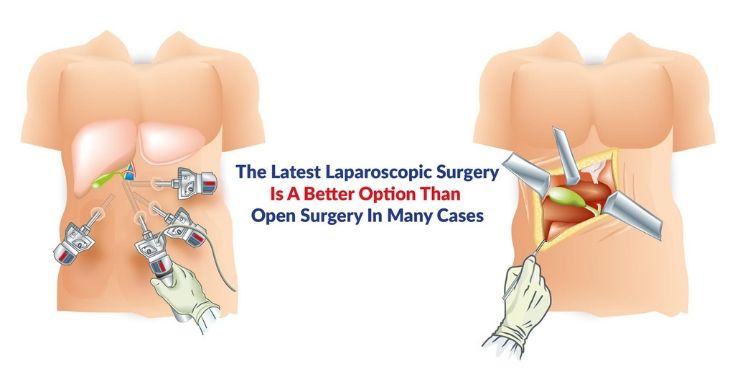
Laparoscopy, also known as minimally invasive surgery, is a surgical technique that uses small incisions and specialized instruments to perform procedures inside the body. Unlike traditional (open) surgery, which requires larger incisions to access the organs, laparoscopy involves making tiny incisions, usually less than half an inch each, through which a thin, lighted tube called a laparoscope and other surgical tools are inserted.
Here are the main differences between laparoscopy and traditional surgery:
1. Incision Size:
Laparoscop: Small incisions (about 0.5–1 cm each).
Traditional Surgery: Larger incisions (several inches long).
2. Recovery Time:
Laparoscopy: Generally shorter recovery time and less postoperative pain. Patients often experience quicker return to normal activities.
Traditional Surgery: Longer recovery period and more postoperative discomfort due to the larger incision.
3. Scarring:
Laparoscopy: Smaller scars that are less noticeable.
Traditional Surgery: Larger scars that may be more prominent.
4. Hospital Stay
Laparoscopy: Often results in a shorter hospital stay, Liver Transplant Near Me sometimes even allowing for outpatient procedures.
Traditional Surgery: Typically requires a longer hospital stay.
5. Risk of Infection:
Laparoscopy: Lower risk of infection due to smaller incisions.
Traditional Surgery: Higher risk due to larger incisions.
6. Precision and Visualization:
Laparoscopy: Provides excellent visualization through a camera on the laparoscope, Pancreatic Cancer in Jaipur allowing for precise movements in tight spaces.
Traditional Surgery: Provides direct access to the area but with a larger field of view.
Laparoscopy is commonly used for procedures in various fields, including gynecology, urology, and general surgery. While it offers many advantages, it might not be suitable for all types of surgery, and some complex cases may still require traditional open surgery.




Comments