Rosacea is a common, chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes acne-like bumps. Although it is more prevalent in fair-skinned individuals, it can affect all skin types. Understanding the causes, triggers, and available treatments is key to managing this condition effectively.
What Causes Rosacea?
The exact cause of Rosacea Treatment in Dubai is still not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Research suggests that people with rosacea have a hyperactive immune system, a tendency for their blood vessels to dilate more easily, and a higher concentration of a specific skin mite, Demodex folliculorum, which may trigger inflammation. Some potential contributing factors include:
- Genetics: A family history of rosacea increases the likelihood of developing the condition. Certain genetic factors can make an individual more prone to this skin condition, particularly those of Northern European descent.
- Immune System Response: People with rosacea tend to have an overactive immune system, which may cause their skin to react strongly to triggers. This heightened response may contribute to the persistent redness and inflammation associated with rosacea.
- Vascular Abnormalities: Blood vessel issues play a significant role in the development of rosacea. Dilated blood vessels can lead to visible redness and flushing, especially in the central area of the face.
- Demodex Mites: These mites are common on human skin, but individuals with rosacea may have a higher density of these mites, which could stimulate an inflammatory response.
- Environmental Factors: Sun exposure, extreme temperatures, and other environmental elements can worsen rosacea symptoms, though they are not necessarily the root cause.
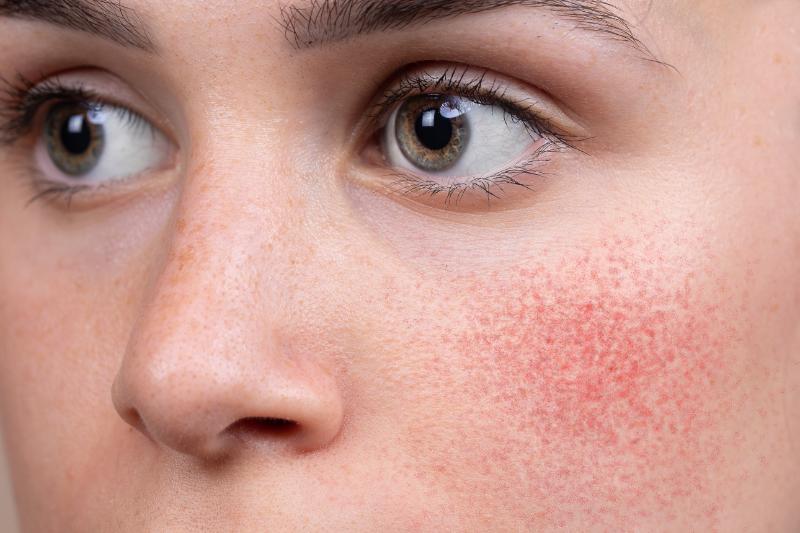
Common Rosacea Triggers
Although rosacea can flare up unexpectedly, several well-known triggers are linked to worsening symptoms. These triggers vary from person to person but commonly include:
- Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is one of the most common triggers for rosacea. Protecting the skin from the sun’s harmful rays is essential to managing the condition.
- Hot or Cold Weather: Extreme temperatures, whether too hot or too cold, can cause blood vessels to dilate, leading to flare-ups.
- Spicy Foods: Consuming spicy foods can trigger rosacea symptoms by increasing blood flow to the face, resulting in redness and flushing.
- Alcohol: Alcohol, particularly red wine, is known to trigger flushing and worsen rosacea symptoms for some people.
- Stress: Emotional stress is a significant trigger for many rosacea patients, leading to heightened facial redness and irritation.
- Hot Beverages: Drinking hot coffee or tea can cause the skin to flush, as the heat raises the body’s core temperature, triggering a flare-up.
- Exercise: While exercise is beneficial for overall health, intense physical activity can lead to flushing and trigger rosacea flare-ups due to increased body heat and blood flow.
- Skincare Products: Using harsh skincare products with fragrances, alcohol, or abrasive ingredients can irritate sensitive skin, leading to flare-ups.
Types of Rosacea
There are four primary subtypes of rosacea, each with its own set of symptoms:
- Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR): This type is characterized by facial redness, visible blood vessels, and a tendency to blush or flush easily. The redness may be persistent and is often concentrated on the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin.
- Papulopustular Rosacea: Often mistaken for acne, this type of rosacea involves red, swollen bumps that resemble pimples. These bumps may also be filled with pus and are typically accompanied by facial redness.
- Phymatous Rosacea: This rare form of rosacea causes thickening of the skin, usually around the nose. Over time, the nose may become bulbous or enlarged, a condition known as rhinophyma.
- Ocular Rosacea: Affecting the eyes, this subtype causes redness, dryness, irritation, and swollen eyelids. If left untreated, it can lead to more serious eye problems like corneal damage.
Treatment Options for Rosacea
While rosacea cannot be cured, it can be managed effectively with a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and skincare routines. Here are some of the most effective treatment options for rosacea:
1. Topical Medications
Dermatologists often prescribe topical medications to reduce inflammation and redness. These include:
- Metronidazole: A commonly prescribed antibiotic gel or cream that helps reduce inflammation.
- Azelaic Acid: Another anti-inflammatory that reduces redness and the appearance of bumps.
- Ivermectin: A topical treatment that targets Demodex mites, reducing inflammation and skin irritation.
2. Oral Medications
Oral antibiotics are sometimes used to treat moderate to severe rosacea. Doxycycline is a commonly prescribed antibiotic with anti-inflammatory properties that helps control papules, pustules, and redness.
For more severe cases, isotretinoin (a powerful acne medication) may be prescribed, particularly for individuals with phymatous rosacea. This medication reduces the size of oil glands and prevents new papules from forming.
3. Laser and Light-Based Therapies
Laser treatments, such as pulsed dye lasers (PDL) and intense pulsed light (IPL), are often used to reduce redness and visible blood vessels in rosacea patients. These therapies target the small blood vessels under the skin, effectively diminishing facial redness and flushing.
4. Skincare for Rosacea
Gentle skincare is essential for managing rosacea. A good routine should include:
- Non-irritating cleansers: Use a fragrance-free, non-foaming cleanser to avoid irritation.
- Moisturizers: Keeping the skin hydrated helps maintain the skin’s barrier function and reduces sensitivity.
- Sunscreen: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 daily to protect the skin from UV radiation. Physical sunscreens with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide are preferred for sensitive skin.
5. Dietary Adjustments
Certain foods and drinks can trigger rosacea, so it’s important to identify and avoid them. Common triggers include spicy foods, alcohol, and hot beverages. Some individuals benefit from a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, to reduce flare-ups.
6. Stress Management
Since stress is a major trigger for rosacea flare-ups, incorporating stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help manage symptoms.
7. Avoiding Triggers
It is important to be aware of and avoid known triggers to minimize flare-ups. Keeping a rosacea diary can help track triggers and reduce the likelihood of future flare-ups.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes and triggers of rosacea is key to effectively managing the condition. While it can be a frustrating and persistent skin condition, there are numerous treatments available, from topical and oral medications to laser therapies and lifestyle changes. By working closely with a dermatologist and adopting a gentle skincare routine, individuals with rosacea can manage symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve their overall skin health.





Comments