Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune disorder that results in unpredictable hair loss. While the exact cause of this condition remains unknown, it is thought to occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss on the scalp and other parts of the body. For those affected, finding effective ways to regrow hair is a key concern. This guide explores various treatments and methods that have shown promise in managing alopecia areata and promoting hair regrowth.
1. Understanding Alopecia Areata
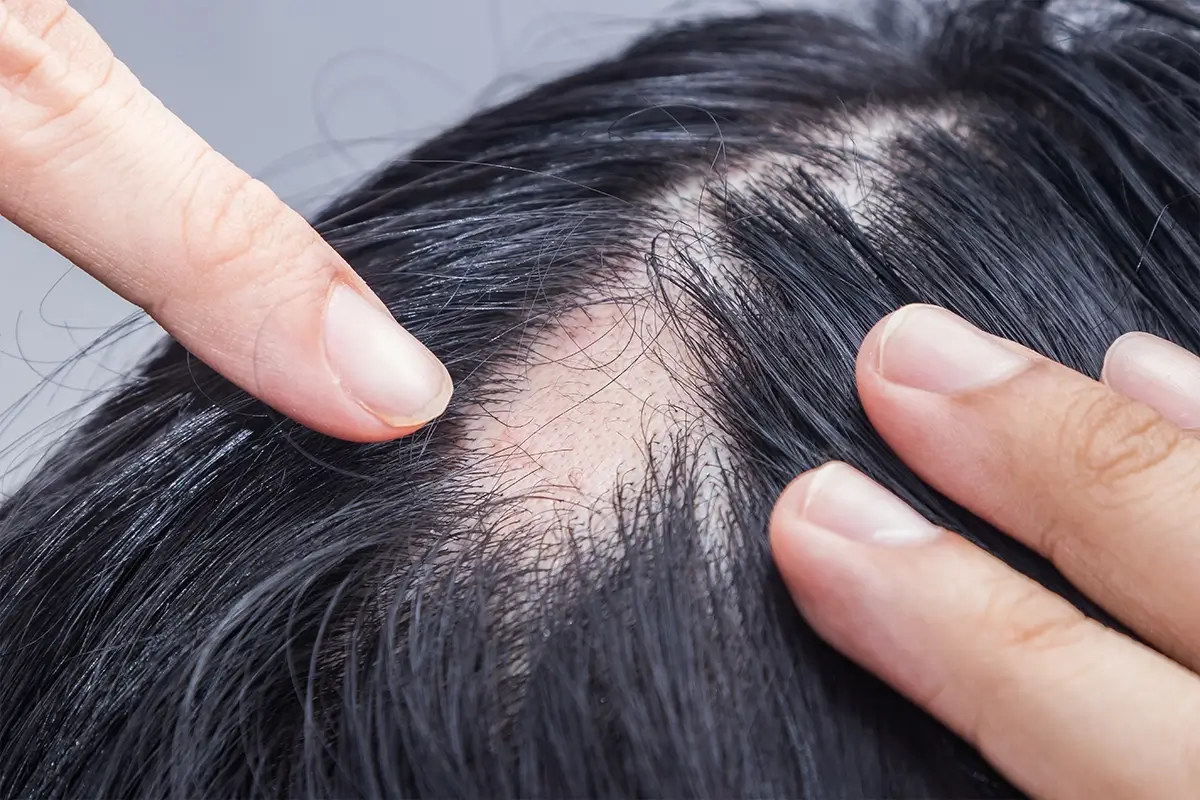
Alopecia Areata Treatment in Dubai can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. Typically, it starts with small, round patches of hair loss on the scalp, but it can progress to total scalp hair loss (alopecia totalis) or even full-body hair loss (alopecia universalis). While some people experience spontaneous regrowth, others may require treatment to manage the condition and encourage hair regrowth.
1.1 Causes of Alopecia Areata
While the exact cause of alopecia areata is unknown, several factors are believed to contribute, including:
- Genetics: A family history of alopecia or other autoimmune diseases may increase risk.
- Immune System Dysfunction: The immune system mistakenly targets hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
- Environmental Triggers: Stress, infections, or other environmental factors may exacerbate or trigger hair loss in susceptible individuals.
1.2 Symptoms and Diagnosis
The primary symptom of alopecia areata is patchy hair loss, but other symptoms may include tingling or itching in the affected area. Dermatologists diagnose the condition by examining the pattern of hair loss and may use a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
2. Medical Treatments for Alopecia Areata
Several medical treatments are available to help manage alopecia areata and promote hair regrowth. However, the effectiveness of each treatment varies based on individual response, and not all treatments work for everyone.
