FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) and FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) are two primary techniques used in hair transplantation, each with distinct differences in how they harvest and transplant hair follicles. Here’s a detailed comparison of FUE and FUT:
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction):
- Harvesting Method:
- Individual Extraction: In FUE, individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the donor area (usually the back or sides of the scalp) using a small punch tool (typically 0.6mm to 1.0mm in diameter).
- No Linear Scar: FUE leaves tiny, dot-like scars scattered throughout the donor area, which are less noticeable and easier to conceal than the linear scar of FUT.
2. Suitability:
- Limited Donor Supply: FUE is suitable for patients with limited donor hair supply or those who prefer to wear their hair very short, as it does not leave a linear scar.
- Multiple Sessions: It may require multiple sessions to achieve the desired hair transplant density due to the limitation of follicles that can be harvested in one session.
3. Recovery Time:
- Faster Recovery: Patients typically experience quicker healing and less discomfort compared to FUT, as the wounds are smaller and heal faster.
4. Procedure Time:
- Time-consuming: FUE can be more time-consuming than FUT, especially for large sessions, due to the manual extraction process of individual follicles.
5. Scarring:
- Scattered Scars: Leaves small, round scars in the donor area, which are less noticeable and more easily camouflaged by surrounding hair.
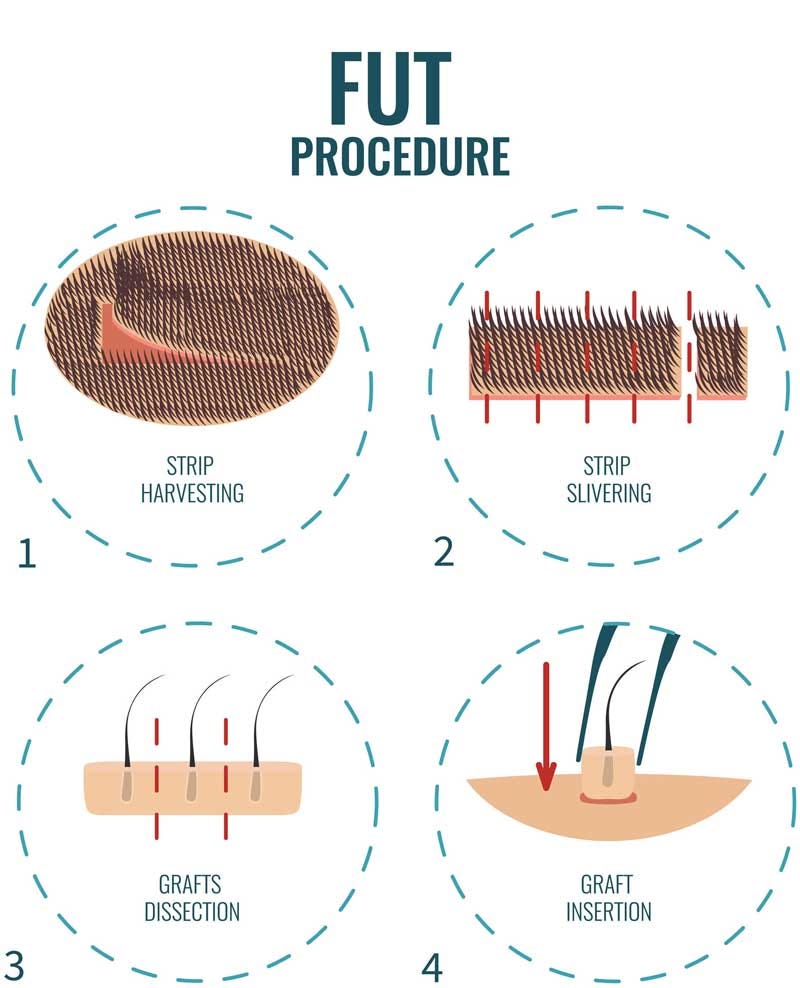
FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation):
- Harvesting Method:
- Strip Harvesting: In FUT, a strip of scalp tissue containing hair follicles is surgically removed from the donor area. The strip is then dissected under a microscope to obtain individual follicular units for transplantation.
2. Suitability:
- High Follicle Yield: FUT is ideal for patients who need a large number of grafts in a single session, as more follicles can typically be harvested in one go compared to FUE.
- Longer Hair Styles: It is suitable for patients who prefer to keep their hair longer, as the linear scar can be easily hidden under the surrounding hair.
3. Recovery Time:
- Longer Recovery: FUT involves a longer recovery period compared to FUE, as it requires healing of the linear scar and may involve more discomfort initially.
4. Procedure Time:
- Efficient for Large Sessions: FUT can be more time-efficient for larger transplant sessions, as the harvesting process is quicker compared to individual extraction in FUE.
5. Scarring:
- Linear Scar: Leaves a linear scar in the donor area, which can be more noticeable if the hair is cut very short. However, skilled surgeons can minimize scar visibility through proper closure techniques.
Conclusion:
Choosing between FUE and FUT depends on various factors such as the patient’s hair loss pattern, desired hair style, donor hair characteristics, and the number of grafts needed. Consulting with a qualified hair transplant surgeon is crucial to determine which technique is most suitable based on individual circumstances and goals. Both FUE and FUT can provide natural-looking results when performed by experienced professionals, offering effective solutions for hair restoration and addressing hair loss concerns.




Comments