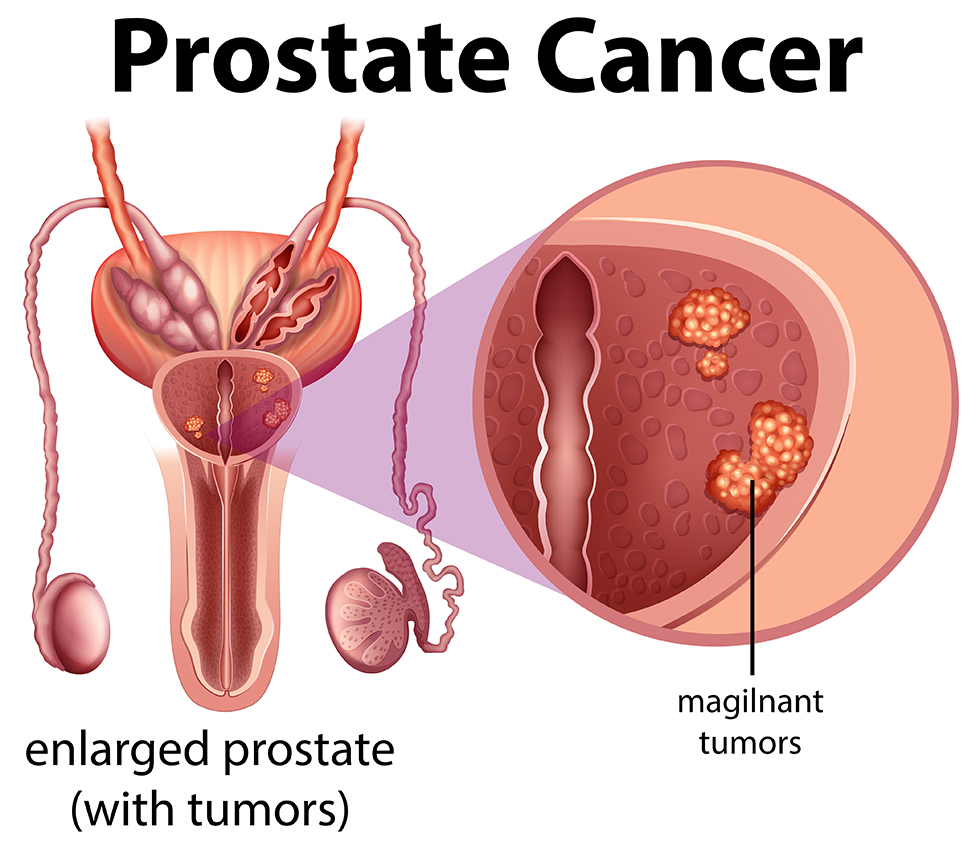
Prostate cancer is one of the most frequent kinds of cancer in men, although many people are unaware of the signs until the illness has advanced. Understanding the early warning symptoms can lead to quick diagnosis and treatment, resulting in better results. In this article, we’ll look at the primary signs of prostate cancer and why it’s critical to be watchful.
Early Symptoms
Prostate cancer typically exhibits little or no symptoms in its early stages. This is why routine screenings, such as PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) testing, are essential for early detection. When symptoms appear, they may include:
Urinary Issues
- Frequent urination: Needing to urinate more often, especially at night (nocturia).
- Weak or interrupted urine flow: Difficulty starting or stopping urination.
- Inability to urinate: In severe cases, prostate cancer can block the flow of urine entirely.
- Pain or burning during urination: This can indicate irritation or infection alongside cancer.
Blood in Urine or Semen
- Hematuria: Blood in the urine can be a sign of prostate cancer, although it is often associated with other conditions as well.
- Hemospermia: Blood in semen can also be an indicator, although less common.
Advanced Symptoms
As prostate cancer progresses, it can spread beyond the prostate gland, leading to more pronounced and severe symptoms. These might include:
Pain and Discomfort
- Persistent pain: Continuous pain in the lower back, hips, or thighs can indicate that cancer has spread to nearby bones.
- Pelvic discomfort: A feeling of pressure or pain in the pelvic area.
Sexual Dysfunction
- Erectile dysfunction: Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection can be a symptom of prostate cancer or its treatment.
- Painful ejaculation: Discomfort during ejaculation can also be a sign.
Systemic Symptoms
- Unexplained weight loss: Sudden and unexplained weight loss can occur in advanced cancer stages.
- Fatigue: Persistent fatigue and a general feeling of weakness may be present as the body fights cancer.
When to See a Doctor
If you come across any of these symptoms, you should see a doctor. While these symptoms can be caused by illnesses other than prostate cancer, early detection and treatment are crucial for the best results.
Risk Factors and Screening
Age, family history, race, and lifestyle can all contribute to an increased risk of prostate cancer. Men over the age of 50, those with a family history of prostate cancer, and African American men are at an increased risk and should consider routine screening with their doctors.
Conclusion
Prostate cancer can be a stealthy illness in its early stages, but understanding the signs might lead to earlier discovery and improved treatment outcomes. Regular screenings and timely attention to urinary abnormalities, blood in urine or sperm, and persistent discomfort can help detect the condition early. Stay knowledgeable and proactive about your health to receive the best possible treatment.





Comments