2.1 Corticosteroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections are one of the most common treatments for alopecia areata. These injections suppress the immune system locally, reducing inflammation around hair follicles and allowing hair to regrow. Typically administered every four to six weeks, corticosteroid injections are particularly effective for small, localized patches of hair loss.
2.2 Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids, available as creams or lotions, can be applied directly to the affected areas. While less effective than injections, topical corticosteroids are non-invasive and may be a preferred option for children or those with larger areas of hair loss.
2.3 Minoxidil (Rogaine)
Minoxidil is a topical solution that stimulates hair growth by increasing blood flow to hair follicles. Though originally developed for pattern baldness, minoxidil has shown promise in treating alopecia areata as well. It is often used in combination with other treatments for better results.
2.4 Anthralin Cream
Anthralin, a synthetic form of tar, is applied to the scalp to stimulate hair growth in individuals with alopecia areata. It works by irritating the skin, which may distract the immune system from attacking hair follicles. Anthralin cream is usually applied for a short period before being washed off to prevent skin irritation.
2.5 Immunotherapy
Topical immunotherapy involves applying chemicals like diphencyprone (DPCP) to the scalp to provoke an allergic reaction, which may stimulate hair regrowth by shifting the immune response. Although effective for some, this treatment requires ongoing applications and may cause side effects like itching and blisters.
3. Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatments, some people find natural remedies and lifestyle changes beneficial in managing alopecia areata. While the effectiveness of these methods varies, they can often complement medical treatments and improve overall hair health.
3.1 Essential Oils
Certain essential oils, such as rosemary, peppermint, and lavender, have been found to promote hair growth. These oils improve scalp circulation, which may help support hair follicle health. For safe use, essential oils should be diluted in carrier oils like coconut or jojoba oil before being applied to the scalp.
3.2 Onion Juice
Onion juice is rich in sulfur, which may promote hair regrowth by increasing collagen production and improving blood circulation. Applying onion juice to the scalp and leaving it on for 15-20 minutes before rinsing may yield results after several weeks of consistent use.
3.3 Diet and Nutrition
A well-balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support hair health and potentially improve alopecia areata outcomes. Key nutrients include:
- Vitamin D: Low levels of vitamin D are associated with alopecia areata; supplements or sun exposure may help.
- Iron: Iron deficiency is linked to hair loss; foods like leafy greens, beans, and lean meats can help.
- Biotin: Often used for hair health, biotin-rich foods like eggs and nuts may support hair growth.
3.4 Reducing Stress
Chronic stress is thought to exacerbate alopecia areata, as stress hormones may negatively impact hair follicles. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress, potentially reducing flare-ups.
4. Emerging and Advanced Treatments
Research into alopecia areata is ongoing, with several promising new treatments and approaches being developed. Advanced treatments may be an option for individuals who have not responded to conventional methods.
4.1 JAK Inhibitors
JAK inhibitors are a new class of drugs that target specific pathways in the immune system. Medications like tofacitinib and ruxolitinib have shown promising results in clinical trials for alopecia areata, helping to regrow hair in many patients. However, JAK inhibitors may have side effects, and their long-term efficacy is still under study.
4.2 Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves drawing a patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and injecting the platelet-rich plasma into areas affected by alopecia areata. PRP is believed to stimulate hair follicles and promote regrowth. While some patients experience positive results, this treatment requires multiple sessions and can be costly.
4.3 Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
LLLT uses red light or near-infrared light to stimulate hair follicles and improve hair growth. This non-invasive treatment can be administered through laser combs, helmets, or caps designed for home use. Although LLLT is considered safe, its effectiveness in treating alopecia areata varies.
5. Managing Emotional Well-being with Alopecia Areata
Coping with hair loss can be emotionally challenging, impacting self-esteem and mental health. Managing the psychological aspects of alopecia areata is essential for overall well-being.
5.1 Support Groups and Counseling
Connecting with others who have alopecia areata can provide emotional support and a sense of community. Many people benefit from joining support groups, either in person or online. Professional counseling may also help individuals process their emotions and develop coping strategies.
5.2 Embracing Alternative Hairstyles
Some people choose to embrace their alopecia by exploring alternative hairstyles or shaving their heads. Others use wigs, scarves, or hats to cover hair loss. Finding a personal style that feels comfortable can boost confidence.
5.3 Practicing Self-Care
Engaging in activities that foster self-care and well-being, such as exercise, mindfulness, and hobbies, can help individuals cope with alopecia areata. Focusing on overall health may also support better treatment outcomes.
6. Conclusion: Creating a Personalized Approach
Managing alopecia areata and promoting hair regrowth often requires a combination of medical treatments, natural remedies, lifestyle changes, and emotional support. Each person's response to treatment varies, so finding the right approach may involve some trial and error. With advancements in medical research, new treatments continue to emerge, offering hope for those affected by alopecia areata.





Comments