Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is a treatment option primarily used for men with low testosterone levels, a condition known as hypogonadism. This therapy aims to restore testosterone to normal levels and alleviate associated symptoms.
Here’s an overview of how testosterone replacement therapy is administered and its potential side effects:
Administration of Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT):
- Forms of Administration:
- Injections: Testosterone can be administered through intramuscular injections, typically given every 1–2 weeks. This method provides a consistent release of testosterone into the bloodstream.
- Transdermal: Testosterone can also be administered via patches or gels that are applied to the skin daily. The testosterone is absorbed through the skin and enters the bloodstream.
- Implants: Testosterone pellets can be implanted under the skin, usually every few months, providing a slow release of testosterone over time.
- Oral: Although less commonly used due to potential liver toxicity, testosterone can be administered orally in the form of tablets or capsules.
2. Monitoring: During TRT, regular monitoring of testosterone levels and potential side effects is crucial. Blood tests are typically conducted to ensure testosterone levels are within the normal range and to adjust treatment as needed.
3. Individualized Treatment: The choice of administration method often depends on factors such as patient preference, convenience, and the severity of testosterone deficiency.
Potential Side Effects of Testosterone Replacement Therapy:
- Polycythemia: TRT can stimulate the production of red blood cells, leading to an increase in hematocrit and hemoglobin levels. This condition, known as polycythemia, can potentially increase the risk of blood clots and cardiovascular events.
- Acne and Oily Skin: Testosterone can stimulate sebaceous gland activity, leading to acne and oily skin in some individuals.
- Fluid Retention: Some men may experience fluid retention, causing swelling in the ankles or feet.
- Sleep Apnea: TRT may worsen sleep apnea or contribute to its development, particularly in men with underlying risk factors.
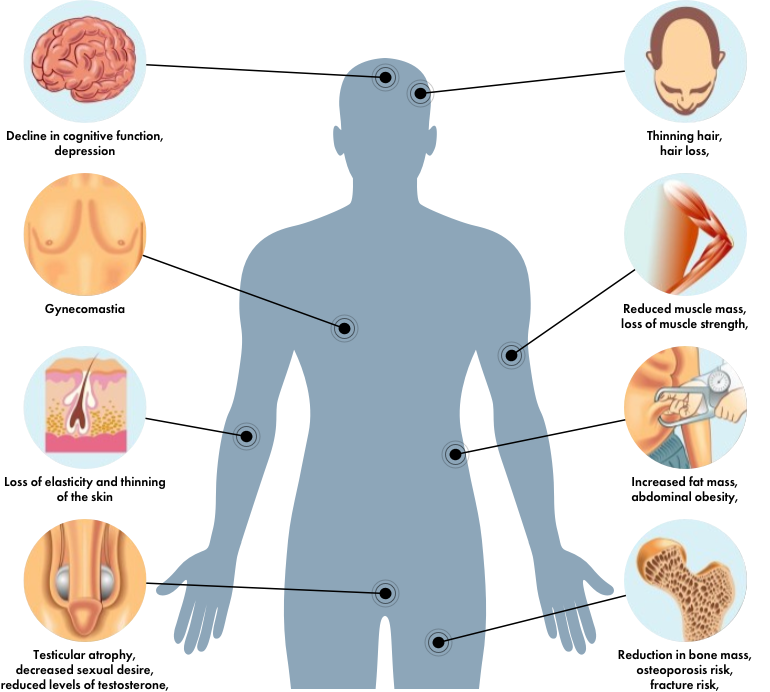
- Gynecomastia: An imbalance in testosterone and estrogen levels can occasionally lead to breast tissue enlargement (gynecomastia).
- Infertility: TRT can suppress sperm production, potentially causing reversible infertility in some men. Fertility considerations are important for younger men considering TRT.
- Mood Changes: While testosterone replacement therapy is intended to improve mood and energy levels, some men may experience mood swings, irritability, or anxiety.
- Prostate Health: There is ongoing debate about the effects of TRT on prostate health. Some studies suggest a potential risk of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate cancer, although the evidence is not conclusive.
- Skin Reactions: Transdermal testosterone applications (patches or gels) may cause skin reactions such as itching, irritation, or allergic dermatitis.
Conclusion:
Testosterone replacement therapy can be highly effective in alleviating symptoms of low testosterone and improving quality of life for many men. However, it is not without potential risks and side effects. Before initiating TRT, it’s essential for individuals to undergo a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider specializing in men’s health to determine if TRT is appropriate and to monitor for any adverse effects during treatment. Close monitoring and adherence to treatment guidelines can help minimize risks and maximize the benefits of testosterone replacement therapy.




Comments