Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects cognitive functions such as memory, thinking, and behavior. As the most common cause of dementia, it poses significant challenges for individuals, families, and healthcare systems worldwide. With the aging population on the rise, understanding Alzheimer's disease and exploring potential treatments like cerebrolysin injection becomes increasingly vital.
Alzheimer's Disease: A Growing Concern
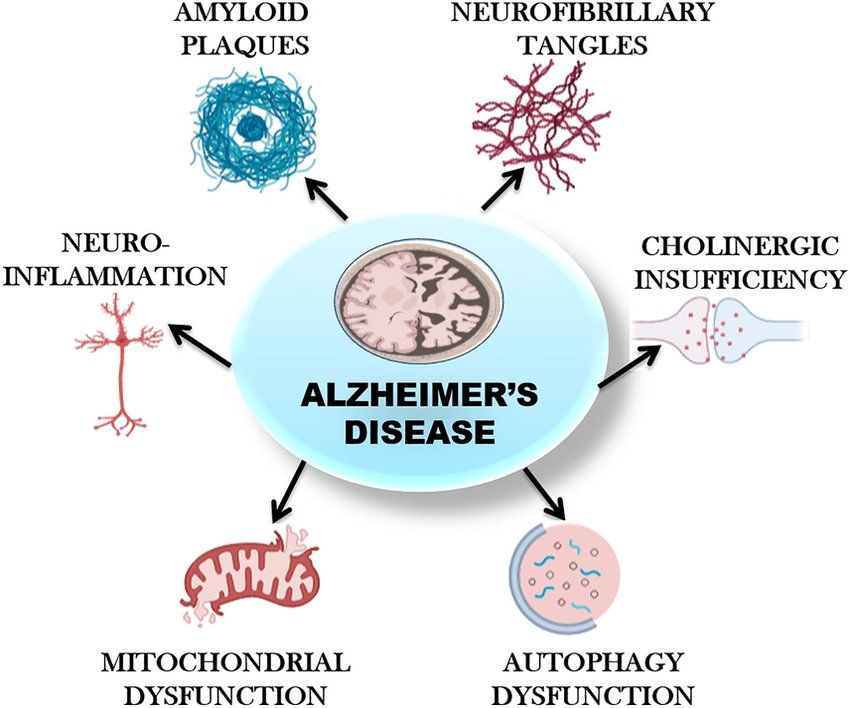
Alzheimer's disease is characterized by the accumulation of abnormal protein deposits in the brain, including beta-amyloid plaques and tau tangles, which disrupt neuronal communication and lead to cell death. This pathological process results in the gradual deterioration of cognitive abilities, starting with mild memory lapses and progressing to severe impairment in daily functioning.
The impact of Alzheimer's disease extends beyond the individual diagnosed with the condition. Family members and caregivers often shoulder the emotional, physical, and financial burdens associated with caregiving. Moreover, healthcare systems face the challenge of providing comprehensive care and support for a growing population of individuals living with Alzheimer's disease.
Current Treatment Landscape
While there is no cure for Alzheimer's disease, various treatments aim to alleviate symptoms and slow disease progression. These include cholinesterase inhibitors, such as donepezil and rivastigmine, which enhance neurotransmitter activity in the brain, temporarily improving cognitive function and behavior in some individuals. Another class of medications, N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists like memantine, regulates glutamate activity to manage symptoms.
Despite these treatment options, the need for more effective therapies remains pressing. Researchers are actively exploring novel approaches to target the underlying mechanisms of Alzheimer's disease and potentially modify its course.
Cerebrolysin Injection: A Promising Intervention
The cerebrolysin injection is a peptide-based drug derived from pig brain tissue, containing a mixture of neurotrophic factors and active peptides. It has shown promise in enhancing neuronal survival, promoting neurogenesis, and protecting against neurodegeneration in preclinical and clinical studies.
The potential benefits of cerebrolysin injection in Alzheimer's disease have garnered attention from researchers and clinicians alike. By delivering neurotrophic support directly to the brain, cerebrolysin aims to counteract the neurotoxic effects of beta-amyloid and tau pathology, thereby preserving cognitive function and slowing disease progression.
Clinical Evidence and Outcomes
Several clinical trials have investigated the efficacy and safety of cerebrolysin in Alzheimer's disease. While results have been mixed, some studies have reported positive outcomes, including improvements in cognitive performance, activities of daily living, and global functioning scores in patients receiving cerebrolysin treatment compared to placebo.
Moreover, neuroimaging studies have provided insights into the potential mechanisms of action underlying cerebrolysin's effects. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans have revealed changes in brain structure, connectivity, and metabolism following cerebrolysin administration, suggesting neuroprotective and neurorestorative effects.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite promising findings, challenges remain in the development and clinical implementation of cerebrolysin as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease. These include variability in patient response, optimal dosing regimens, and long-term safety considerations. Additionally, the need for further research to elucidate cerebrolysin's mechanisms of action and identify biomarkers of treatment response is paramount.
Looking ahead, ongoing clinical trials and translational research efforts hold the potential to advance our understanding of cerebrolysin's role in Alzheimer's disease management. Collaborative initiatives involving multidisciplinary teams of scientists, clinicians, and industry partners are essential for accelerating progress toward effective treatments that address the complex needs of individuals affected by Alzheimer's disease.
Conclusion
Alzheimer's disease represents a significant public health challenge with far-reaching implications for individuals, families, and societies. While current treatments provide symptomatic relief, the quest for disease-modifying therapies continues. Cerebrolysin injection emerges as a promising intervention, harnessing the neurotrophic properties of peptides to support neuronal health and function in Alzheimer's disease. By advancing our knowledge and refining treatment approaches, we move closer to improving outcomes and enhancing quality of life for those affected by this devastating condition.




Comments