Hydrogen energy storage is emerging as a pivotal technology in the transition to a sustainable energy future. As the world seeks to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change, hydrogen offers a versatile and clean alternative. Hydrogen energy storage involves the capture and storage of hydrogen gas, which can be used as an energy source in various applications. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the energy sector by providing a means to store excess energy, balance supply and demand, and support the use of renewable energy sources.
Hydrogen, the most abundant element in the universe, can be stored and used in various forms, including compressed gas, liquid hydrogen, and chemical compounds. The storage and utilization of hydrogen offer numerous benefits, including zero emissions when used in fuel cells and the ability to store large amounts of energy for long periods. As the hydrogen energy storage market continues to grow, it is poised to play a crucial role in achieving global energy and environmental goals.
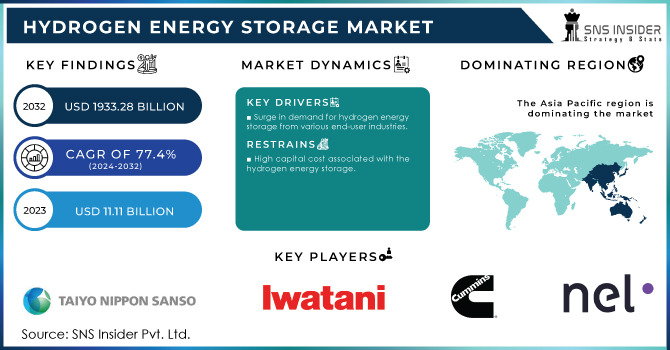
The Hydrogen Energy Storage Market Size was valued at USD 11.11 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 1933.28 billion by 2032 and grow at a CAGR of 77.4% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Types of Hydrogen Energy Storage Technologies
Several technologies are employed for hydrogen energy storage, each with its own advantages and applications:
l Compressed Hydrogen Storage: In this method, hydrogen gas is compressed to high pressures (typically around 350-700 bar) and stored in high-strength composite cylinders. This is one of the most common methods for hydrogen storage and is used in various applications, including fuel cell vehicles and industrial processes. Compressed hydrogen storage systems are well-established and benefit from a relatively mature technology base.
l Liquid Hydrogen Storage: Hydrogen can also be stored in its liquid form, achieved by cooling it to extremely low temperatures (around -253°C or -423°F). Liquid hydrogen storage offers higher energy density compared to compressed gas storage, making it suitable for applications requiring large volumes of hydrogen, such as rocket propulsion and large-scale industrial use. However, the energy required for liquefaction and the challenges of cryogenic storage present technical and cost challenges.
l Hydrogen Storage in Metal Hydrides: Metal hydrides are chemical compounds formed by metals and hydrogen. These compounds can absorb and release hydrogen gas reversibly, providing a compact and efficient storage solution. Metal hydride storage systems are particularly useful for applications requiring high-density hydrogen storage, such as portable fuel cells and small-scale energy systems. Research is ongoing to develop new hydride materials with improved performance and cost-effectiveness.
l Chemical Hydrogen Storage: Chemical hydrogen storage involves the use of chemical compounds, such as ammonia or liquid organic hydrogen carriers, to store and transport hydrogen. These compounds release hydrogen when needed through chemical reactions. This method offers advantages in terms of energy density and ease of handling but requires efficient and cost-effective methods for hydrogen release and recovery.
l Underground Hydrogen Storage: Underground storage involves storing hydrogen in geological formations such as salt caverns, depleted oil and gas fields, or aquifers. This method provides a large-scale storage solution and is particularly suited for balancing seasonal fluctuations in hydrogen demand. Underground storage is being explored as a means to support the integration of hydrogen into the energy grid and manage energy supply and demand.
Benefits and Applications
Hydrogen energy storage offers several key benefits and applications that make it an attractive option for various sectors:
l Energy Storage and Grid Balancing: Hydrogen energy storage can help balance supply and demand on the energy grid by storing excess energy generated from renewable sources, such as wind and solar, and releasing it when needed. This capability supports the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources and enhances grid stability.
l Decarbonization of Industrial Processes: Hydrogen can be used as a clean energy source in industrial processes, such as steel production, refining, and chemical manufacturing. By replacing fossil fuels with hydrogen, industries can significantly reduce their carbon emissions and contribute to global decarbonization efforts.
l Transportation: Hydrogen fuel cells are used in various transportation applications, including fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), buses, and trains. Hydrogen offers a clean and efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engines, with the advantage of fast refueling times and long driving ranges.
l Energy Storage for Remote and Off-Grid Locations: Hydrogen energy storage provides a reliable power source for remote and off-grid locations where traditional energy infrastructure is lacking. By generating hydrogen locally from renewable sources, these areas can achieve energy independence and reduce reliance on diesel generators or other fossil fuels.
l Support for Renewable Energy Integration: Hydrogen energy storage plays a crucial role in supporting the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid. By storing excess energy generated during periods of high renewable output, hydrogen storage systems help smooth out fluctuations and ensure a stable supply of clean energy.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
The hydrogen energy storage market is experiencing rapid growth driven by several key trends and factors:
Technological Advancements: Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving the efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness of hydrogen storage technologies. Advances in materials science, engineering, and manufacturing are contributing to the development of new and improved storage solutions.
Government Policies and Investments: Governments worldwide are increasingly supporting hydrogen energy storage through policies, incentives, and investments. This support is aimed at promoting the adoption of hydrogen technology, advancing research, and facilitating large-scale deployment.
Growing Demand for Clean Energy: The increasing demand for clean and sustainable energy solutions is driving the growth of the hydrogen energy storage market. As industries and governments seek to reduce carbon emissions and transition to renewable energy sources, hydrogen storage is becoming a key component of the energy landscape.
Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaboration between industry stakeholders, research institutions, and government agencies is fostering innovation and accelerating the development of hydrogen energy storage technologies. Partnerships and joint ventures are enabling the sharing of expertise, resources, and knowledge.
Expansion into Emerging Markets: The hydrogen energy storage market is expanding into emerging markets as technology becomes more affordable and accessible. This expansion is driven by the need for reliable energy solutions in developing regions and the growing interest in hydrogen as a clean energy source.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, hydrogen energy storage faces several challenges:
Cost of Technology: The cost of hydrogen storage technologies, particularly for advanced methods like liquid hydrogen and metal hydrides, remains high. Reducing costs is crucial for widespread adoption and commercialization.
Infrastructure Development: The development of infrastructure for hydrogen production, storage, and distribution is a significant challenge. Investments in infrastructure are needed to support the growth of the hydrogen economy.
Safety and Regulations: Hydrogen is highly flammable and requires careful handling and storage. Ensuring safety and establishing regulatory standards are essential for the safe deployment of hydrogen energy storage systems.
Conclusion
Hydrogen energy storage represents a promising technology in the transition to a sustainable and clean energy future. By capturing and storing hydrogen gas, this technology offers numerous benefits, including energy storage, grid balancing, and support for renewable energy integration. As technological advancements and market trends drive growth, hydrogen energy storage is poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of energy.
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Akash Anand – Head of Business Development & Strategy
Phone: +1-415-230-0044 (US) | +91-7798602273 (IND)




Comments