Introduction
Ozempic (semaglutide) is a medication prescribed for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus. It belongs to the class of drugs known as GLP-1 receptor agonists, which work by mimicking the action of the hormone GLP-1, helping to regulate blood sugar levels.
Process
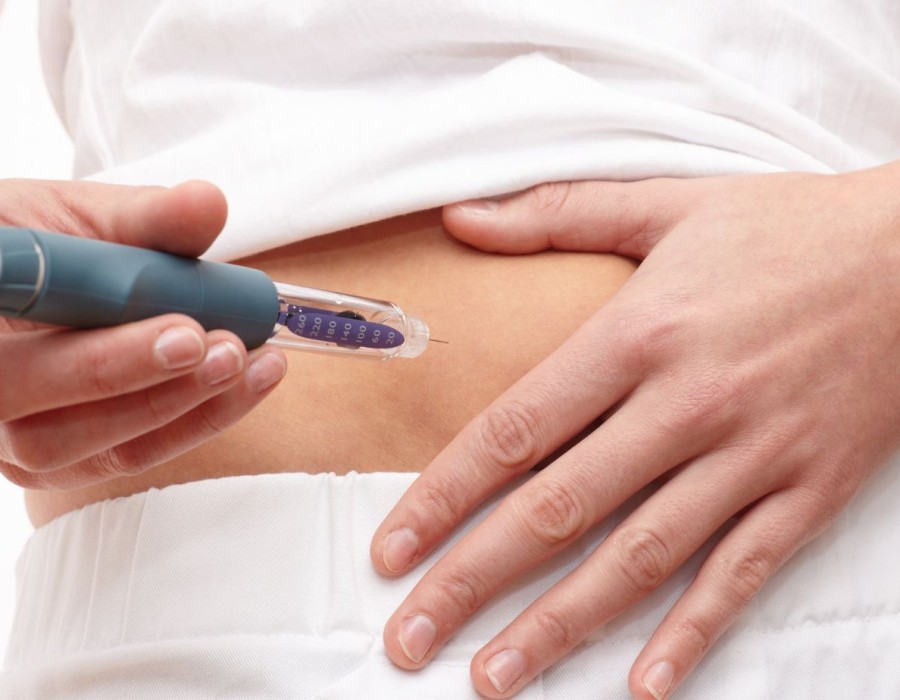
Ozempic is typically administered via subcutaneous injection once a week. It stimulates insulin production in response to glucose intake, slows gastric emptying, and suppresses appetite, aiding in blood sugar control and potentially promoting weight loss.
Benefits
- Blood Sugar Control: Ozempic helps lower blood sugar levels by stimulating insulin release when needed, reducing the risk of hyperglycemia.
- Weight Management: Many patients experience weight loss as a result of decreased appetite and slowed gastric emptying induced by Ozempic.
- Cardiovascular Benefits: Some studies suggest that GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic may have cardiovascular benefits, including reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Side Effects
While Ozempic is generally well-tolerated, it can cause certain side effects, including:
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. These symptoms usually diminish over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
- Hypoglycemia: Low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia) can occur, especially when Ozempic is used in combination with other diabetes medications that lower blood sugar.
- Injection Site Reactions: Mild reactions such as redness, itching, or swelling at the injection site may occur.
- Thyroid Tumors: There have been reports of thyroid tumors, including cancer, in animal studies with Ozempic. Patients need to undergo regular thyroid examinations as recommended by their healthcare provider.
Characteristics
- Long-Acting: Due to its once-weekly dosing schedule, Ozempic provides sustained blood sugar control with minimal fluctuations throughout the week.
- Weight Loss Aid: Ozempic is recognized for its potential to aid in weight loss, making it beneficial for patients struggling with obesity alongside diabetes management.
- User-Friendly Administration: The medication is administered using a prefilled injection pen, allowing for easy and convenient self-administration at home.
How to Manage Side Effects
- Nausea and Digestive Discomfort: Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it can help minimize gastrointestinal side effects. Taking Ozempic with food may also reduce nausea.
- Hypoglycemia: Monitor blood sugar levels regularly, especially during the initial weeks of treatment. Patients should be educated on recognizing and treating low blood sugar episodes promptly.
- Injection Site Reactions: Rotate injection sites and follow proper injection techniques to reduce discomfort and minimize the risk of skin reactions.
- Thyroid Monitoring: Regular thyroid function tests are recommended to detect any abnormalities early.
Conclusion
Ozempic is a valuable treatment option for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus, offering benefits such as improved blood sugar control, potential weight loss, and cardiovascular benefits. While it may cause side effects like gastrointestinal discomfort and hypoglycemia, these can often be managed effectively with proper guidance and monitoring from healthcare professionals. Patients considering Ozempic should discuss its benefits and potential risks with their doctor to determine if it's the right choice for their diabetes management plan





Comments