Cryogenic oxygen, a key product of advanced air separation processes, is an ultra-cold form of oxygen produced in specialized cryogenic oxygen plants. This substance is critical for industries such as healthcare, aerospace, metallurgy, and scientific research. In this article, we will delve into how cryogenic oxygen is produced, its temperature, and the various applications and benefits of cryogenic oxygen plants.
What is a Cryogenic Oxygen Plant?
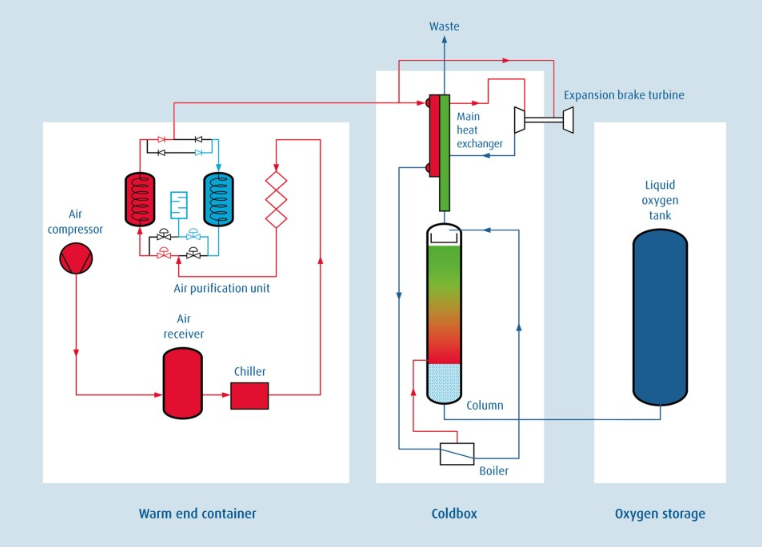
A cryogenic oxygen plant is a facility designed to produce oxygen in liquid or gaseous form by utilizing cryogenic air separation technology. This method involves cooling atmospheric air to extremely low temperatures until its components—oxygen, nitrogen, and argon—liquefy. The oxygen is then separated and stored at cryogenic temperatures, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial and medical uses.
The Temperature of Cryogenic Oxygen
Cryogenic oxygen is stored at temperatures as low as -183°C (-297°F), which is its boiling point under standard atmospheric pressure. This ultra-cold state is necessary to maintain oxygen in its liquid form, which significantly reduces its volume, making it easier to store and transport.
Maintaining such low temperatures requires specialized equipment, such as insulated storage tanks and cryogenic piping systems, all of which are integral to the operation of a cryogenic oxygen plant.
How Does a Cryogenic Oxygen Plant Work?
The production process in a cryogenic oxygen plant involves several critical steps:
1. Air Compression
Ambient air is drawn into the plant and compressed to high pressure using air compressors. This step removes water vapor, carbon dioxide, and hydrocarbons to ensure clean air for processing.
2. Air Cooling
The compressed air is cooled to sub-zero temperatures using advanced refrigeration systems. This step initiates the liquefaction process required for air separation.
3. Air Separation
Once liquefied, the air is fed into a distillation column. Here, oxygen is separated from nitrogen and other gases based on their boiling points. The process produces highly pure oxygen, typically exceeding 99.5% purity.
4. Storage and Distribution
The separated liquid oxygen is stored in cryogenic tanks or converted into gaseous form for immediate use. The ultra-cold oxygen is then transported to end users in insulated containers or pipelines.
Applications of Cryogenic Oxygen Plants
Cryogenic oxygen plants are crucial for industries requiring large-scale oxygen supply. Their ability to produce high-purity oxygen at ultra-low temperatures makes them indispensable in the following sectors:
1. Healthcare and Medical Applications
Medical Oxygen Supply: Hospitals rely on liquid oxygen from cryogenic oxygen plants for life-support systems, surgical procedures, and emergency care.
Cryotherapy: Liquid oxygen is used in medical cryotherapy for treating certain skin conditions and pain relief.
2. Metallurgy and Steel Manufacturing
In steelmaking, oxygen aids in reducing impurities and increasing furnace efficiency. The availability of high-purity oxygen from cryogenic oxygen plants enhances production quality.
3. Aerospace and Aviation
Liquid oxygen is a critical component in rocket propulsion systems, where it serves as an oxidizer for fuel combustion. Cryogenic oxygen plants play a vital role in the aerospace industry.
4. Chemical and Petrochemical Industries
High-purity oxygen is used in chemical reactions to produce products like ethylene oxide and synthesis gas. The consistent supply from cryogenic oxygen plants ensures operational efficiency.
5. Scientific Research
Laboratories and research facilities use cryogenic oxygen in experiments requiring precise atmospheric control and ultra-cold conditions.
Benefits of Cryogenic Oxygen Plants
Cryogenic oxygen plants offer numerous advantages, making them the preferred choice for oxygen production on an industrial scale.
1. High Oxygen Purity
Cryogenic air separation delivers oxygen with purity levels exceeding 99.5%, making it suitable for applications demanding stringent quality standards.
2. Scalability
These plants can be designed to meet the oxygen demands of industries ranging from small-scale operations to large manufacturing facilities.
3. Energy Efficiency
Modern cryogenic oxygen plants utilize advanced technology to optimize energy consumption, reducing operational costs.
4. Long-Term Storage
The ultra-cold nature of liquid oxygen enables long-term storage without significant losses, making it ideal for remote or high-demand locations.
Notable Global Projects Featuring Cryogenic Oxygen Plants
Cryogenic oxygen plants have been implemented in various industries worldwide. Hangzhou Z-Oxygen Intelligent Device Co., Ltd. has been instrumental in delivering high-quality cryogenic oxygen plants to countries such as:
· Russia: Cryogenic air separation plants for large-scale industrial oxygen supply.
· Turkey: Liquid oxygen storage tanks and gas stations.
· South Africa: Oil-free compressors for clean oxygen production.
· Chile: Containerized oxygen generators for remote industrial sites.
These projects underscore the global reliance on cryogenic oxygen technology for critical applications.
Challenges in Cryogenic Oxygen Production
Despite its benefits, producing cryogenic oxygen involves challenges:
· High Initial Investment: Setting up a cryogenic oxygen plant requires significant capital for equipment and infrastructure.
· Technical Expertise: Operating and maintaining such plants demands skilled personnel and advanced knowledge.
· Energy Consumption: The cooling and separation processes are energy-intensive, necessitating energy-efficient systems.
Innovations in plant design and energy recovery systems are helping to mitigate these challenges, making cryogenic oxygen production more accessible and sustainable.
Conclusion
Cryogenic oxygen plants are indispensable in modern industries and healthcare, providing high-purity oxygen at ultra-low temperatures of -183°C. From metallurgy to medicine, these plants enable countless applications that rely on the unique properties of cryogenic oxygen. With advancements in technology and expertise, companies like Hangzhou Z-Oxygen Intelligent Device Co., Ltd. continue to play a pivotal role in delivering customized solutions to meet global demands for cryogenic oxygen.
Whether for liquid oxygen storage, nitrogen generation, or air separation components, cryogenic oxygen plants remain a cornerstone of industrial and scientific innovation.




Comments