Choosing the right projector involves more than just picking a brand or resolution. One of the key considerations is the type of lens the projector uses. Projectors generally come with either a fixed lens or a zoom lens, and the difference between these two types significantly affects the Projector Throw Ratio. Understanding how throw ratio interacts with lens type is essential for proper projector placement and achieving the ideal image size in your home theater, office, or classroom.
Understanding Projector Throw Ratio
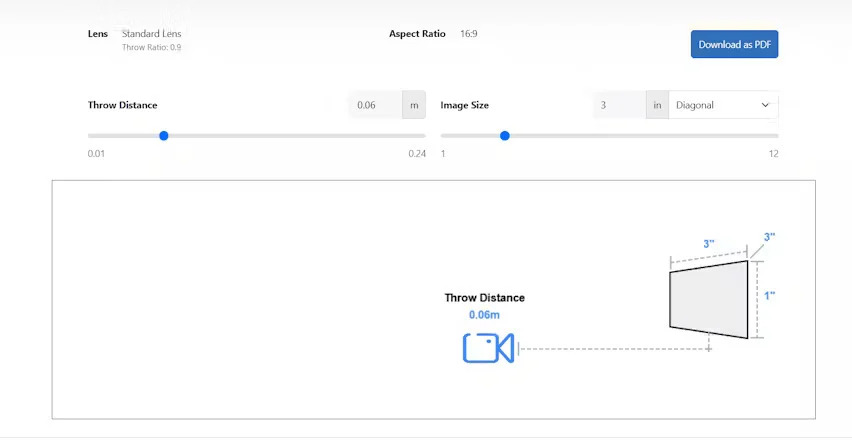
The Projector Throw Ratio is the ratio between the distance from the projector to the screen (throw distance) and the width of the projected image. It is calculated using the formula:
Throw Ratio = Throw Distance ÷ Image Width
For example, a projector placed 12 feet from a screen that is 8 feet wide has a throw ratio of 1.5. The throw ratio determines how far the projector needs to be to achieve a specific image size. It also influences whether you need a fixed or zoom lens to suit your room layout.
Fixed Lens Projectors
A fixed lens projector has a lens with a single throw ratio. This means that the projector must be placed at a specific distance from the screen to achieve the desired image size.
Advantages of Fixed Lens Projectors:
- Simplicity: Fixed lens projectors are straightforward to install. Once placed at the correct throw distance, no further adjustments are required.
- Cost-Effective: Typically, fixed lens projectors are less expensive than zoom lens models.
- Sharpness: Since the lens is designed for one throw ratio, it can offer optimal sharpness across the screen.
Disadvantages of Fixed Lens Projectors:
- Limited Placement Flexibility: The throw ratio is fixed, so you must place the projector precisely at the required distance from the screen.
- Less Adaptable for Room Changes: Moving the projector closer or farther from the screen may require a new projector with a different throw ratio.
Fixed lens projectors are ideal for dedicated home theaters or classrooms where the projector placement is unlikely to change.
Zoom Lens Projectors
Zoom lens projectors allow you to adjust the focal length of the lens, effectively changing the throw ratio. This flexibility enables the projector to create the desired image size from a range of distances.
Advantages of Zoom Lens Projectors:
- Flexible Placement: Zoom lens projectors can adjust to fit different room sizes and layouts.
- Adaptable for Multiple Screen Sizes: You can use the same projector for screens of different widths by adjusting the zoom.
- Easier Retrofitting: Zoom lens projectors are ideal for rooms where the projector cannot be mounted at an ideal throw distance.
Disadvantages of Zoom Lens Projectors:
- Higher Cost: The added complexity makes zoom lens projectors more expensive than fixed lens models.
- Potential Slight Sharpness Loss: Some zoom lens projectors may have slight loss of sharpness at extreme zoom settings compared to fixed lens models.
Throw Ratio Differences Between Fixed and Zoom Lenses
The main difference between fixed and zoom lens projectors lies in how they handle throw ratio:
- Fixed Lens Projector: The throw ratio is constant. For instance, a 1.5 throw ratio means the projector must always be 1.5 times the image width away from the screen. This makes room planning straightforward but inflexible.
- Zoom Lens Projector: The throw ratio can vary within a specified range. A projector with a throw ratio range of 1.3–2.0 can adjust its distance to fit the same screen, providing more installation flexibility.
Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right projector for your space. Rooms with variable layouts or multiple screen sizes benefit from zoom lens projectors, while fixed lens projectors are ideal for consistent, dedicated setups.
Practical Example
Suppose you have a 120-inch screen that is 105 inches wide:
- A fixed lens projector with a 1.5 throw ratio must be placed 1.5 × 105 inches = 157.5 inches (approximately 13 feet) from the screen.
- A zoom lens projector with a throw ratio range of 1.3–2.0 can be placed anywhere between 1.3 × 105 inches = 136.5 inches (approximately 11.4 feet) and 2.0 × 105 inches = 210 inches (approximately 17.5 feet), giving you more flexibility in room placement.
This example highlights how zoom lens projectors allow for adjustments without changing the projector or screen.
Other Considerations
When choosing between fixed and zoom lens projectors, consider:
- Room Size and Layout: If the room is small or has unique architectural constraints, a zoom lens projector offers better placement options.
- Budget: Fixed lens projectors are generally more affordable, which may be a deciding factor for budget-conscious buyers.
- Screen Size: If you plan to use multiple screens or occasionally change screen dimensions, a zoom lens projector provides necessary adaptability.
- Installation Type: Ceiling-mounted projectors benefit from zoom lenses in rooms with high ceilings or long throw distances.
Conclusion
The Projector Throw Ratio is a critical specification that affects projector placement, image size, and viewing experience. Fixed lens projectors offer simplicity and sharpness but lack placement flexibility. Zoom lens projectors provide adjustable throw ratios, making them suitable for versatile room setups and variable screen sizes. Understanding the differences between fixed and zoom lens projectors helps in making the right choice for your home theater, office, or classroom. By considering room size, budget, and throw ratio requirements, you can select a projector that delivers optimal image quality and a seamless viewing experience.
Read more: https://avprohub.jimdofree.com/2025/09/17/how-to-read-and-use-a-throw-ratio-chart-effectively/




Comments