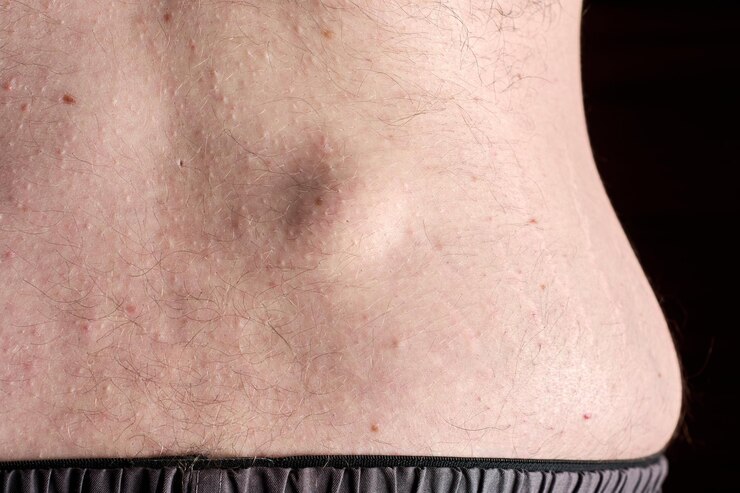
Lipomas are benign tumors made up of adipose (fat) tissue, commonly found just beneath the skin. Although generally harmless, many individuals seek removal due to cosmetic concerns, discomfort, or growth. When it comes to treatment options, there are both surgical and non-surgical methods available. Understanding the differences, benefits, and drawbacks of each can help you make an informed decision about the best approach for your situation.
Surgical Lipoma Removal
Overview
Surgical removal is the most common and effective method for treating lipomas. It involves excising the Lipoma Treatment In Dubai along with its surrounding capsule.
Benefits
- Complete Removal: Surgical excision allows for the entire lipoma to be removed, significantly reducing the chance of recurrence.
- Immediate Results: Patients typically see immediate results post-surgery, as the lump is removed entirely.
- Diagnosis: The removed tissue can be sent for histological examination, confirming the diagnosis and ruling out other conditions.

Procedure
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to numb the area.
- Incision: A small incision is made over the lipoma.
- Excision: The lipoma and its capsule are carefully excised.
- Closure: The incision is closed with stitches, and the area is bandaged.
Considerations
- Scarring: Surgical excision may leave a scar, the size of which depends on the lipoma's size and location.
- Recovery Time: Some downtime may be required for recovery, and patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities for a short period.
- Risks: As with any surgical procedure, there are risks of infection, bleeding, and adverse reactions to anesthesia.
Non-Surgical Lipoma Removal
Overview
Non-surgical options primarily include liposuction and injection therapies. These methods are less invasive and often appeal to patients seeking to avoid surgery.
Benefits
- Minimally Invasive: Non-surgical methods involve less trauma to the surrounding tissue, leading to reduced recovery time and discomfort.
- Less Scarring: These methods typically result in smaller incisions, leading to minimal scarring compared to surgical excision.
- Quick Recovery: Patients often return to normal activities shortly after the procedure.
Procedure Options
- Liposuction:
- A small incision is made, and a thin tube (cannula) is inserted to suction out the fatty tissue.
- While effective in reducing the size of the lipoma, it may not remove the entire tumor, leading to a risk of recurrence.
- Injection Therapies:
- Steroid Injections: Some practitioners use steroid injections to shrink the lipoma, although this method may not fully eliminate it.
- Deoxycholic Acid: This compound is sometimes used for fat dissolution, but its effectiveness for lipomas is not widely established.
Considerations
- Incompleteness: Non-surgical methods may leave behind some of the lipoma, increasing the risk of recurrence.
- Variable Results: The effectiveness of non-surgical treatments can vary from person to person, and not all lipomas may respond well to these methods.
- Cost: Some insurance plans may not cover non-surgical options, especially if they are considered cosmetic.
Comparative Analysis
Effectiveness
Surgical removal is generally the most effective method for complete lipoma removal, ensuring that the tumor is entirely excised. Non-surgical methods may provide satisfactory results for small lipomas but often do not guarantee complete removal.
Safety
Both surgical and non-surgical methods have associated risks. Surgical procedures may carry risks typical of any surgery, while non-surgical methods may lead to complications such as infection or insufficient treatment.
Recovery and Scarring
Surgical procedures typically require a longer recovery time and may result in more noticeable scarring compared to non-surgical methods, which generally allow for quicker recovery and minimal scarring.
Cost Considerations
Surgical removal is often covered by insurance, especially if the lipoma is symptomatic. Non-surgical treatments may not be covered, potentially leading to higher out-of-pocket costs.
Conclusion
The choice between surgical and non-surgical lipoma removal largely depends on individual circumstances, including the size and location of the lipoma, patient preferences, and overall health. Surgical removal is the gold standard for complete excision, while non-surgical methods offer less invasive options that may be suitable for specific cases. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine the best approach tailored to your needs and ensure the most effective treatment for your lipoma.




Comments