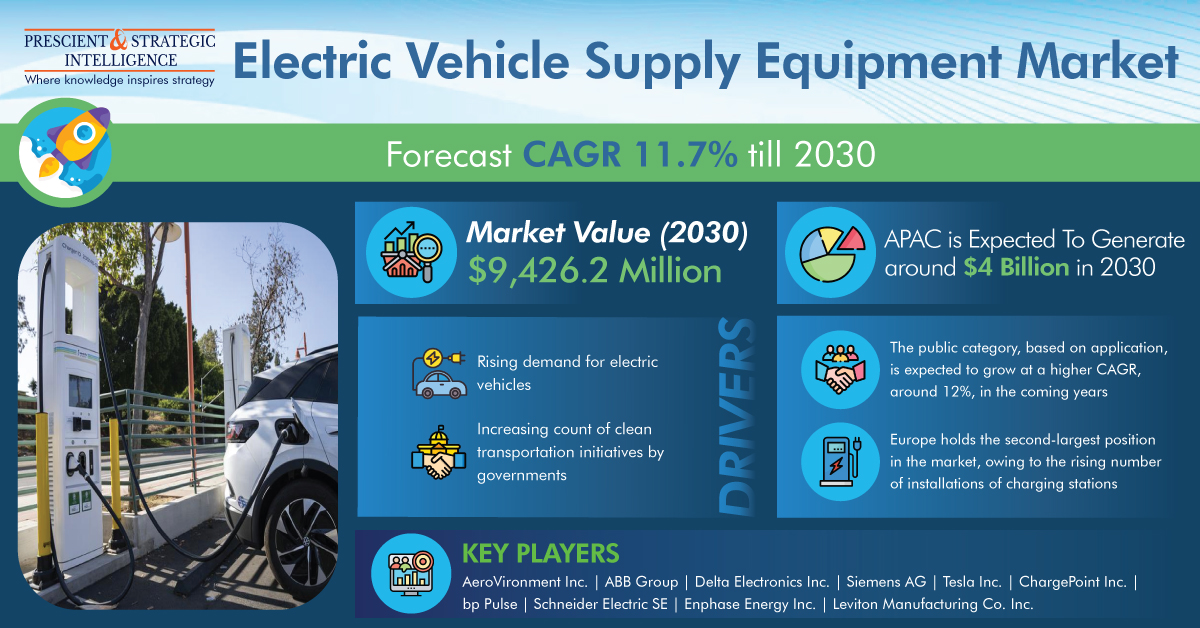
Electric energy is supplied to recharge electric vehicles at various residential and commercial locations using electric vehicle supply equipment, or EVSEs. The market for electric vehicle supply equipment was worth around USD 3,897.5 million in 2022, and it will reach USD 9,426.2 million by 2030, as per P&S Intelligence.
The primary causes of the expansion are the expanding need for electric vehicles, the escalating government efforts to promote the development of this technology, the rising pollution levels, and the explosive uptake of charging stations.
Since AC charging is the most popular way to charge electric vehicles with plugs, AC chargers predominate in the market. The output power of the charging point and the convertor's ability to convert the power to DC both affect how quickly batteries charge.
These chargers have minimal manufacturing, installation, and operating costs, which contributes to their widespread adoption and increased popularity for general day-to-day charging. For instance, there are 806 thousand AC charging outlets among the approximately 1.4 million EV charging stations in China.
Level 1 and level 2 chargers are further divided into AC chargers. Due to the long charging times of electric vehicles, which make these chargers appropriate for overnight charging at residences, level 1 chargers of retained a bigger market share.
Based on application, the public category is predicted to experience faster growth in the coming years—roughly 12% CAGR. This is due to the strong commitments made by automakers, governments, and manufacturers to the improvement of the infrastructure for electric vehicle use in many nations.
The private group, however, represents a greater industry share. The increased use of home chargers around the world is to blame for this. Charging an electric vehicle takes a long time. As a result, the majority of clients prefer private or home charging because they are simple to set up and may be used overnight.




Comments