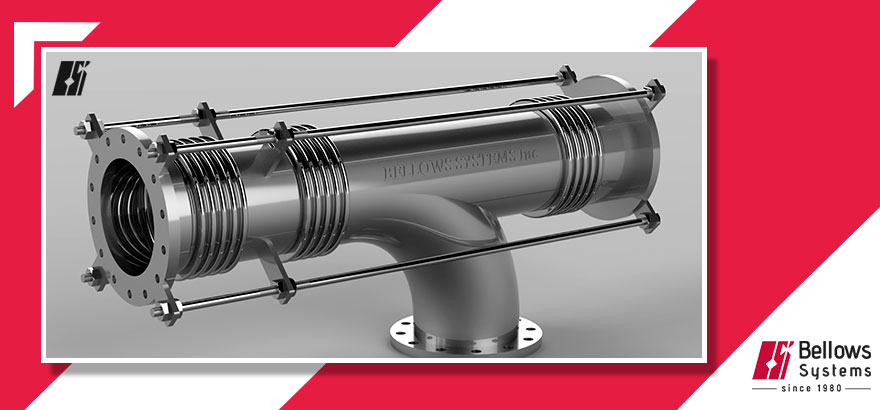
Expansion Joints with Tie Rods
Expansion joints are an essential component of various structures, including buildings, bridges, and pipelines. They are designed to allow for the expansion and contraction of the structures due to temperature changes, seismic activity, or other factors. Tie rods are often used in conjunction with expansion joints to provide additional support and stability. In this article, we will explore what expansion joints with tie rods are and how they work.
What are Expansion Joints with Tie Rods?
Expansion joints with tie rods are designed to withstand the movement of structures caused by temperature changes or other factors. They consist of two main components: the expansion joint itself and the tie rods.
The expansion joint is a flexible joint that can expand and contract as the structure moves. It is usually made of materials such as rubber, neoprene, or metal. The type of material used depends on the application and the environment in which the joint will be installed.
The tie rods are metal rods that are connected to the expansion joint on either side. They are used to provide additional support and stability to the joint. Tie rods are usually made of steel and are designed to withstand the forces that are exerted on the joint.
How Do Expansion Joints with Tie Rods Work?
Expansion joints with tie rods work by allowing for the movement of structures while providing support and stability. When a structure expands or contracts due to temperature changes, the expansion joint flexes to accommodate the movement. The tie rods provide additional support and prevent the joint from overextending.
Expansion joints with tie rods are also designed to absorb vibrations caused by seismic activity or other factors. The joint and tie rods work together to distribute the forces generated by the movement of the structure, ensuring that the structure remains stable and safe.
In addition to their functional benefits, expansion joints with tie rods can also help to extend the lifespan of a structure. By allowing for movement, the joints prevent the structure from experiencing undue stress and strain, which can lead to premature failure.
Where are Expansion Joints with Tie Rods Used?
Expansion joints with tie rods are used in a wide range of applications, including buildings, bridges, pipelines, and other structures. They are particularly important in structures that are exposed to extreme temperatures or seismic activity.
In buildings, expansion joints with tie rods are often used to allow for the movement of floors and walls. They are commonly found in high-rise buildings, where the height of the structure can cause significant temperature differentials between the upper and lower floors.
In bridges, expansion joints with tie rods are used to accommodate the movement caused by changes in temperature and traffic loads. They are usually installed at the ends of the bridge spans and are designed to withstand the forces generated by the movement of the structure.
In pipeline expansion joints with tie rods are used to allow for the expansion and contraction of the pipeline due to temperature changes. They are often installed at pipeline bends or intersections and are designed to prevent damage to the pipeline caused by excessive movement.
Conclusion:
Expansion joints with tie rods are an essential component of many structures, providing support and stability while allowing for movement. They are used in a wide range of applications, including buildings, bridges, pipelines, and other structures. By accommodating the movement of structures and distributing forces generated by seismic activity or other factors, expansion joints with tie rods can help to extend the lifespan of a structure and ensure its safety. If you have any questions about expansion
joints with tie rods or would like to discuss your specific needs, please contact a qualified engineer or contractor.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------





Comments