Hyperhidrosis, characterized by excessive sweating beyond what is necessary for thermoregulation, can be an uncomfortable and distressing condition. Understanding its symptoms and diagnostic processes is crucial for those affected, as well as for healthcare providers seeking to offer effective treatment. This guide explores the various symptoms of Hyperhidrosis Treatment in Dubai, the types of the condition, and the diagnostic criteria used to identify it.
1. What is Hyperhidrosis?
Hyperhidrosis is a medical condition that causes excessive sweating, either localized to specific areas or generalized throughout the body. It can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life, leading to social anxiety, embarrassment, and emotional distress.
2. Types of Hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis is generally classified into two main types:
A. Primary Hyperhidrosis
- Definition: This type is often hereditary and occurs without an underlying medical cause. It typically affects specific areas of the body, such as the underarms, palms, feet, and face.
- Onset: Symptoms usually begin in childhood or adolescence.
- Patterns: Sweating is often triggered by heat, stress, or emotional factors.
B. Secondary Hyperhidrosis
- Definition: This form of hyperhidrosis is caused by underlying medical conditions or medications. It leads to generalized sweating across the body rather than localized sweating.
- Common Causes: Conditions like hyperthyroidism, diabetes, infections, or hormonal imbalances can lead to secondary hyperhidrosis. Certain medications, such as antidepressants and opioids, may also contribute.
- Onset: Can occur at any age and may arise suddenly or gradually, depending on the underlying condition.
3. Symptoms of Hyperhidrosis
The primary symptom of hyperhidrosis is excessive sweating, but it can manifest in various ways depending on the type and individual circumstances:
A. Localized Symptoms
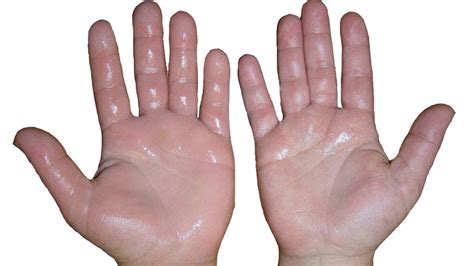
- Sweaty Palms and Feet: Excessive moisture on the palms or soles of the feet, which can affect grip and cause discomfort.
- Underarm Sweating: Profuse sweating in the underarm area, often leading to visible sweat stains on clothing.
- Facial Sweating: Noticeable sweating on the forehead, scalp, and face, which may occur even in cool environments.
- Night Sweats: Episodes of excessive sweating during sleep, which may disrupt sleep quality.
B. Generalized Symptoms
- Whole Body Sweating: Profuse sweating affecting the entire body, often triggered by heat or stress.
- Skin Irritation: Increased sweating can lead to skin problems such as rashes, chafing, or fungal infections due to prolonged moisture.
- Odor: Excessive sweating can lead to body odor, causing embarrassment and affecting social interactions.
4. Emotional and Psychological Impact
Hyperhidrosis can have significant emotional and psychological effects, including:
- Social Anxiety: Fear of social situations due to the embarrassment of excessive sweating.
- Reduced Self-Esteem: Concerns about appearance and personal hygiene may lead to decreased confidence.
- Avoidance Behavior: Individuals may avoid activities, clothing, or social situations that exacerbate sweating, leading to isolation.
5. Diagnosis of Hyperhidrosis
Diagnosing hyperhidrosis involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider, including a detailed medical history and physical examination. The following steps are typically involved:
A. Medical History
- Symptom Description: The provider will ask about the nature and frequency of sweating, including when it occurs, how long it has been present, and any potential triggers.
- Family History: A family history of hyperhidrosis may be relevant, especially for primary cases.
B. Physical Examination
- Visual Assessment: The healthcare provider will visually assess the affected areas to determine the extent and severity of sweating.
- Rule Out Other Conditions: The provider may look for signs of underlying medical issues that could contribute to secondary hyperhidrosis.
C. Diagnostic Tests
In some cases, additional tests may be conducted to confirm the diagnosis or identify underlying causes:
- Sweat Test (Gravimetry): This test measures the amount of sweat produced in a specific area over a set period, helping to quantify hyperhidrosis severity.
- Starch-Iodine Test: Iodine solution is applied to the skin, and starch is sprinkled on top. Areas of sweating will turn dark blue, indicating the locations of excessive sweating.
- Blood Tests: These may be ordered to assess thyroid function or rule out other medical conditions that could cause sweating.
6. Conclusion
Hyperhidrosis is a manageable condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the symptoms and diagnostic criteria is essential for those affected, as well as healthcare providers who aim to provide effective treatment options. If you suspect you have hyperhidrosis, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and to explore potential treatment strategies. Early intervention can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.





Comments