Laparoscopic surgery, often referred to as minimally invasive surgery, is a modern surgical technique that offers numerous advantages over traditional open surgery. This blog will delve into the purpose, procedure, and benefits of laparoscopic surgery(وضع بالون المعدة بالمنظار في الرياض), providing a comprehensive understanding of why it has become a popular choice for many patients and surgeons alike.
What is Laparoscopic Surgery?
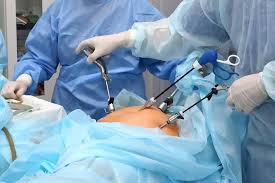
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that uses small incisions and specialized instruments to perform operations. Unlike traditional open surgery, which requires larger cuts, laparoscopic surgery involves making tiny incisions, usually ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 centimeters. A camera, known as a laparoscope, is inserted through one of these incisions to provide real-time images of the surgical area on a monitor.
Key Features of Laparoscopic Surgery
- Small Incisions: Minimizes damage to surrounding tissues and reduces recovery time.
- Real-Time Imaging: Provides clear visuals of the surgical site, enhancing precision.
- Specialized Instruments: Allows for intricate and delicate maneuvers within the body.
Purpose of Laparoscopic Surgery
The primary purpose of laparoscopic surgery is to perform operations with reduced physical trauma to the patient. This technique is used in a variety of surgical fields, including gastrointestinal, gynecological, and urological surgeries. It aims to achieve the same outcomes as traditional surgery but with fewer complications and a faster recovery period.
Common Conditions Treated with Laparoscopic Surgery
- Gallbladder Diseases: Removal of the gallbladder due to gallstones or inflammation.
- Appendicitis: Removal of the appendix when inflamed or infected.
- Hernias: Repair of abdominal hernias with minimal disruption to the surrounding area.
The Procedure of Laparoscopic Surgery
The laparoscopic surgery procedure involves several steps, each contributing to its effectiveness and efficiency. Understanding these steps can help demystify the process and provide insights into how the technique works.
Preparation and Anesthesia
Before the procedure, patients undergo a pre-operative assessment to ensure they are suitable candidates for laparoscopic surgery. Anesthesia is administered to ensure the patient remains comfortable and pain-free throughout the operation. General anesthesia is commonly used, allowing the patient to be unconscious during the procedure.
Incision and Access
Small incisions are made in the abdominal wall to insert the laparoscope and other surgical instruments. A gas, usually carbon dioxide, is introduced into the abdominal cavity to create space and provide a better view of the internal organs. This gas inflates the abdominal area, allowing the surgeon to maneuver the instruments more easily.
Performing the Surgery
Once the laparoscope is inserted, it transmits images of the surgical area to a monitor, allowing the surgeon to perform the operation with high precision. Specialized instruments are used through the other incisions to carry out the necessary surgical tasks. The surgeon navigates these instruments based on the real-time images provided by the laparoscope.
Closing the Incisions
After the surgery is completed, the instruments and laparoscope are removed, and the small incisions are closed with stitches or adhesive strips. The gas is also released from the abdominal cavity. The incisions are typically small enough to heal quickly with minimal scarring.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery offers a range of benefits that make it an attractive option for many patients. These advantages stem from the minimally invasive nature of the technique, which contributes to a more comfortable and efficient recovery process.
Reduced Pain and Discomfort
Because laparoscopic surgery involves smaller incisions, patients experience less post-operative pain compared to traditional open surgery. The smaller cuts cause less damage to surrounding tissues, leading to reduced discomfort and a lower need for pain medications.
Shorter Recovery Time
Patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery often experience a faster recovery compared to those who have open surgery. The minimal invasiveness of the procedure allows for quicker healing, which means patients can return to their normal activities sooner. Many laparoscopic procedures can be performed on an outpatient basis, meaning patients can go home the same day.
Minimal Scarring
The small incisions used in laparoscopic surgery result in minimal scarring. This cosmetic advantage is particularly appealing to patients who are concerned about the appearance of surgical scars. The tiny incisions are often barely noticeable once healed.
Lower Risk of Infection
Smaller incisions mean a reduced risk of post-operative infections. The limited exposure of internal tissues to external elements decreases the likelihood of infections, contributing to a safer surgical experience.
Enhanced Precision
The use of a laparoscope and specialized instruments allows for high precision during the surgery. The real-time images provided by the laparoscope enable the surgeon to see and navigate the surgical site with great accuracy, leading to better outcomes and fewer complications.
Considerations and Limitations
While laparoscopic surgery offers many benefits, it is not suitable for every patient or every condition. Some considerations and limitations include:
Not Suitable for All Conditions
Certain medical conditions or anatomical factors may make laparoscopic surgery less feasible. For example, complex surgeries or conditions with extensive scar tissue may require traditional open surgery for better access and visibility.
Learning Curve for Surgeons
Surgeons must undergo specialized training to perform laparoscopic procedures effectively. The learning curve associated with laparoscopic surgery can be steep, and not all surgeons may have the necessary expertise or experience.
Potential Complications
Although rare, complications can occur with laparoscopic surgery. These may include issues such as bleeding, infection, or damage to surrounding organs. It is important for patients to discuss potential risks with their healthcare provider before undergoing the procedure.
Post-Operative Care and Recovery
The recovery process after laparoscopic surgery is generally swift and straightforward. However, patients should follow specific post-operative care instructions to ensure a smooth recovery.
Follow-Up Appointments
Patients will need to attend follow-up appointments to monitor their progress and ensure proper healing. During these visits, the healthcare provider will assess the incisions, review any symptoms, and provide guidance on resuming normal activities.
Activity Restrictions
While recovery is faster, patients should still adhere to activity restrictions to avoid complications. This may include avoiding heavy lifting, strenuous exercise, or any activities that could strain the surgical area.
Pain Management
Mild pain or discomfort is normal after laparoscopic surgery. Patients are typically prescribed pain medications to manage this discomfort. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and consult with the healthcare provider if pain persists or worsens.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic surgery represents a significant advancement in surgical techniques, offering numerous benefits over traditional open surgery. With its minimal invasiveness, reduced recovery time, and enhanced precision, laparoscopic surgery has become a preferred choice for many procedures. Understanding the purpose, procedure, and benefits of laparoscopic surgery can help patients make informed decisions about their surgical options and contribute to a smoother, more efficient recovery process.




Comments