In a pioneering effort to revolutionize life science research, a wide range of cost-effective animal disease models, from Drosophila to non-human primates, from knockout models to different disease models, are released. These groundbreaking models are set to empower researchers worldwide by enabling them to unravel the mysteries of various diseases more efficiently and affordably than ever before.
Animal models can provide valuable information about various diseases and can be used to study disease progression, develop new treatments, and test the efficacy of experimental drugs. However, the exorbitant costs associated with traditional animal models have proven to be a substantial barrier for many researchers. Addressing this challenge head-on, cost-effective animal disease models have been developed as an innovative solution that promises to streamline scientific advancements by offering affordable yet robust animal disease models.
Based on different disease model studies, researchers can understand complex animal behaviors such as learning, memory, and social behavior through a variety of animal behavioral tests. Besides,
these animal models can also be used in the initial evaluation of new drug efficacy and toxicity, providing vital information for determining the suitability of these drugs for clinical trials. Moreover, the custom transgenic or gene-edited animal model can support the advancement of rare disease therapy development, providing a valuable platform for studying rare disease mechanisms, target validation, and drug screening.
Harnessing the in-depth expertise and experience of the scientific team, these animal models feature with controllability, rapidity, and interpretability. As the environment and conditions of animal models can be controlled, comparison under the same experimental conditions can be allowed. Certain animals like mice and Salmonella have short reproduction cycles, making experiments more economical and efficient. Additionally, since the disease progression mode of animal models is highly similar to that of humans, these models offer a better understanding of the mechanisms and pathophysiological phenomena of human diseases. Combining stable modeling methods and cutting-edge gene editing techniques, the scientific validity and reproducibility of animal models can be ensured.




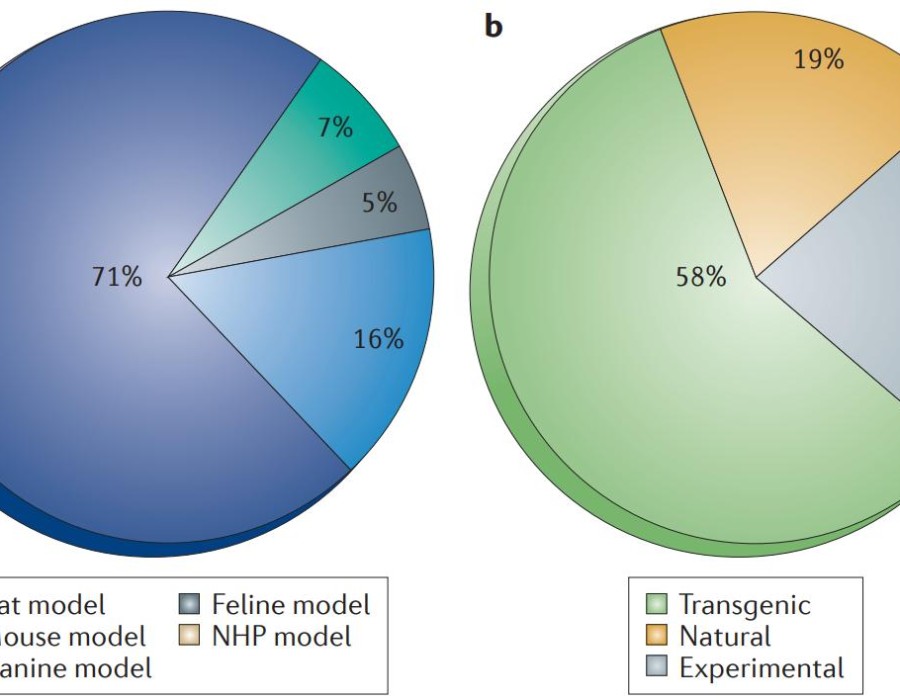
Comments