Introduction
Benzhexol hydrochloride is a class of antimuscarinic drug with the chemical name (±)-a-cyclohexyl-1-phenyl-3-(1-piperidinyl)-propanol hydrochloride. It was approved by the FDA for the treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD) in the United States in 2003. By improving muscle stiffness, benzhexol hydrochloride allows the body to move normally. The structure is shown in fig. 1.
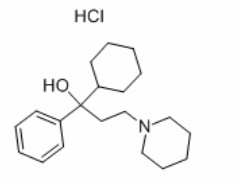 Fig. 1 Structure of benzhexol hydrochloride
Fig. 1 Structure of benzhexol hydrochloride
Application in the treatment of PD
- Introduction of PD
PD, or simply Parkinson's, is a chronic degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. Early symptoms of PD are tremor, rigidity, slowness of movement, and difficulty with walking. As the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms become more common. The cause of PD remains unknown, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors is believed to play an important role in PD. People who have family members with PD are at a higher risk of developing the disease. While coffee drinkers, tea drinkers, and tobacco smokers have a lower risk of developing the disease. PD has a large effect on society, and the incidence and prevalence have risen rapidly in the past two decades. There were about 6.1 million people who had been affected worldwide in 2016[1].

- Mechanism of action
The precise mechanism of action of benzhexol hydrochloride remains inadequately understood. Current research suggests that benzhexol hydrochloride acts on the parasympathetic nervous system by inhibiting efferent impulses directly. Structures innervated by the parasympathetic nervous system, such as the salivary glands, eyes, and smooth muscles, are affected even at small doses of benzhexol hydrochloride. Research indicates that the receptors affected are dopamine and M1 muscarinic in the treatment of PD by benzhexol hydrochloride.
- Side effects
Common side effects of benzhexol hydrochloride mainly include:
- Ocular side effects: Benzhexol hydrochloride may cause mydriasis in both photophobic and non-photophobic patients, which can lead to blurred vision or precipitate narrow-angle glaucoma.
- Peripheral side effects: As an anticholinergic, benzhexol hydrochloride causes impaired sweating, dry mouth, abdominal discomfort, nausea, urinary retention, and constipation. Some patients also develop tachycardia.
- Central nervous system side effects: Frequently reported central nervous system side effects of benzhexol hydrochloride are headache, dizziness, drowsiness, and vertigo. Patients taking high doses of benzhexol hydrochloride experience anxiety, nervousness, confusion, and agitation.




Comments