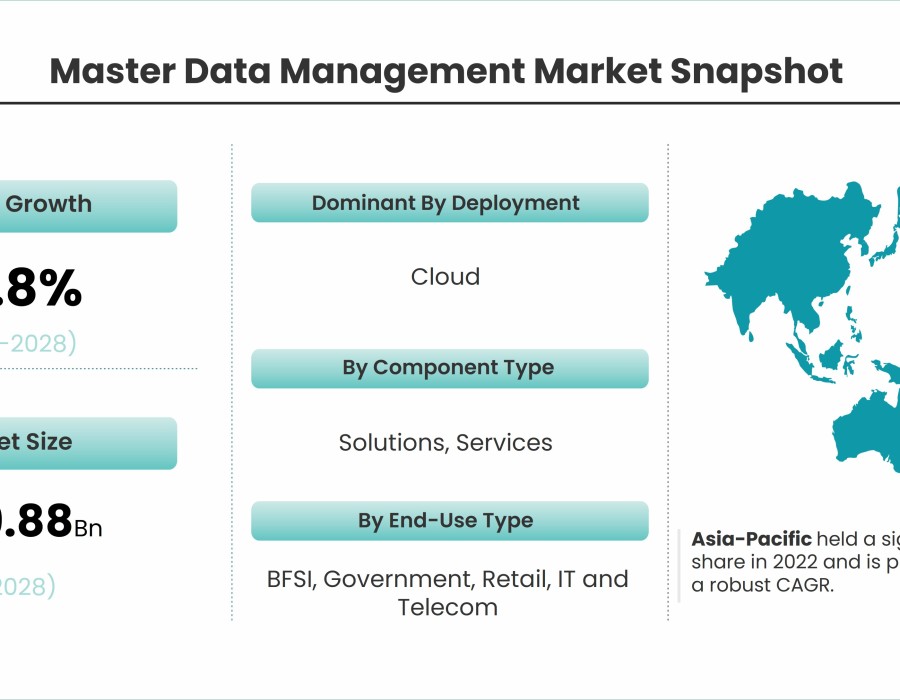
According to Stratview Research, the master data management market was estimated at USD 16.5 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 15.8% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 39.88 billion in 2028.
In today's data-driven world, organizations are inundated with vast amounts of information from disparate sources. Amidst this data deluge, mastering and harnessing the power of data has become imperative for businesses to gain a competitive edge, drive innovation, and enhance decision-making. At the heart of this endeavor lies Master Data Management (MDM), a strategic approach to managing and integrating critical data assets across an enterprise. In this article, we delve into the dynamics of the Master Data Management market, exploring the trends, challenges, and opportunities in unlocking the power of data.
The Essence of Master Data Management:
Master Data Management (MDM) is the process of creating and maintaining a single, accurate, and consistent version of key data entities, such as customers, products, suppliers, and locations, across an organization. By establishing a trusted source of master data, MDM enables organizations to improve data quality, enhance decision-making, and drive operational efficiency.
Insights into the MDM Market:
Rising Demand for Data Quality and Governance: With the proliferation of data sources and the increasing complexity of data landscapes, organizations are placing greater emphasis on data quality and governance. MDM solutions play a pivotal role in ensuring data integrity, standardization, and compliance with regulatory requirements, driving demand for robust MDM platforms.
Integration with Emerging Technologies: The integration of MDM with emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Big Data analytics is reshaping the MDM landscape. AI and ML algorithms are being used to automate data cleansing, matching, and enrichment processes, while Big Data analytics enables organizations to derive deeper insights from their master data.
Cloud Adoption and SaaS Models: The adoption of cloud-based MDM solutions is on the rise, driven by the scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness offered by cloud platforms. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) models enable organizations to rapidly deploy MDM solutions without the need for upfront infrastructure investments, accelerating time-to-value and reducing total cost of ownership.
Industry-specific Solutions: MDM vendors are increasingly offering industry-specific solutions tailored to the unique data management requirements of vertical markets such as banking and financial services, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing. These specialized solutions address industry-specific challenges and regulatory requirements, driving adoption across diverse sectors.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Data Silos and Fragmentation: One of the key challenges in MDM implementation is the presence of data silos and fragmentation across disparate systems and departments. Breaking down silos and integrating data from multiple sources is essential for achieving a unified view of master data and realizing the full benefits of MDM.
Change Management and Organizational Alignment: Successful MDM implementation requires strong leadership, change management, and organizational alignment across business units and stakeholders. Aligning business processes, defining clear roles and responsibilities, and fostering a culture of data governance are critical success factors for MDM initiatives.
Data Privacy and Security: With increasing concerns around data privacy and security, organizations must prioritize data protection and compliance with regulatory mandates such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA. Implementing robust data encryption, access controls, and audit trails is essential for safeguarding sensitive master data and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Emerging Trends and Growth Opportunities: Despite these challenges, the Master Data Management market is ripe with opportunities for growth and innovation. The convergence of MDM with emerging technologies, industry-specific solutions, and cloud adoption presents new avenues for vendors to differentiate themselves and address evolving customer needs.
Conclusion:
As organizations continue to grapple with the complexities of data management in an increasingly interconnected and data-driven world, Master Data Management emerges as a strategic imperative for unlocking the power of data. By investing in robust MDM solutions, embracing emerging technologies, and fostering a culture of data governance, organizations can realize the full potential of their data assets and drive business transformation. With a focus on data quality, integration, and governance, MDM vendors can capitalize on the burgeoning demand for MDM solutions and propel the industry forward into a new era of data-driven innovation and growth





Comments