Circumcision is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the foreskin, the retractable fold of skin that covers the head (glans) of the penis. This procedure is commonly performed for medical, cultural, religious, or personal reasons.
Here’s an overview of how circumcision is performed and the different techniques used:
Procedure Overview:
- Preparation: The patient is usually given local anesthesia to numb the area, which ensures minimal discomfort during the procedure. In some cases, general anesthesia may be used, especially for infants or young children.
- Technique: The technique used depends on various factors such as the patient’s age, medical condition, and preferences. The two primary techniques are:
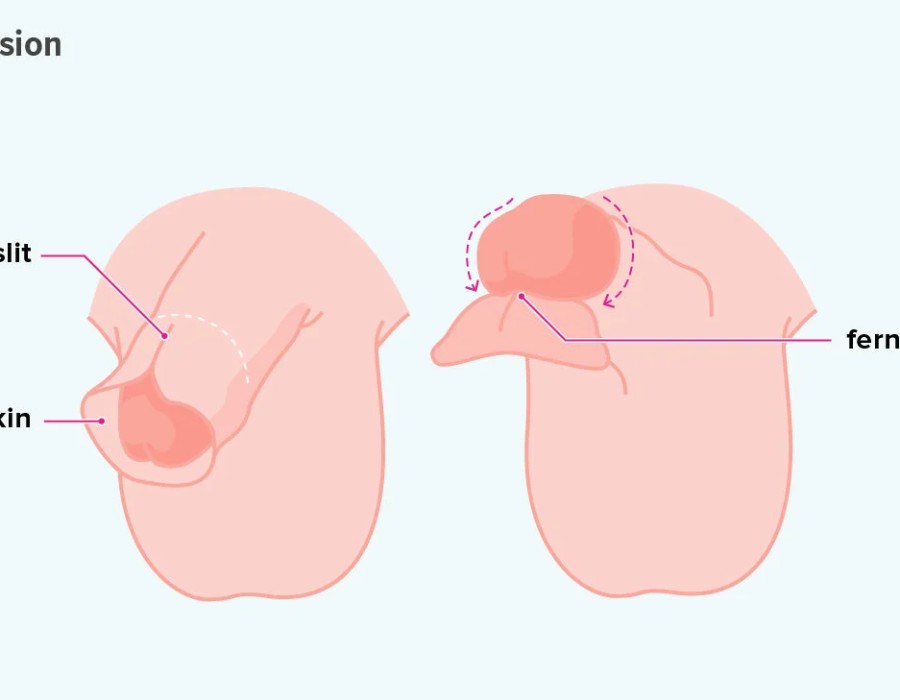
- Conventional (Dorsal Slit) Technique: This involves making a small incision along the top of the foreskin lengthwise and then separating the foreskin from the glans. The excess foreskin is then removed with surgical scissors.
- Plastibell Technique: This method is commonly used for infants and involves placing a small plastic ring (Plastibell device) under the foreskin. The foreskin is then pulled over the ring, and a ligature (tie) is tied tightly around the foreskin. Over the next several days, the foreskin and the ring fall off together as the wound heals.
3. Post-Operative Care: After the procedure, the patient may be given instructions on wound care, such as keeping the area clean and applying antibiotic ointment to prevent infection. Pain relief medications may also be prescribed if necessary.
Different Techniques:
- Gomco Clamp Technique: This method involves using a clamp to isolate and secure the foreskin, which is then excised. It is commonly used in medical settings and allows for precise control during the procedure.
- Preputioplasty: This is a surgical technique used to treat conditions like phimosis (tight foreskin). Instead of complete removal, the surgeon makes a small incision to widen the opening of the foreskin, allowing it to retract comfortably over the glans.
- ZSR Circumcision: This is a newer technique that uses a disposable circumcision device with a sliding ring mechanism. It’s designed to simplify the procedure and potentially reduce operating time and complications.
Considerations:
- Medical Necessity: Circumcision may be recommended for conditions such as phimosis (tight foreskin), recurrent balanitis (inflammation of the glans), or in some cases to reduce the risk of certain infections.
- Cultural and Religious Reasons: Circumcision is also performed for cultural or religious reasons in many communities around the world.
- Risks: Like any surgical procedure, circumcision carries risks such as bleeding, infection, or adverse reactions to anesthesia. However, these risks are generally low when performed by trained medical professionals in sterile environments.
Circumcision remains a personal decision influenced by medical advice, cultural beliefs, and individual preferences. It’s essential for individuals considering circumcision to discuss the procedure thoroughly with a healthcare provider to understand the potential benefits, risks, and alternatives available based on their specific circumstances.




Comments