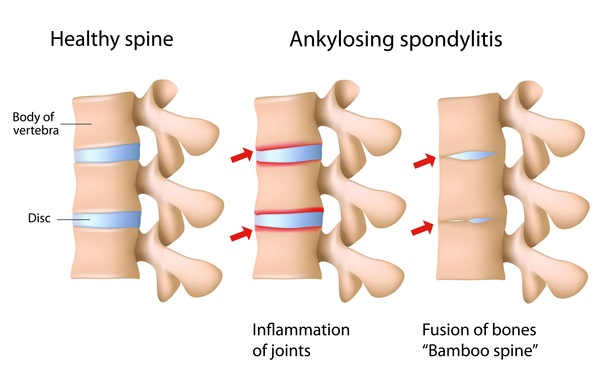
What Is Spondylarthritis?
Spondylarthritis is different from other types of arthritis in that it also involves the entheses, where ligaments and tendons are attached to bones. There are two major types of presentations. The first is inflammation causing pain and stiffness of the spine and, in some, pain and swelling of the arms and legs. The second type is bone destruction causing deformities of the spine and disabilities of the shoulders and hips.
How Is Spondylarthritis Diagnosed?
Correct diagnosis requires a physician to evaluate the patient’s history and do a physical examination. Thephysicianalsomaydotwoother types of evaluation. One is ordering an X-ray of the sacroiliac joints, a pair of joints in the pelvis. X-ray changes of the sacroiliac joints known as sacroiliitis is a key sign of spondylarthritis. If X-rays do not show adequate changes, but the symptoms are highly suspicious, a physician might decide to visualize the sacroiliac joints with MRI. Besides imaging, the second type of supplementary tests are blood tests for HLA-B27, and sometimes also for acute phase reactants such as C-reactive protein. Ultimately, diagnosis relies on the judgment of the attending physician. There are people who have a positive HLA-B27 gene test, but do not have arthritis and never develop arthritis. Therefore, a positive test does not mean that someone will develop spondylarthritis in the future.
How Is Spondylarthritis Treated?
Physical therapy and joint-directed exercises are recommended for all patients. Smoking aggravates spondylarthritis. There is a possibility of ankylosing spondylitis treatment dubai.
There are many drug treatment options. The first lines of treatment are the NSAIDs, such as etoricoxib, naproxen, ibuprofen, meloxicam or indomethacin. No one NSAID is considered superior to another. Given in the correct dose and duration, these in and of themselves will generate considerable relief for most patients.
For localized joint swelling, injections of corticosteroid medications into joints or tendon sheaths can be rapidly effective.
For those resistant to the above lines of treatment, disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (commonly called DMARDs) such as sulfasalazine might be effective, particularly in those with arthritis affecting the joints of the arms and legs.
Although they may be effective, corticosteroids taken by mouth are not recommended, because the doses required will lead to many side effects.
Antibiotics are considered only for those with reactive arthritis.
TNF alpha blockers (one of the drugs known as biologics) have been shown to be very effective in treating both the spinal and peripheral joint symptoms of spondylarthritis. The TNF alpha blockers currently approved by the FDA for use in ankylosing spondylitis are:
- Infliximab (Remicade), which is used at a dose of 5 mg/kg given intravenously every 6
- etanercept (Enbrel), given 50 mg by injection under the skin once weekly;
- Adalimumab (Humira), injected at a dose of 40 mg every other week under the skin;
- Golimumab (Simponi), injected at a dose of 50 mg, once a month





Comments