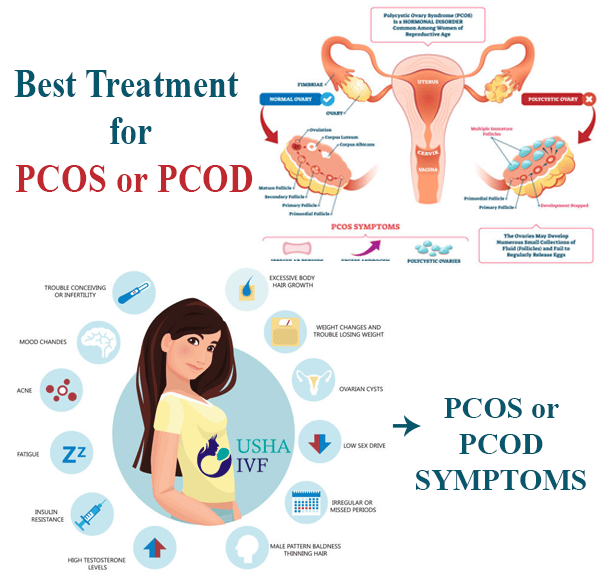
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects people with ovaries during their reproductive years. It's characterized by a combination of symptoms, including irregular periods, excess androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries.
Symptoms:
- Irregular periods: PCOS can cause infrequent, irregular, or prolonged menstrual cycles. Some individuals may experience heavy bleeding during menstruation.
- Excess androgen: Elevated levels of androgen hormones, such as testosterone, can lead to symptoms like acne, excess facial and body hair (hirsutism), and male-pattern baldness.
- Polycystic ovaries: The ovaries may become enlarged and contain numerous small fluid-filled sacs (follicles) which surround the eggs. Despite the name, not all individuals with PCOS have cysts.
- Weight gain: Many individuals with PCOS experience weight gain or have difficulty losing weight. This can exacerbate other symptoms and increase the risk of complications like diabetes and heart disease.
- Skin problems: In addition to acne, PCOS can cause skin tags, darkening of the skin (acanthosis nigricans), and patches of thickened, velvety skin (acrochordons).
- Infertility: PCOS is a common cause of infertility due to irregular ovulation or failure to ovulate.
Treatment:
- Lifestyle changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help manage PCOS symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and managing stress levels.
- Medications:
- Birth control pills: Oral contraceptives can help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels, improving symptoms like acne and hirsutism.
- Anti-androgen medications: Spironolactone or finasteride may be prescribed to reduce excess hair growth and acne.
- Metformin: This medication is commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes but can also help improve insulin resistance and regulate menstrual cycles in individuals with PCOS.
- Fertility medications: If fertility is a concern, medications such as clomiphene or letrozole may be prescribed to induce ovulation.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be recommended to remove ovarian cysts or to perform ovarian drilling to stimulate ovulation.
- Psychological support: Living with PCOS can be challenging, so seeking support from healthcare providers, support groups, or therapists can be beneficial in managing the emotional impact of the condition.
It's important for individuals with PCOS to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to their specific symptoms and needs. Early diagnosis and intervention can help prevent long-term complications and improve overall quality of life.




.png)
Comments