Hair transplant procedures have become a popular solution for those looking to restore a full head of hair. Whether combating baldness or seeking to fill in thinning areas, understanding how these procedures work and the techniques involved is essential for making an informed decision.
How Hair Transplant Works:
- Consultation: The process typically begins with a consultation with a qualified hair transplant surgeon. During this consultation, the surgeon will assess the patient’s hair loss pattern, hair density, and overall health to determine if they are a suitable candidate for a hair transplant.
- Donor Area Selection: In most cases, the donor hair is harvested from the back or sides of the scalp, where hair is genetically resistant to balding. This area is known as the donor site.
- Hair Harvesting: There are two primary methods for harvesting donor hair: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
- FUT: In this technique, a strip of tissue containing hair follicles is surgically removed from the donor area. The strip is then dissected into individual follicular units under a microscope before being transplanted into the recipient area.
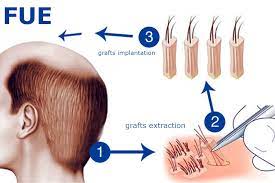
- FUE: FUE involves the extraction of individual follicular units directly from the donor area using a small punch tool. These follicular units are then implanted into the recipient area.
4. Recipient Site Preparation: Once the donor hair is harvested, the recipient area (balding or thinning area) is prepared by creating tiny incisions or recipient sites where the follicular units will be transplanted.
5. Hair Transplantation: The harvested follicular units are carefully implanted into the recipient sites, following the natural hair growth pattern to ensure a natural-looking result.
6. Post-Procedure Care: After the transplant, patients are advised to follow specific post-operative care instructions provided by their surgeon. This may include avoiding strenuous activities, protecting the scalp from sun exposure, and taking prescribed medications to promote healing and prevent infection.
Different Hair Transplant Techniques:
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT):
- Also known as the strip method, FUT involves harvesting a strip of tissue from the donor area and then dissecting it into individual follicular units for transplantation.
- FUT may leave a linear scar at the donor site, which can be concealed by surrounding hair.
2. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE):
- FUE involves the extraction of individual follicular units directly from the donor area using a small punch tool.
- FUE does not leave a linear scar, making it a preferred option for patients who prefer to wear their hair short.
3. Robotic Hair Transplantation:
- Robotic hair transplantation utilizes robotic technology to assist in the extraction and transplantation of hair follicles.
- The robotic system can enhance the precision and speed of the procedure, leading to potentially better outcomes.
4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
- PRP therapy involves injecting platelet-rich plasma derived from the patient’s own blood into the scalp to stimulate hair growth and improve the health of existing hair follicles.
- PRP therapy is often used in conjunction with hair transplant procedures to enhance results and promote faster healing.
5. Stem Cell Therapy:
- Stem cell therapy involves using stem cells to stimulate hair growth and rejuvenate hair follicles.
- While still in the experimental stages, stem cell therapy shows promise as a potential future treatment for hair loss.
Each hair transplant technique has its own advantages and considerations, and the choice of technique depends on factors such as the patient’s hair loss pattern, donor hair availability, and personal preferences. Consulting with a qualified hair transplant surgeon is crucial for determining the most suitable approach for achieving the desired results.




Comments