Kidney stones are a common urological issue that can cause substantial discomfort and health consequences if not treated immediately. Dr. Deepesh Kalra, a prominent urologist in Jaipur, discusses the many risk factors that lead to the production of kidney stones. Understanding these variables allows patients to take preventive actions to lower their risk.
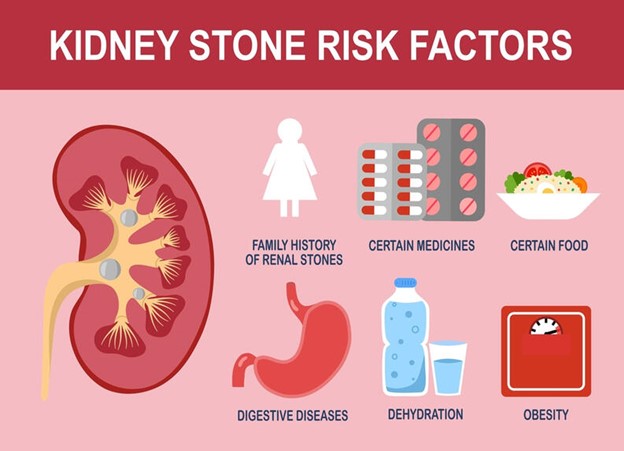
1. Dehydration
One of the most important risk factors for kidney stones is dehydration. When you don’t drink enough water, your urine gets more concentrated with minerals and salts, which can crystallize and cause stones. To keep your urine diluted and avoid stone formation, drink at least 8–10 glasses of water every day.
2. Dietary Choices
Certain foods may raise the risk of acquiring kidney stones. Diets heavy in salt, animal protein, and oxalate-rich foods (such as spinach, almonds, and chocolate) may increase the risk. Reduced salt intake, moderate meat consumption, and a balance of oxalate-rich and calcium-rich meals can all assist to reduce the risk.
3. Obesity
Obesity is associated with an increased risk of kidney stones. Excess body weight can cause an acid-base imbalance in the urine, resulting in stone formation. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is critical for lowering this risk.
4. Medical Conditions
Several medical problems might increase an individual’s risk of developing kidney stones. These include hyperparathyroidism, renal tubular acidosis, and inflammatory bowel disease. In addition, those with a history of urinary tract infections or certain genetic diseases are more likely to develop stones.
5. Medications
Certain drugs might raise the risk of kidney stones. These include diuretics, calcium-based antacids, and certain antibiotics. It is critical to examine the potential side effects of any drug with your healthcare professional in order to fully understand its influence on kidney stone risk.
6. Family History
A family history of kidney stones greatly increases your risk. If your parents or siblings have kidney stones, you are more likely to get them as well. Understanding this hereditary propensity can lead to preventative steps to avoid stone development.
7. Low Calcium Intake
Contrary to popular opinion, a low calcium intake may increase the incidence of kidney stones. Calcium binds to oxalate in the stomach, lowering the quantity absorbed into the circulation and then eliminated in the urine. As a result, it is essential to get enough calcium through your diet.
8. Sedentary Lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle might lead to kidney stone production. Physical exercise improves good weight maintenance, hydration, and metabolism, lowering the chance of stone production. Regular exercise is good for your overall health and helps avoid kidney stones.
Conclusion
Knowing the risk factors for kidney stone production is the first step toward prevention. Staying hydrated, making educated food choices, keeping a healthy weight, and managing medical issues can all help to minimize your risk. If you believe you are at risk of kidney stones or are experiencing symptoms, speak with an expert like Dr. Deepesh Kalra for tailored advice and treatment options. Taking preemptive measures now will assist assure improved kidney health and avoid the agony of kidney stones in the future.





Comments