but frequent profits by taking advantage of small price changes.
Key Characteristics
- Holding Period: Seconds to minutes.
- Time Commitment: High; requires constant monitoring.
- Risk Level: High; trades are frequent, and fees can add up.
Scalping Techniques
- Order Flow Analysis: Observing buy and sell orders to anticipate short-term price moves.
- Range Trading: Identifying price ranges and buying at support while selling at resistance.
4. Position Trading
Position trading is a long-term strategy where traders hold positions for weeks, months, or even years. This strategy is often used in stock and forex markets.
Key Characteristics
- Holding Period: Weeks to years.
- Time Commitment: Low; requires less monitoring than other strategies.
- Risk Level: Low to moderate; the goal is to capture large price moves.
Position Trading Techniques
- Trend Following: Buying and holding during uptrends and selling during downtrends.
- Buy and Hold: Long-term investing approach often used in stocks and ETFs.
5. Algorithmic Trading (Algo Trading)
Algorithmic trading uses computer programs and mathematical models to execute trades at high speed. Algorithms follow pre-set rules for entering and exiting trades.
Key Characteristics
- Holding Period: Varies; can range from seconds to weeks.
- Time Commitment: Low; trades are automated.
- Risk Level: Varies; depends on the quality of the algorithm.
Algorithmic Trading Techniques
- High-Frequency Trading (HFT): Making thousands of trades in milliseconds.
- Arbitrage Trading: Taking advantage of price differences across different markets.
6. News-Based Trading
This strategy revolves around reacting to market-moving news and economic releases. Traders attempt to capitalize on sudden price movements caused by significant news events.
Key Characteristics
- Holding Period: Minutes to hours.
- Time Commitment: High; requires monitoring of news releases and market reactions.
- Risk Level: High; news-driven volatility can result in significant price swings.
News-Based Trading Techniques
- Earnings Announcements: Trading on stock movements after a company's earnings report.
- Economic Reports: Trading forex and indices after key economic data releases (like Non-Farm Payrolls).
How to Develop a Profitable Trading Strategy
Step 1: Identify Your Trading Goals
Define your objectives, risk tolerance, and time commitment. Are you aiming for short-term gains (day trading) or long-term growth (position trading)?
Step 2: Choose Your Market
Select the market where you will trade. Options include stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies.
Step 3: Select a Trading Style
Based on your goals, time availability, and risk appetite, choose the best style for you: day trading, swing trading, scalping, or position trading.
Step 4: Define Entry and Exit Rules
Set clear criteria for entering and exiting trades. Use technical indicators, candlestick patterns, or moving averages to guide decisions.
Step 5: Backtest Your Strategy
Backtest your strategy using historical market data to see how it performs in various conditions. Make adjustments where necessary.
Step 6: Use Risk Management Rules
Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Proper position sizing and risk-reward ratios are essential to preserve capital.
Tools and Indicators to Support Trading Strategies
1. Technical Indicators
- Moving Averages: Identify trends and reversals.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Detect overbought and oversold conditions.
- Bollinger Bands: Identify market volatility and price breakouts.
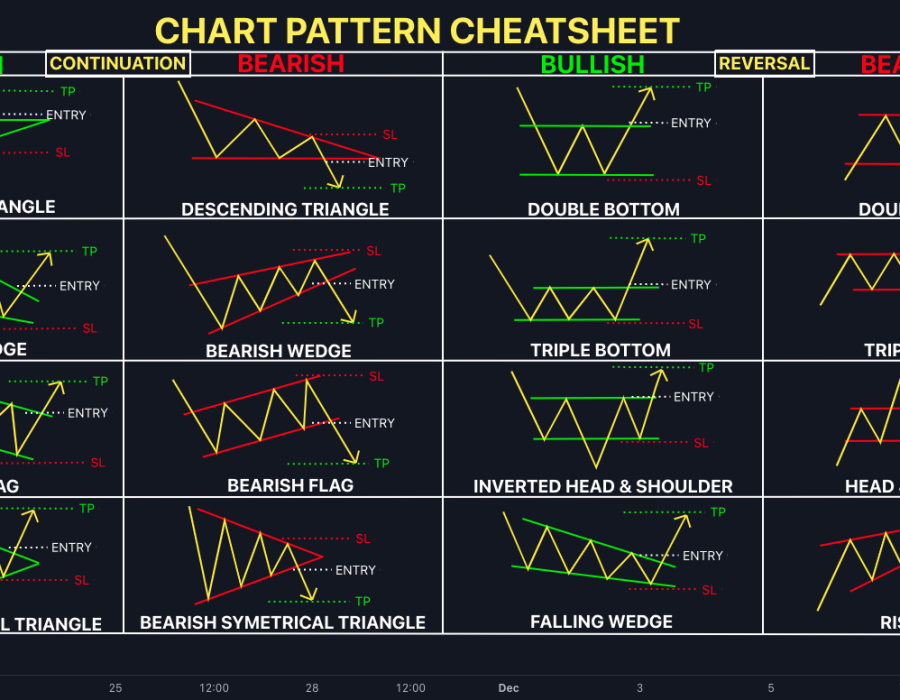
2. Chart Patterns
- Head and Shoulders: Signals a trend reversal.
- Double Tops and Bottoms: Indicate potential price reversals.
- Triangles: Identify potential breakouts.
3. Risk Management Tools
- Stop-Loss Orders: Automatically close losing trades.
- Take-Profit Orders: Lock in profits at a target price.
- Position Sizing: Ensure you never risk too much on a single trade.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Creating a Trading Strategy
- Overtrading: Placing too many trades, leads to excessive fees and emotional fatigue.
- Neglecting Risk Management: Failing to set stop-loss orders can lead to catastrophic losses.
- No Backtesting: Not testing a strategy on historical data results in unprepared traders.
- Ignoring Market Conditions: Strategies must be adapted to changing market conditions.
- Emotional Trading: Making decisions based on fear, greed, or impatience can lead to poor results.
How to Optimize Your Trading Strategy
- Review Performance: Track wins and losses to refine your strategy.
- Adjust Based on Market Changes: Markets evolve, so your strategy must adapt too.
- Diversify Strategies: Use a mix of swing, day, and position trading for stability.
- Use Technology: Leverage trading bots and software to automate your strategy.
Conclusion
A well-defined trading strategy is a trader's roadmap to success. Whether you choose day trading, swing trading, or scalping, having a structured approach can significantly enhance your chances of profitability. Remember to backtest your strategy, use technical indicators, and incorporate risk management rules. Trading requires patience, discipline, and continuous learning. By mastering the strategies outlined in this guide, you’ll be better equipped to achieve consistent trading success.
Take action today by developing a strategy that suits your goals, practicing it in a demo account, and refining it as you gain experience. Success in trading is not a matter of luck but a result of careful planning, strategy, and execution.




Comments