Introduction: Understanding Hair Loss and Restoration
Hair loss can result from various factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, and aging. For many, it is not just a cosmetic issue but can also impact self-esteem and confidence. To address this, the beauty and medical industries have developed numerous hair restoration techniques in the Best Hair Transplant Clinic in Muscat. These methods range from non-invasive treatments like topical solutions to surgical procedures such as hair transplants. Understanding the advantages, disadvantages, and effectiveness of each can guide you in making an informed decision.
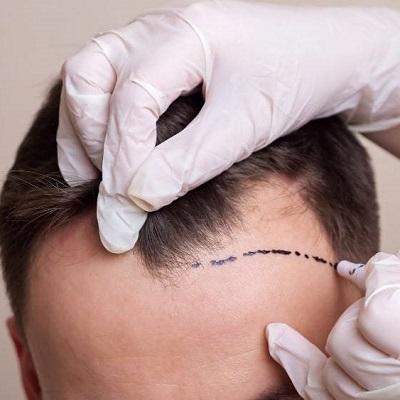
Hair Transplant: The Gold Standard in Hair Restoration
Process
A hair transplant involves the surgical removal of hair follicles from one part of the body, known as the donor site, to a bald or thinning area, known as the recipient site. There are two primary techniques used:
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): In this method, a strip of scalp is removed from the donor site, usually the back of the head, and then divided into small grafts. These grafts are then implanted into the recipient site.
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): This technique involves individually extracting hair follicles from the donor area and implanting them directly into the recipient site. FUE is less invasive and leaves minimal scarring compared to FUT.
Benefits
- Permanent Results: Hair transplants offer long-lasting results as the transplanted hair continues to grow naturally.
- Natural Appearance: When performed by a skilled surgeon, the results look natural, making it difficult to distinguish transplanted hair from natural hair.
- High Success Rate: Hair transplants have a high success rate, particularly when using advanced techniques like FUE.
Characteristics
- Invasive Procedure: Hair transplants are surgical and require anesthesia, making them more invasive than other methods.
- Recovery Time: Post-surgery, there is a recovery period during which swelling, redness, and scabbing may occur.
- Cost: Hair transplants are generally more expensive than other hair restoration methods.
Other Hair Restoration Methods: Exploring Alternatives
1. Topical Solutions (e.g., Minoxidil)
Process: Minoxidil is a topical solution applied directly to the scalp to stimulate hair growth and slow down hair loss. It is available over the counter and is often recommended for early-stage hair loss.
Benefits:
- Non-Invasive: No surgery or needles are required.
- Ease of Use: Simple application process that can be done at home.
- Accessibility: Available without a prescription and at a lower cost compared to surgical options.
Characteristics:
- Temporary Results: The effects of Minoxidil only last as long as the product is used; discontinuing use can lead to hair loss resuming.
- Effectiveness: It is most effective for mild to moderate hair loss and may not work for everyone.
2. Oral Medications (e.g., Finasteride)
Process: Finasteride is an oral medication that reduces levels of DHT, a hormone linked to hair loss. It is typically prescribed for men and can help slow hair loss and promote regrowth.
Benefits:
- Convenient: Taken as a daily pill, making it easy to incorporate into a routine.
- Proven Efficacy: Clinical studies have shown that Finasteride can be effective in treating male pattern baldness.
Characteristics:
- Side Effects: Potential side effects include sexual dysfunction and decreased libido.
- Limited Use: It is generally only prescribed for men, and results vary.
3. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
Process: PRP therapy involves drawing the patient's blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and injecting it into the scalp to promote hair growth. The growth factors in PRP are believed to stimulate hair follicles and increase hair density.
Benefits:
- Natural Treatment: Utilizes the patient’s blood, reducing the risk of allergic reactions or complications.
- Minimally Invasive: While it involves injections, it is less invasive than surgery.
Characteristics:
- Multiple Sessions Required: PRP therapy often requires several sessions to see results.
- Varied Effectiveness: Results can vary, and some individuals may not experience significant improvement.
4. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LT)
Process: LLLT uses low-level lasers to stimulate hair follicles and encourage hair growth. It is usually delivered via a cap or comb that the patient uses regularly at home.
Benefits:
- Non-Invasive: No surgery, needles, or medication required.
- Ease of Use: Can be done at home with the appropriate device.
Characteristics:
- Gradual Results: Hair growth may be slow, and consistent use is necessary to see improvements.
- Cost: LLLT devices can be expensive, and the treatment may not be covered by insurance.
5. Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP)
Process: SMP involves tattooing tiny dots on the scalp to mimic the appearance of hair follicles. It creates the illusion of a fuller head of hair or a closely shaved scalp.
Benefits:
- Immediate Results: The visual effect is immediate and can be completed in a few sessions.
- No Maintenance Required: Unlike other methods, there’s no ongoing treatment or medication needed.
Characteristics:
- Cosmetic Solution: SMP does not promote hair growth but offers a cosmetic solution to baldness.
- Permanent: While the results are long-lasting, they are not reversible and require careful consideration.
Conclusion: Which Method is Best?
Choosing the best hair restoration method depends on individual factors such as the extent of hair loss, budget, desired results, and tolerance for invasive procedures.
- Hair Transplants are ideal for those seeking a permanent solution with natural-looking results, especially if they are willing to undergo surgery and a recovery period.
- Topical Solutions and Oral Medications are suitable for individuals in the early stages of hair loss who prefer non-invasive treatments.
- PRP Therapy and LLLT offer a middle ground with minimally invasive options that require ongoing sessions.
- Scalp Micropigmentation is best for those looking for a cosmetic enhancement without actual hair regrowth.





Comments