Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by dark, discolored patches on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip. It is often triggered by hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy or with the use of birth control pills. Understanding Melasma Treatment In Dubai involves exploring various approaches, including topical therapies, procedural options, and lifestyle adjustments. This comprehensive guide will help you navigate the available treatments and strategies for managing melasma effectively.
What is Melasma?
Melasma is a form of hyperpigmentation that presents as dark, irregularly shaped patches on the skin. It is often referred to as "the mask of pregnancy" because it frequently affects pregnant women, although it can occur in anyone. The condition is more common in women than men and is often linked to hormonal changes, sun exposure, and genetic predisposition.
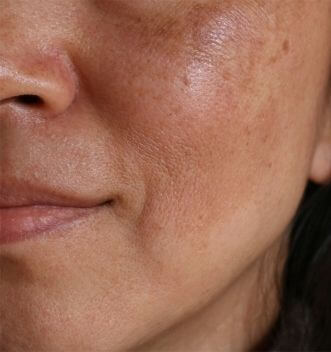
Causes of Melasma
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels, such as those experienced during pregnancy, menopause, or while taking birth control pills, can trigger melasma.
- Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun stimulate melanocytes (the cells that produce pigment) to produce more melanin, which can worsen melasma.
- Genetics: A family history of melasma may increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Skin Type: Individuals with darker skin tones are more prone to melasma due to increased melanin production.
Diagnosis of Melasma
Diagnosing melasma typically involves a visual examination by a dermatologist. In some cases, a Wood's lamp examination or a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Visual Examination
A dermatologist will examine the skin for characteristic patterns of hyperpigmentation. Melasma often appears as symmetrical patches on the face, especially on sun-exposed areas.
Wood's Lamp Examination
This test uses ultraviolet light to examine the skin and determine the depth of pigmentation. It helps differentiate melasma from other types of pigmentation disorders.
Skin Biopsy
In rare cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of pigment involvement.
Treatment Options for Melasma
Treatment for melasma aims to reduce pigmentation, prevent further darkening, and improve the overall appearance of the skin. A combination of treatments is often the most effective approach.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are the first line of defense against melasma. They work by lightening the pigmented areas and preventing the formation of new dark patches.
1. Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone is a popular skin-lightening agent that inhibits melanin production. It is available in various strengths, and its use should be monitored by a dermatologist due to potential side effects.
2. Retinoids
Topical retinoids, such as tretinoin, help improve skin turnover and reduce pigmentation. They are often used in combination with other treatments for enhanced results.
3. Azelaic Acid
Azelaic acid has both lightening and anti-inflammatory properties. It is suitable for individuals with sensitive skin and can help reduce melasma pigmentation.
4. Vitamin C
Vitamin C is an antioxidant that can help brighten the skin and inhibit melanin production. It is often included in serums and creams for melasma treatment.
Procedural Treatments
Procedural treatments can provide more immediate results for melasma and are often used in conjunction with topical therapies.
1. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution to exfoliate the outer layers of skin and reduce pigmentation. Commonly used peels include glycolic acid, salicylic acid, and trichloroacetic acid (TCA).
2. Laser Therapy
Laser treatments target pigmented cells and break down melanin. Options include fractional lasers, Q-switched lasers, and intense pulsed light (IPL). Laser therapy requires multiple sessions and may cause temporary redness or irritation.
3. Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion involves the mechanical exfoliation of the skin's surface to remove dead skin cells and reduce pigmentation. It can be combined with other treatments for enhanced results.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage melasma and prevent recurrence.
1. Sun Protection
Daily sun protection is crucial for managing melasma. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, and reapply every two hours when outdoors. Wearing hats and seeking shade can also help protect the skin from UV damage.
2. Avoid Hormonal Triggers
If melasma is linked to hormonal changes, consult with your healthcare provider about adjusting or discontinuing hormonal medications. Consider alternative birth control options if applicable.
3. Healthy Skin Care Routine
Maintain a gentle skincare routine using products formulated for sensitive skin. Avoid harsh scrubs or products that may irritate the skin.
4. Home Remedies
Some people find relief using natural remedies, such as aloe vera, green tea extracts, or licorice extract. While these may offer some benefits, they should be used with caution and in conjunction with other treatments.
Managing Expectations and Results
Melasma treatment is often a gradual process, and results can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the chosen treatment approach. It is essential to have realistic expectations and understand that maintaining results requires ongoing care.
Expected Results
- Topical Treatments: Improvement can typically be seen within 8-12 weeks of consistent use. Full results may take several months.
- Procedural Treatments: Results from chemical peels, laser therapy, or microdermabrasion may become visible within a few weeks to months. Multiple sessions may be required for optimal results.
Maintenance and Prevention
Once melasma is under control, ongoing maintenance is crucial to prevent recurrence. Continue using sun protection, avoid hormonal triggers, and follow a consistent skincare routine.
When to Consult a Dermatologist
If melasma is not responding to over-the-counter treatments or if you experience significant discomfort, consult a dermatologist. They can provide personalized treatment recommendations and adjust your regimen as needed.
Signs to Seek Professional Help
- Severe or Worsening Symptoms: If your melasma worsens despite treatment, a dermatologist can assess and adjust your approach.
- Side Effects: If you experience severe side effects from topical treatments or procedures, seek professional advice.
- Persistent or Recurring Melasma: For cases that do not improve with standard treatments, specialized therapies or combination treatments may be necessary.
Conclusion
Melasma treatment requires a multifaceted approach involving topical therapies, procedural options, and lifestyle adjustments. Understanding the condition, exploring various treatments, and maintaining a consistent regimen are key to managing and improving melasma. Consulting with a dermatologist can provide personalized guidance and help you achieve the best results.




Comments