Introduction:
Are you tired of sweating through your shirts, avoiding handshakes, and feeling self-conscious about your clammy hands or damp feet? If so, you might be dealing with hyperhidrosis. This comprehensive guide will help you understand what hyperhidrosis is, explore its causes and symptoms, and most importantly, discover effective treatment options to take control of excessive sweating.
Understanding Hyperhidrosis:
What is Hyperhidrosis?
While sweating is a normal bodily function, those with hyperhidrosis experience an overactive sweat response, which can interfere with daily activities and cause significant discomfort.
Types of Hyperhidrosis:
Primary Hyperhidrosis:
Primary hyperhidrosis is not caused by any underlying medical condition. It typically begins in childhood or adolescence and often affects specific areas like the palms, soles, underarms, and face. This type of hyperhidrosis is thought to be linked to genetic factors and usually runs in families.
Secondary Hyperhidrosis:
Secondary hyperhidrosis is excessive sweating caused by an underlying medical condition or medication. Unlike primary Hyperhidrosis Treatment in Abu Dhabi, it can affect larger areas of the body and usually starts in adulthood. Conditions such as diabetes, hyperthyroidism, and menopause, as well as certain medications, can trigger secondary hyperhidrosis.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Common Symptoms:
The hallmark symptom of hyperhidrosis is excessive sweating that is not related to heat or physical activity. This sweating can occur at any time, even when you're at rest or in cool environments. Other symptoms may include skin maceration, body odor due to bacteria, and social anxiety stemming from self-consciousness about sweating.
How Hyperhidrosis is Diagnosed:
Diagnosis usually starts with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Doctors may use various tests, such as the starch-iodine test or the paper test, to measure the severity of sweating. Additionally, underlying conditions will be evaluated to determine if the hyperhidrosis is primary or secondary.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Genetic Factors:
Many individuals with this condition have a family history of excessive sweating, indicating a hereditary link. Researchers believe that certain genes may make the sweat glands more responsive to stimuli.
Medical Conditions:
Secondary hyperhidrosis can be caused by a variety of medical conditions. These include endocrine disorders (like hyperthyroidism), infections, diabetes, menopause, and neurological conditions.
Treatment Options:
Over-the-Counter Solutions:
Antiperspirants:
The first line of defense against hyperhidrosis often involves over-the-counter antiperspirants. These products contain aluminum-based compounds that block sweat glands temporarily. Look for clinical-strength formulas for more effective results.
Absorbent Pads:
Absorbent pads or sweat shields can be worn inside clothing to absorb excess sweat and prevent visible stains. These pads are particularly useful for underarm sweating and can provide a confidence boost in social situations.
Prescription Treatments:
Prescription Antiperspirants:
When over-the-counter options aren't enough, doctors may prescribe stronger antiperspirants with higher concentrations of aluminum chloride. These are applied at night and washed off in the morning to reduce sweating.
