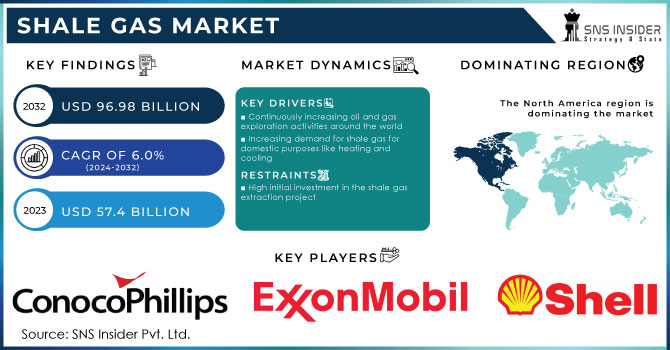
Shale gas has emerged as a significant game-changer in the global energy market over the past two decades. Unlike conventional natural gas, which is found in large, permeable reservoirs, shale gas is trapped within fine-grained sedimentary rock formations known as shale. Extracting this gas requires advanced techniques such as hydraulic fracturing (fracking) and horizontal drilling, which have enabled the commercial viability of shale gas reserves. The exploitation of shale gas has revolutionized the energy sector, particularly in the United States, where it has transformed the country into one of the leading producers of natural gas globally. The Shale Gas Market size is valued at USD 57.4 billion in 2023. It is estimated to be USD 96.98 billion by 2032 and is likely to expand at a CAGR of 6.0% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Shale gas is considered a cleaner alternative to coal and oil, producing lower carbon emissions when burned for energy. This characteristic has contributed to its rising popularity as countries seek to reduce their carbon footprints while meeting energy demands. Furthermore, the abundance of shale gas reserves has led to a decrease in natural gas prices, making it an attractive energy source for various industries and power generation.
The Technology Behind Shale Gas Extraction
The extraction of shale gas is made possible through two key technologies: hydraulic fracturing and horizontal drilling. Hydraulic fracturing, commonly known as fracking, involves injecting a high-pressure fluid mixture into the shale rock formations to create fractures. These fractures allow the trapped gas to flow to the surface, where it can be collected. The fluid used in fracking is primarily water, mixed with sand and a small percentage of chemical additives that help to keep the fractures open.
Horizontal drilling, on the other hand, allows for greater access to the gas-bearing shale formations. Unlike traditional vertical drilling, horizontal drilling involves drilling a well vertically to a certain depth and then extending the well horizontally through the shale layer. This technique significantly increases the surface area in contact with the gas-rich shale, thereby maximizing the amount of gas that can be extracted.
These technological advancements have not only made shale gas extraction economically viable but have also enabled the development of vast reserves that were previously considered inaccessible. The combination of fracking and horizontal drilling has unlocked significant quantities of natural gas, reshaping the energy landscape and contributing to energy security in various regions.
Environmental and Economic Impacts of Shale Gas
The rise of shale gas has had profound environmental and economic impacts. On the economic front, the development of shale gas has created jobs, stimulated local economies, and reduced energy costs. In the United States, for example, the shale gas boom has led to a resurgence in manufacturing, as lower energy prices have made domestic production more competitive. Additionally, the increased supply of natural gas has reduced reliance on imported energy, enhancing national energy security.
However, the environmental impact of shale gas extraction is a subject of ongoing debate. While natural gas burns cleaner than coal, the process of extracting shale gas has raised concerns about water usage, groundwater contamination, and the release of methane—a potent greenhouse gas. The large volumes of water required for fracking, coupled with the potential for chemical spills, pose risks to local water supplies. Furthermore, methane leaks during extraction and transportation can negate the climate benefits of switching from coal to natural gas.
Despite these concerns, advancements in technology and regulatory oversight are helping to mitigate the environmental risks associated with shale gas extraction. Improved well design, better waste management practices, and the development of less water-intensive fracking techniques are some of the measures being implemented to reduce the environmental footprint of shale gas operations.
Conclusion
Shale gas has undeniably changed the dynamics of the global energy market. Its emergence as a viable and abundant energy source has provided economic benefits and contributed to energy security in many regions. However, the environmental challenges associated with its extraction cannot be overlooked. As the industry continues to evolve, balancing the economic advantages of shale gas with the need for environmental protection will be crucial. The ongoing advancements in extraction technology and regulatory frameworks will play a key role in shaping the future of the shale gas industry.
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Akash Anand – Head of Business Development & Strategy
Phone: +1-415-230-0044 (US) | +91-7798602273 (IND)




Comments