Hydrogen fueling stations are pivotal in the development and expansion of hydrogen fuel cell technology. These facilities provide the infrastructure necessary for refueling hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) and support the broader adoption of hydrogen as a clean energy source. As the world moves towards sustainable energy solutions, hydrogen fueling stations are becoming increasingly important in creating a robust hydrogen economy.
A hydrogen fueling station is designed to store, compress, and dispense hydrogen gas to vehicles. The process involves several key steps, including hydrogen production, storage, compression, and dispensing. Each step is critical to ensuring that the hydrogen is delivered safely and efficiently. The growth of hydrogen fuel cell technology and the corresponding increase in FCVs on the road highlight the need for a comprehensive network of hydrogen fueling stations.
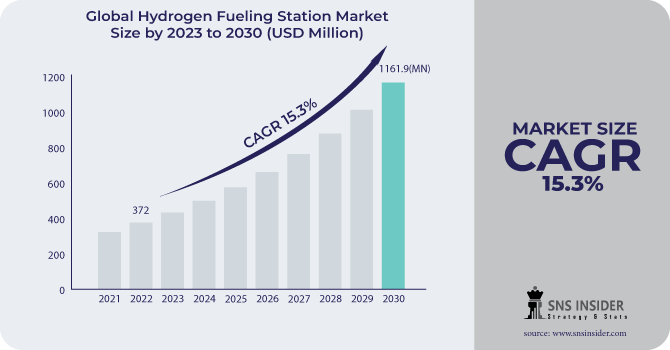
The Hydrogen Fueling Station Market size was valued at USD 385 million in 2023 and is expected to grow to USD 1181.7 million by 2031 and grow at a CAGR of 15.37% over the forecast period of 2024-2031.
Components and Operation of Hydrogen Fueling Stations
Hydrogen fueling stations consist of several key components that work together to ensure a smooth refueling process:
l Hydrogen Production: Hydrogen can be produced through various methods, including steam methane reforming (SMR), electrolysis, and biomass gasification. SMR is the most common method, where natural gas is reacted with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon dioxide. Electrolysis involves splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity, and biomass gasification converts organic materials into hydrogen.
l Storage and Compression: Once produced, hydrogen is stored in high-pressure tanks. The storage process involves compressing hydrogen to reduce its volume, allowing for efficient storage and transportation. High-pressure tanks are designed to safely contain hydrogen at pressures ranging from 350 to 700 bar (5,000 to 10,000 psi).
l Dispensing: The dispensing unit at a hydrogen fueling station is responsible for delivering hydrogen to vehicles. This unit controls the flow of hydrogen, monitors the pressure, and ensures that the fuel is dispensed accurately and safely. The dispensing process typically takes around 3-5 minutes, similar to traditional gasoline refueling.
l Safety Systems: Safety is a paramount concern in hydrogen fueling stations. These facilities are equipped with various safety systems, including leak detection, ventilation, and emergency shutdown mechanisms. Safety protocols are strictly followed to prevent accidents and ensure the safe operation of the station.
l Hydrogen Purification: Before dispensing, hydrogen may need to be purified to remove impurities and ensure high fuel quality. Purification processes help maintain the performance and longevity of fuel cell systems.
The Importance of Hydrogen Fueling Stations
Hydrogen fueling stations are essential for several reasons:
l Supporting Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs): The growth of the FCV market relies heavily on the availability of hydrogen fueling infrastructure. As the number of FCVs increases, a widespread network of fueling stations is necessary to support their operation and encourage consumer adoption.
l Reducing Emissions: Hydrogen fuel cell technology produces zero tailpipe emissions, making it a clean alternative to conventional fossil fuels. By providing a convenient and accessible means of refueling, hydrogen fueling stations contribute to reducing overall vehicle emissions and improving air quality.
l Promoting Sustainable Energy: Hydrogen is a versatile energy carrier that can be produced from various renewable sources, including wind, solar, and hydroelectric power. Hydrogen fueling stations support the transition to renewable energy by enabling the use of green hydrogen and promoting sustainable energy practices.
l Economic Growth and Job Creation: The development and expansion of hydrogen fueling stations create economic opportunities and jobs in various sectors, including engineering, construction, and maintenance. Investing in hydrogen infrastructure stimulates economic growth and supports the development of a clean energy economy.
Market Trends and Growth Drivers
The hydrogen fueling station market is experiencing rapid growth due to several key factors:
l Government Policies and Incentives: Governments worldwide are implementing policies and providing incentives to support the development of hydrogen infrastructure. These initiatives include funding for research and development, subsidies for hydrogen refueling stations, and mandates for hydrogen adoption in specific sectors.
l Technological Advancements: Advances in hydrogen production, storage, and dispensing technologies are driving improvements in efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Innovations in hydrogen infrastructure contribute to the growth of the market and enhance the viability of hydrogen as a fuel source.
l Rising Demand for FCVs: The increasing adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is driving the demand for hydrogen fueling stations. Automakers are investing in FCVs and expanding their product offerings, which necessitates the development of a comprehensive fueling network.
l Expansion of Infrastructure: Investments in hydrogen refueling infrastructure are essential for the widespread adoption of hydrogen technology. The establishment of new fueling stations and the expansion of existing networks are key to supporting the growth of the hydrogen economy.
l Collaborative Efforts: Partnerships between industry stakeholders, government agencies, and research institutions are fostering collaboration and accelerating the development of hydrogen fueling stations. Joint ventures and collaborative projects contribute to the advancement of hydrogen infrastructure.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the growth potential, the hydrogen fueling station market faces several challenges:
High Infrastructure Costs: The initial investment required for hydrogen fueling stations is relatively high compared to traditional fuel stations. Reducing costs through technological advancements and economies of scale is crucial for market growth.
Hydrogen Production and Distribution: Efficient and cost-effective methods for hydrogen production, storage, and distribution are essential for the success of fueling stations. Developing infrastructure and optimizing production processes are key challenges that need to be addressed.
Public Awareness and Acceptance: Increasing public awareness and acceptance of hydrogen technology is important for driving adoption. Educating consumers about the benefits of hydrogen fuel and addressing misconceptions will help build support for hydrogen fueling stations.
Conclusion
Hydrogen fueling stations are a critical component of the hydrogen economy, supporting the growth of hydrogen fuel cell technology and contributing to a sustainable energy future. As the market continues to expand, investments in hydrogen infrastructure and advancements in technology will play a key role in shaping the future of clean energy. Hydrogen fueling stations are not only essential for supporting fuel cell vehicles but also for advancing the broader transition to renewable energy and reducing environmental impact.
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Akash Anand – Head of Business Development & Strategy
Phone: +1-415-230-0044 (US) | +91-7798602273 (IND)




Comments