Oral Medications:
For more severe cases, oral medications such as anticholinergics can be prescribed. These drugs reduce sweating by blocking the chemical signals that stimulate sweat glands. However, they may come with side effects like dry mouth and blurred vision.
Medical Procedures:
Iontophoresis:
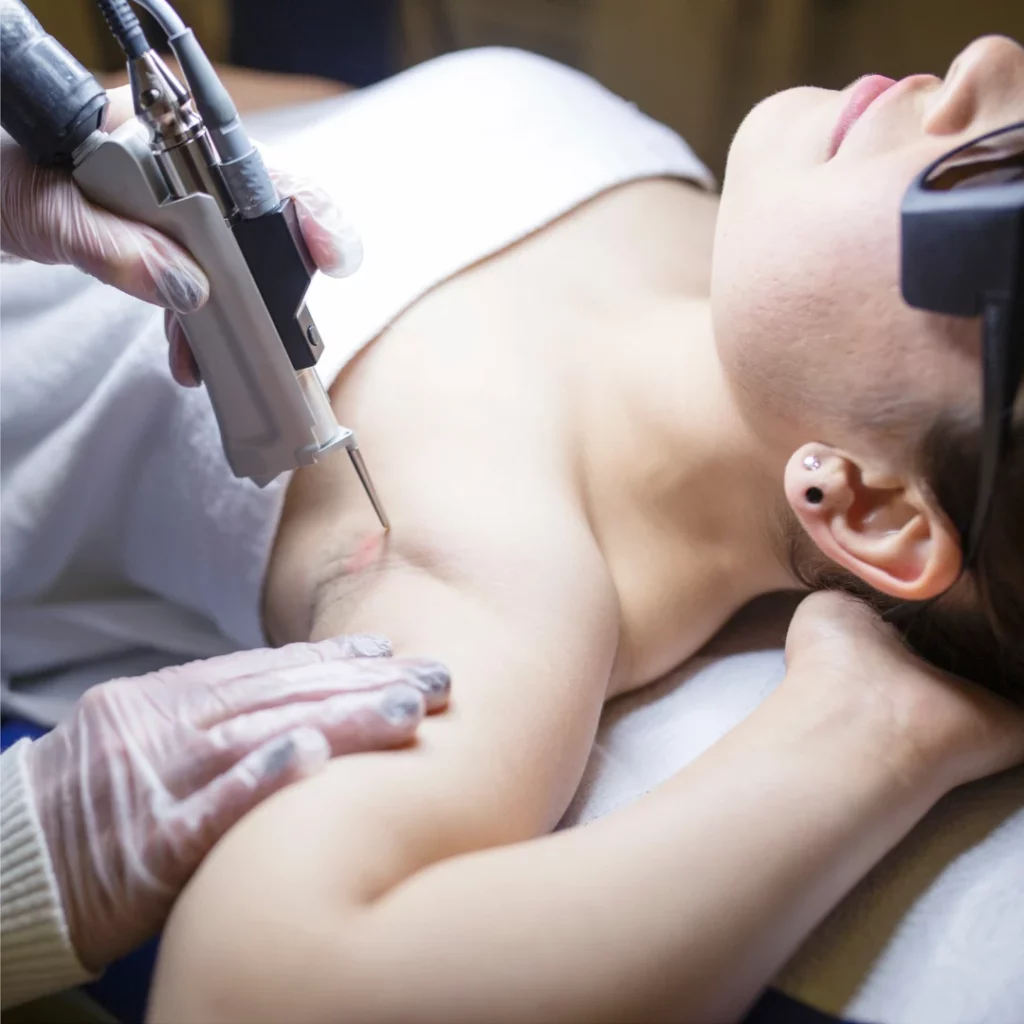
Iontophoresis is a non-invasive procedure where a mild electrical current is passed through water and into the skin's surface to temporarily disable sweat glands. This treatment is particularly effective for sweaty hands and feet and requires regular sessions to maintain results.
Botulinum Toxin Injections (Botox):
Botox injections are commonly used for treating severe underarm sweating. The toxin works by blocking the nerves that trigger sweat glands. Results can last for several months, but the treatment needs to be repeated periodically.
Surgery:
In extreme cases, surgery may be considered. Options include sympathectomy, where certain nerves are cut to reduce sweating or sweat gland removal. Surgery carries risks and is typically reserved for the most severe cases when other treatments have failed.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
Clothing Choices:
Wearing breathable, moisture-wicking fabrics can help manage sweat. Opt for natural fibers like cotton and avoid synthetic materials that trap heat and moisture. Dark colors can help conceal sweat stains.
Dietary Changes:
Certain foods and drinks can trigger sweating. Spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol are common culprits. Keeping a food diary to track and identify your triggers can help you make dietary adjustments to reduce sweating.
Stress Management:
Stress and anxiety can exacerbate hyperhidrosis. Incorporating relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga into your routine can help manage stress levels and reduce sweat.
Psychological Impact and Support:
Mental Health Challenges:
Living with hyperhidrosis can take a toll on mental health, leading to anxiety, depression, and social withdrawal. It's essential to address these psychological aspects to improve overall quality of life.
Support Groups and Therapy:
Joining support groups, whether in person or online, can provide emotional support and practical advice from others who understand what you're going through. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can also help you manage the emotional impact of hyperhidrosis.
Preventing Hyperhidrosis:
Daily Habits:
Establishing good hygiene practices, such as regular showers and using antiperspirants, can help manage sweating. Staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy weight can also make a difference.
Long-term Strategies:
Long-term management of hyperhidrosis involves a combination of treatments and lifestyle changes. Consistency in treatment, regular follow-ups with healthcare providers, and staying informed about new therapies are key to effective management.
Conclusion:
Taking charge of hyperhidrosis involves understanding the condition, exploring various treatment options, and making lifestyle adjustments. While it can be challenging, there are numerous strategies and resources available to help you manage excessive sweating and improve your quality of life. Remember, you're not alone, and effective solutions are within reach.




Comments